The vacuum brazing process is a meticulously controlled sequence designed to join materials by melting a filler metal in an oxygen-free environment. It consists of three primary phases: preparing and assembling the parts, running a precise, automated furnace cycle to melt and solidify the filler, and finally, performing rigorous post-braze inspection and testing to validate the joint's quality.
At its core, successful vacuum brazing is less about simply heating metal and more about creating a pristine, controlled environment. The entire process is engineered to prevent oxidation and manage thermal stress, ensuring the filler metal can flow perfectly into the joint and form an exceptionally strong, clean bond.

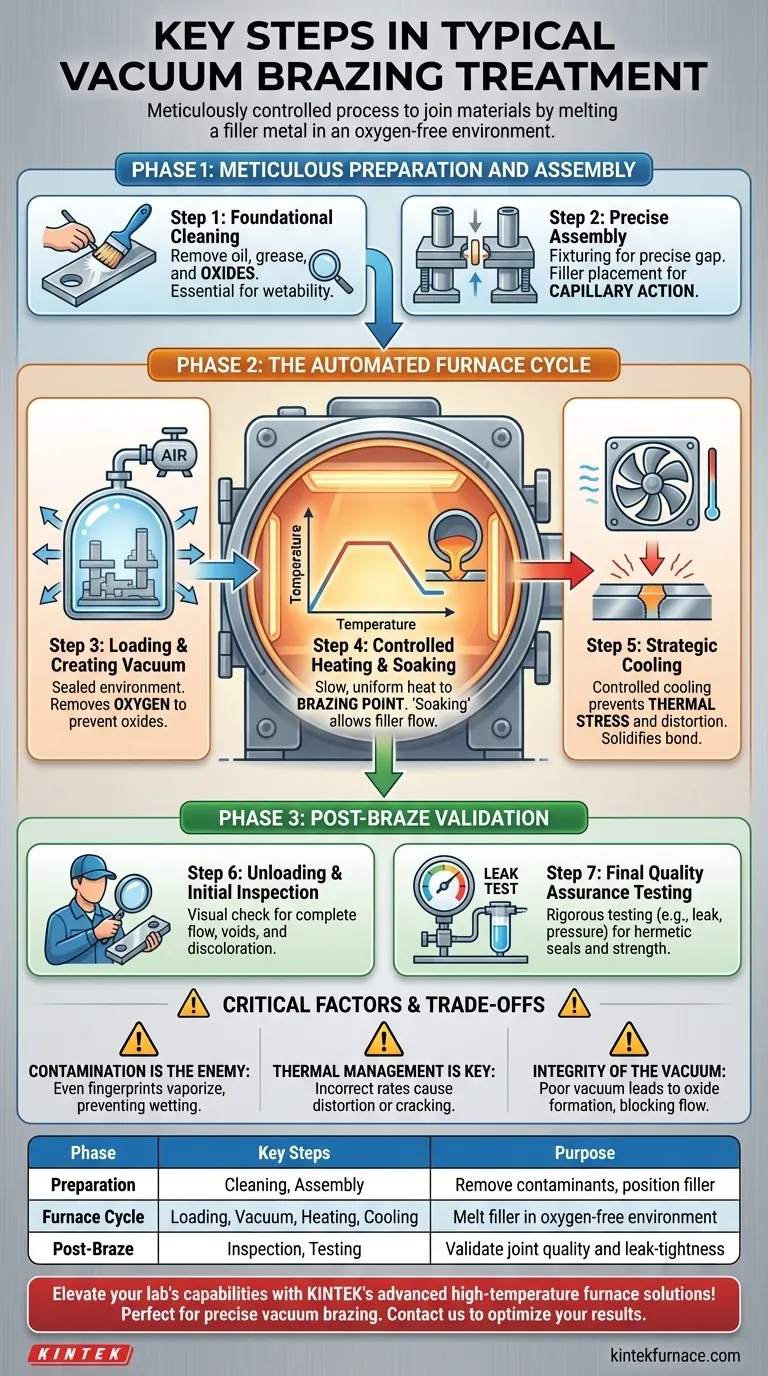
Phase 1: Meticulous Preparation and Assembly
This initial phase is foundational. Errors made here cannot be corrected later in the furnace and are the most common source of brazing failures.
