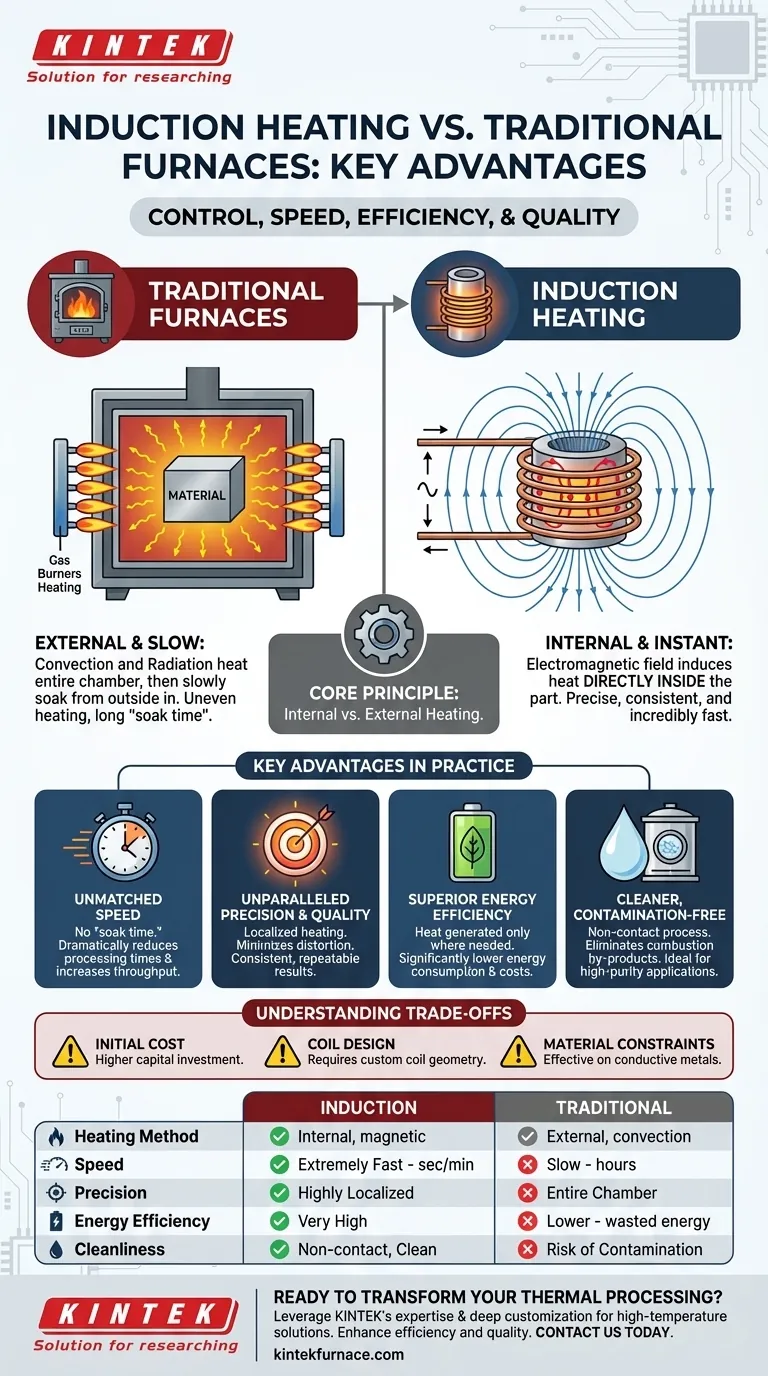
Fundamentally, induction heating's primary advantage is control. Compared to traditional furnaces that heat an entire chamber, induction uses a non-contact electromagnetic field to generate heat directly and instantly inside the target material. This core difference results in a process that is significantly faster, more energy-efficient, highly precise, and produces a more consistent, higher-quality end product.
The core problem with most industrial heating is its indirect and inefficient nature. Induction heating solves this by turning the part itself into the source of the heat, providing a level of speed and precision that external heating methods like convection or radiation simply cannot match.

The Core Principle: Internal vs. External Heating
To understand the benefits of induction, you must first understand the fundamental difference in how heat is delivered.
How Traditional Furnaces Work
Traditional gas or electric resistance furnaces operate on the principles of convection and radiation. They heat a large chamber, and that ambient heat slowly transfers to the surface of the part. The heat must then soak from the outside in, a slow and often uneven process.
