At their core, direct-fired rotary kilns are defined by their method of heating: the fuel is combusted directly within the same rotating drum that holds the material being processed. This design results in extremely high heat transfer efficiency because the combustion gases are in direct contact with the material. They are exceptionally cost-effective and well-suited for processing large volumes of materials that can tolerate exposure to these gases.
A direct-fired rotary kiln is a powerful and efficient tool for thermal processing, but its primary advantage—direct contact between the heat source and the material—is also its main limitation. The choice to use one hinges on whether your material can withstand potential contamination from combustion byproducts.
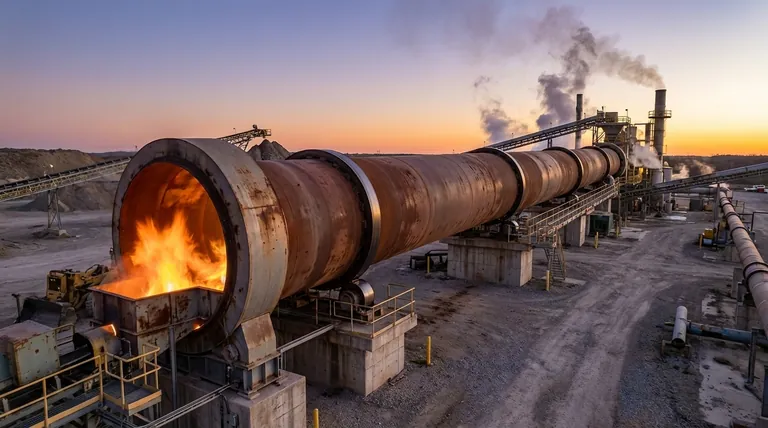

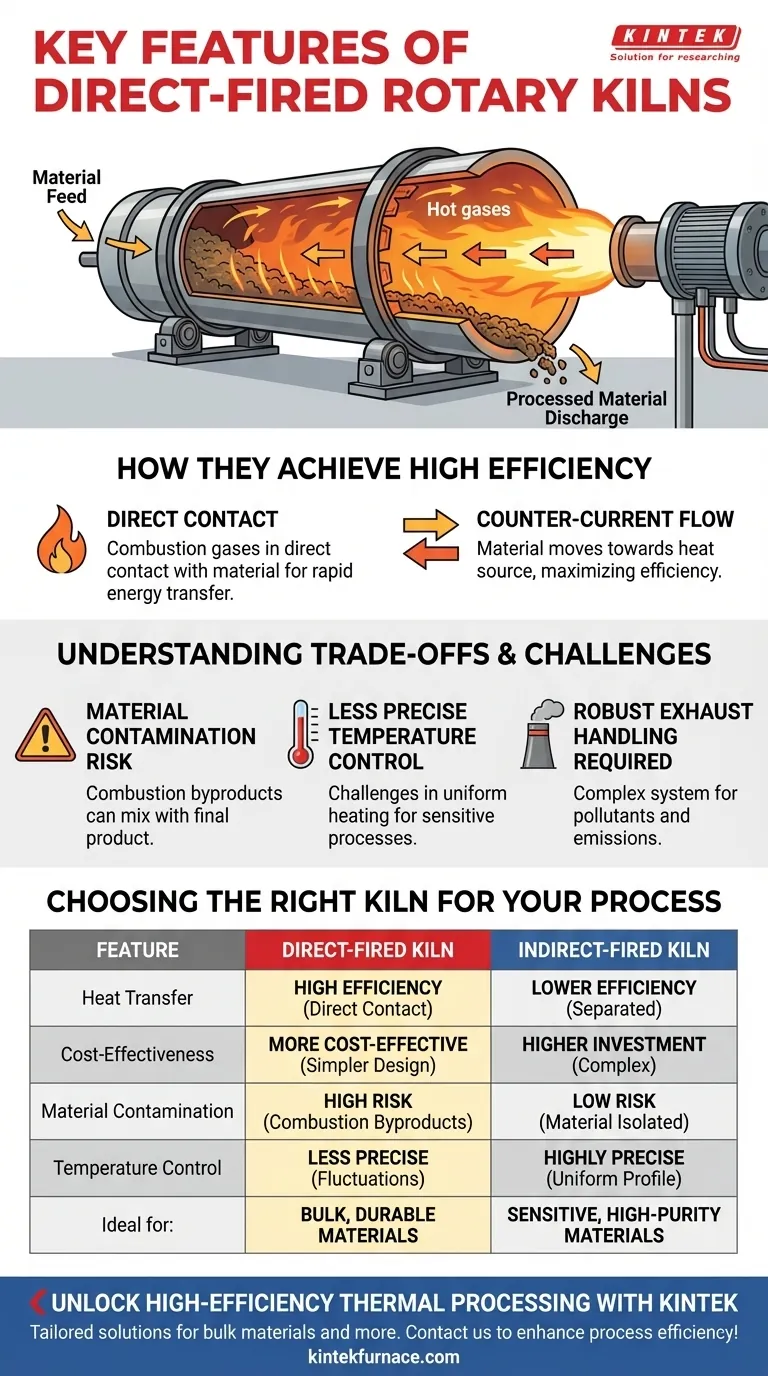
How Direct-Fired Kilns Achieve High Efficiency
The design of a direct-fired kiln is engineered for maximum thermal transfer and throughput, making it a workhorse in many heavy industries like mineral processing and metal recycling.
