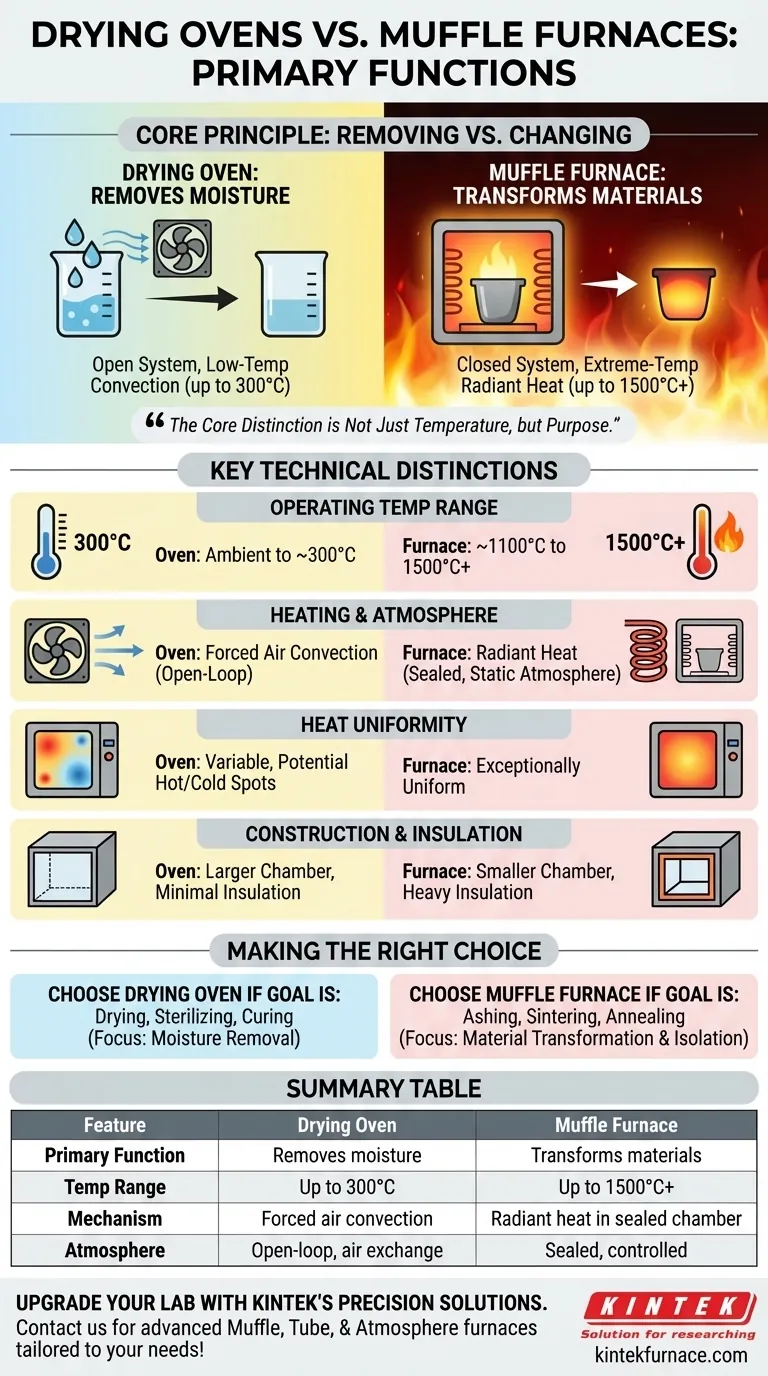
In short, a drying oven removes moisture, while a muffle furnace transforms materials. A drying oven uses forced air convection at relatively low temperatures (up to around 300°C) to dry, harden, or sterilize samples and equipment. In contrast, a muffle furnace uses extreme temperatures (up to 1500°C or higher) in a sealed, insulated chamber to fundamentally alter a material's chemical or physical properties through processes like ashing or sintering.
The core distinction is not just temperature, but purpose. A drying oven is designed to remove something (moisture) from a sample, while a muffle furnace is designed to change the sample itself.