Step 1: Foundational Cleaning
All components to be joined must be rigorously cleaned. The goal is to remove any surface contaminants like oils, greases, and, most importantly, oxides.
A perfectly clean surface is essential for the molten filler metal to "wet" and adhere to the parent materials, which is a prerequisite for a strong bond.
Step 2: Precise Assembly
The cleaned parts are assembled into their final configuration. The brazing filler metal is placed at or near the joint interface.
This filler can be a pre-formed wire or ring, a thin foil, a powder, or a paste. The parts must be fixtured securely with a precise gap to allow capillary action to draw the molten filler into the entire joint.
Phase 2: The Automated Furnace Cycle
Once assembled, the parts are loaded into the furnace for the core process, which is typically managed by a microprocessor for maximum control and repeatability.
Step 3: Loading and Creating the Vacuum
The assembled components are carefully placed on loading tools or frames inside the vacuum furnace. The furnace door is sealed, and a high-power pump system removes the air.
Creating a vacuum is the defining step of this process. It removes oxygen and other reactive gases, preventing the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces as they heat up.
Step 4: Controlled Heating and Soaking
The furnace begins a pre-programmed heating cycle. The temperature is raised in a slow, controlled manner to ensure all parts of the assembly heat uniformly.
The temperature climbs to the designated brazing point, which is above the filler metal's melting point (its liquidus temperature). The assembly is held at this temperature for a short period—a process called "soaking"—allowing the filler to become fully liquid and flow completely into the joint via capillary action.
Step 5: Strategic Cooling
After soaking, the furnace initiates a controlled cooling cycle. The cooling rate is just as critical as the heating rate.
Slowing the cooling process prevents thermal stress, distortion, and cracking, allowing the filler metal to solidify into a strong, uniform, and stable metallurgical bond.
Phase 3: Post-Braze Validation
Once the assembly has cooled completely, it is removed from the furnace for final verification.
Step 6: Unloading and Initial Inspection
The brazed component is carefully unpacked and undergoes a thorough visual inspection. Technicians look for complete and uniform filler flow around the joint, with no signs of voids or discoloration.
Step 7: Final Quality Assurance Testing
Depending on the component's application, it may undergo further testing. For aerospace or hydraulic parts, this often includes pressure or leak testing to ensure the joint is hermetically sealed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Achieving a perfect braze requires mastering several variables. Neglecting any of them can lead to component failure.
Contamination is the Enemy
The most significant risk is improper cleaning. Even a fingerprint can leave behind oils that will vaporize in the furnace, contaminate the surface, and prevent the braze alloy from wetting properly, resulting in a weak or incomplete joint. Clean assembly rooms are a critical facility requirement.
Thermal Management is Key
An incorrect heating or cooling rate is a primary cause of failure. Heating too quickly can cause components to distort, while cooling too fast can induce internal stresses that lead to cracking and joint failure under load.
The Integrity of the Vacuum
A poor or insufficient vacuum will fail to remove all the oxygen. This will cause oxides to form on the hot metal surfaces, acting as a barrier that blocks the flow of the filler metal and compromises the integrity of the entire joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine which phase of the process demands the most attention.
- If your primary focus is joint strength and reliability: Pay obsessive attention to foundational cleaning and ensure your cooling cycle is slow and controlled to minimize thermal stress.
- If your primary focus is producing leak-tight components: Prioritize the quality of your vacuum furnace and implement rigorous final testing protocols like pressure or helium leak checks.
- If your primary focus is avoiding distortion in complex assemblies: Your main concern should be uniform heating and cooling, which requires well-designed fixtures and a precisely controlled furnace profile.
Ultimately, mastering vacuum brazing comes from understanding it as a complete, interconnected system where every step directly impacts the final quality of the bond.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Steps | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Cleaning, Assembly | Remove contaminants, position filler metal for capillary action |
| Furnace Cycle | Loading, Vacuum, Heating, Cooling | Melt filler in oxygen-free environment, prevent thermal stress |
| Post-Braze | Inspection, Testing | Validate joint quality, ensure strength and leak-tightness |
Elevate your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, perfect for precise vacuum brazing processes. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering superior performance and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our products can optimize your brazing results and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control



