How Induction Heating Works
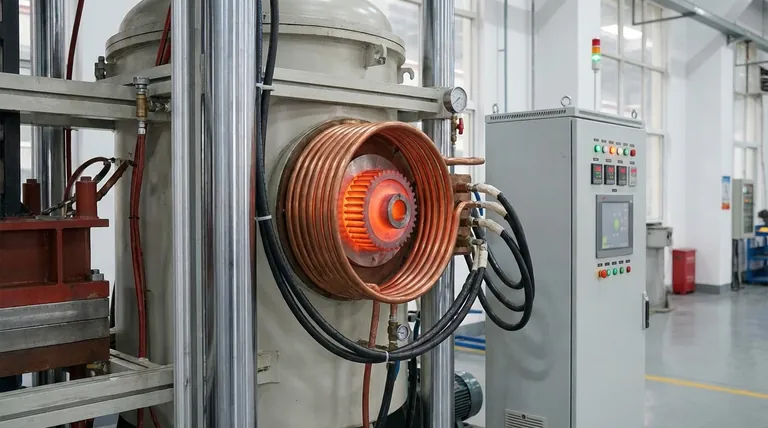
Induction heating uses an alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field. When a conductive part (like steel) is placed within this field, it induces electrical eddy currents inside the part itself. The resistance of the metal to these currents generates precise, instantaneous heat from within.
The Result: Unmatched Speed
Because heat is generated internally, there is no "soak time." The material reaches the target temperature in a fraction of the time required by a furnace. This dramatically reduces processing times and allows for significantly higher production throughput.
Key Advantages in Practice
This unique heating mechanism translates directly into tangible operational benefits.
Unparalleled Precision and Quality
The magnetic field can be precisely shaped by the induction coil's design. This allows for localized heating, targeting only the specific area that needs treatment while leaving adjacent components cool. This precision prevents damage to surrounding tools, minimizes thermal distortion, and creates highly consistent and repeatable results, leading to a higher quality end product.
Superior Energy Efficiency
With induction, energy is only consumed when a part is being heated. There is no need to power a large furnace for hours or waste energy heating the surrounding atmosphere. Heat is generated only where it is needed, resulting in significantly lower energy consumption and reduced utility costs.
Cleaner, Contamination-Free Processing
Induction is a non-contact process. The part never touches a flame or a heating element, eliminating contamination from combustion by-products or surface contact. This is critical for high-purity applications, such as medical implants or aerospace components, and is often performed in a vacuum for ultimate cleanliness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging its specific requirements.
Initial Equipment Cost
The upfront capital investment for an induction heating system, including the power supply and custom coils, can be higher than that for a simple conventional furnace. The return on investment is realized through lower energy bills, higher throughput, and reduced scrap rates over time.
Coil Design and Geometry
The effectiveness of induction heating is heavily dependent on the design of the induction coil. The coil must be carefully engineered to match the geometry of the workpiece to ensure an efficient and even heating pattern. This makes it less flexible for low-volume, high-mix production runs without multiple coils.
Material Constraints
Induction works by inducing current within a material. Therefore, it is most effective on electrically conductive materials, primarily metals. Non-conductive materials like ceramics or polymers cannot be heated directly with induction unless a conductive "susceptor" is used to absorb the energy and transfer it via conduction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To determine if induction is the correct fit, consider your primary operational driver.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and speed: Induction heating's rapid, instant-on heating can dramatically shorten cycle times compared to any furnace-based method.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: The precise, digitally controlled, and repeatable nature of induction heating minimizes defects and ensures uniform results from part to part.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and sustainability: The high energy efficiency and lack of combustion emissions make induction a compelling long-term investment for reducing costs and environmental impact.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or sensitive applications: The non-contact nature and ability to operate in a vacuum make it the superior choice for avoiding all forms of process contamination.
Ultimately, choosing induction heating is an investment in process control, leading to higher quality, greater efficiency, and a more robust manufacturing operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Heating | Traditional Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal (via magnetic field) | External (convection/radiation) |
| Speed | Extremely Fast (seconds/minutes) | Slow (hours) |
| Precision | Highly Localized | Entire Chamber |
| Energy Efficiency | Very High (heat generated in part only) | Lower (energy wasted heating chamber) |
| Process Cleanliness | Non-contact, Contamination-Free | Risk of contamination from flames/elements |
Ready to Transform Your Thermal Processing?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and production facilities with advanced high-temperature solutions. Our expertise in induction heating technology, combined with a strong deep customization capability, allows us to precisely meet your unique process requirements—whether you need to maximize throughput, ensure product quality, reduce operational costs, or maintain high-purity standards.
Contact us today to discuss how our systems can enhance your efficiency and product quality. Let's build a solution tailored for your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does induction heating ensure precision in manufacturing processes? Achieve Superior Thermal Control & Repeatability
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials
- What are the applications of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Performance



