The Principle of Direct Contact
The defining feature is the internal flame and gas path. The burner fires directly into the kiln's cylindrical shell, and the resulting hot gases flow over and through the material as it tumbles.
This direct interaction ensures a rapid and efficient transfer of thermal energy from the gas to the solid material, minimizing wasted heat.
Optimized Gas and Material Flow
Most direct-fired kilns operate on a counter-current flow principle. Material is fed into the high end of the slightly inclined kiln, while the burner fires into the low (discharge) end.
As the kiln rotates, material slowly tumbles toward the heat source. This ensures that the hottest gases make contact with the most processed material, maximizing thermal efficiency across the entire length of the kiln.
Simpler Design Leads to Cost-Effectiveness
By combining combustion and processing into a single vessel, the design avoids the need for external combustion chambers, radiant tubes, or complex heat jackets.
This inherent simplicity reduces the initial capital investment and often leads to lower maintenance costs compared to more complex indirect-fired systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The efficiency of a direct-fired kiln comes with critical trade-offs that make it unsuitable for certain applications. Understanding these limitations is essential for proper equipment selection.
Risk of Material Contamination
Because the combustion gases mix directly with the process material, any byproducts of combustion—such as ash, soot, or specific chemical compounds from the fuel—can be introduced into the final product.
This makes direct-fired kilns inappropriate for high-purity applications or for materials that are sensitive to or reactive with combustion gases.
Less Precise Temperature Control
The nature of a large, open flame within the drum can lead to temperature fluctuations. Achieving a highly uniform and precisely controlled temperature profile across the material bed is more challenging than in an indirect system.
While they deliver consistent and repeatable results for bulk applications, they lack the fine control needed for processes requiring narrow temperature windows.
Requirement for Robust Exhaust Handling
The exhaust gas leaving the kiln contains not only the byproducts of the thermal reaction but also pollutants from fuel combustion.
This necessitates a robust gas handling and pollution control system to manage dust, ash, and gaseous emissions like SOx and NOx, adding complexity and cost to the overall plant design.
How to Choose the Right Kiln for Your Process
Your decision must be driven by your material's properties and your process goals. The choice between a direct and indirect kiln is a fundamental engineering decision based on a clear set of priorities.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and energy efficiency for bulk materials: A direct-fired kiln is almost always the superior choice, especially for durable materials like minerals, ores, or roofing granules.
- If your primary focus is product purity or processing materials sensitive to contamination: An indirect-fired kiln is necessary to isolate the material from combustion gases.
- If your primary focus is precise, uniform temperature control for a sensitive reaction: An indirect-fired kiln offers far greater control over the heating profile.
Ultimately, selecting the correct kiln technology begins with a deep understanding of your specific material and its processing requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High Heat Transfer Efficiency | Direct contact between combustion gases and material ensures rapid energy transfer. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Simple design reduces initial investment and maintenance costs. |
| Suitability for Bulk Materials | Ideal for large volumes of durable materials like minerals and ores. |
| Material Contamination Risk | Combustion byproducts can contaminate sensitive materials. |
| Less Precise Temperature Control | Challenges in achieving uniform heating profiles compared to indirect systems. |
| Robust Exhaust Handling Required | Necessary to manage pollutants from combustion gases. |
Unlock the Power of High-Efficiency Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Are you handling bulk materials like minerals, ores, or recyclables and need a cost-effective, high-throughput solution? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver tailored systems. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces and more, with deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and industrial needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our direct-fired rotary kilns can enhance your process efficiency and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How do pyrolysis rotary kiln reactors function? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Value Conversion
- What is the working principle of a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion
- What are the advantages of a rotary kiln for bio-reductants? Achieve Industrial-Scale Uniformity and Scalability
- Why must precise temperature measurement and upper-limit control be implemented during the rotary furnace melting of ductile iron?
- What is the significance of rotation in a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion



