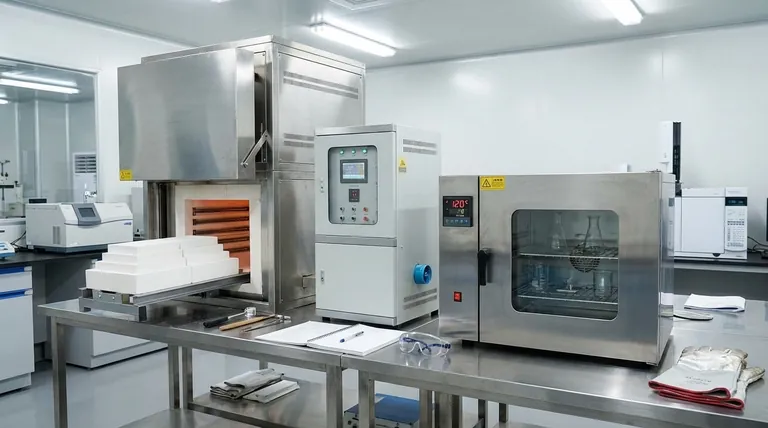

The Core Principle: Removing vs. Changing
Understanding the fundamental design goal of each instrument clarifies its function. One is an open system designed for removal, and the other is a closed system designed for transformation.
Drying Ovens: Low-Temperature Moisture Removal
A drying oven functions much like a high-precision convection oven. Its primary goal is to create a uniform temperature to efficiently remove moisture.
It achieves this by circulating heated air through the chamber. Vents allow fresh air to enter and moisture-laden air to exit, making it ideal for drying glassware, sterilizing equipment, or curing coatings.
Muffle Furnaces: High-Temperature Material Transformation
A muffle furnace is a specialized high-temperature kiln. The "muffle" is a sealed inner chamber that isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and atmospheric contaminants.
This design allows it to perform processes that fundamentally change a material, such as ashing (burning off organics), sintering (fusing powders into a solid), or annealing (altering a metal's microstructure). The sealed chamber and lack of airflow are critical for these applications.
Key Technical Distinctions
The different purposes of these instruments lead to significant differences in their construction and operation.
Operating Temperature Range
A drying oven typically operates at temperatures between ambient and 300°C (572°F).
A muffle furnace is built for extreme heat, with common models reaching 1100°C to 1500°C (2012°F to 2732°F), and specialized versions going even higher.
Heating Mechanism and Atmosphere
Drying ovens rely on forced air convection. A fan circulates air past heating elements and throughout the chamber to ensure efficient drying. This is an open-loop system that constantly exchanges air.
Muffle furnaces use radiant heat from electric coils surrounding the sealed chamber. During operation, the chamber is completely sealed with no airflow, creating a controlled, static atmosphere around the sample.
Heat Uniformity
Drying ovens can struggle with perfect heat distribution, sometimes creating hot and cold spots due to the nature of circulating air.
Muffle furnaces, with their heavy insulation and radiant heating design, provide exceptionally uniform heat distribution, which is critical for precise material processing.
Construction and Insulation
Drying ovens often have larger chambers with minimal insulation, as their goal is not to sustain extreme temperatures.
Muffle furnaces are built with thick, multi-layered insulation and smaller, robust chambers to safely contain intense heat and maintain temperature stability for long periods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong instrument can lead to failed processes, damaged samples, or inefficient energy use.
Why Not Use a Furnace for Simple Drying?
Using a muffle furnace for a low-temperature drying task is highly inefficient. Its massive insulation and power draw are overkill, and the sealed, static atmosphere is ineffective at removing moisture compared to the airflow of a drying oven.
The Limits of a Drying Oven
A drying oven simply cannot reach the temperatures required for metallurgical or advanced materials applications. Furthermore, its open-loop air circulation would introduce oxygen and other contaminants, ruining processes like annealing or high-purity sintering that require a controlled atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select your equipment based on the specific thermal process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or curing: A drying oven is the correct, energy-efficient tool designed specifically for removing moisture with forced air.
- If your primary focus is ashing, sintering, or annealing: A muffle furnace is the only choice, as it provides the extreme temperatures and controlled atmosphere required to transform materials.
- If your primary focus is protecting a sample from contamination: The sealed chamber of a muffle furnace is non-negotiable for isolating your material from the atmosphere during high-temperature heating.
Ultimately, choosing the right tool begins with clearly defining whether your goal is to dry an object or to fundamentally change it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Drying Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Removes moisture | Transforms materials |
| Temperature Range | Up to 300°C | Up to 1500°C or higher |
| Heating Mechanism | Forced air convection | Radiant heat in sealed chamber |
| Key Applications | Drying, sterilizing, curing | Ashing, sintering, annealing |
| Atmosphere | Open-loop with air exchange | Sealed, controlled atmosphere |
Upgrade your lab with precision high-temperature solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for processes such as ashing, sintering, and annealing. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your material transformation and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















