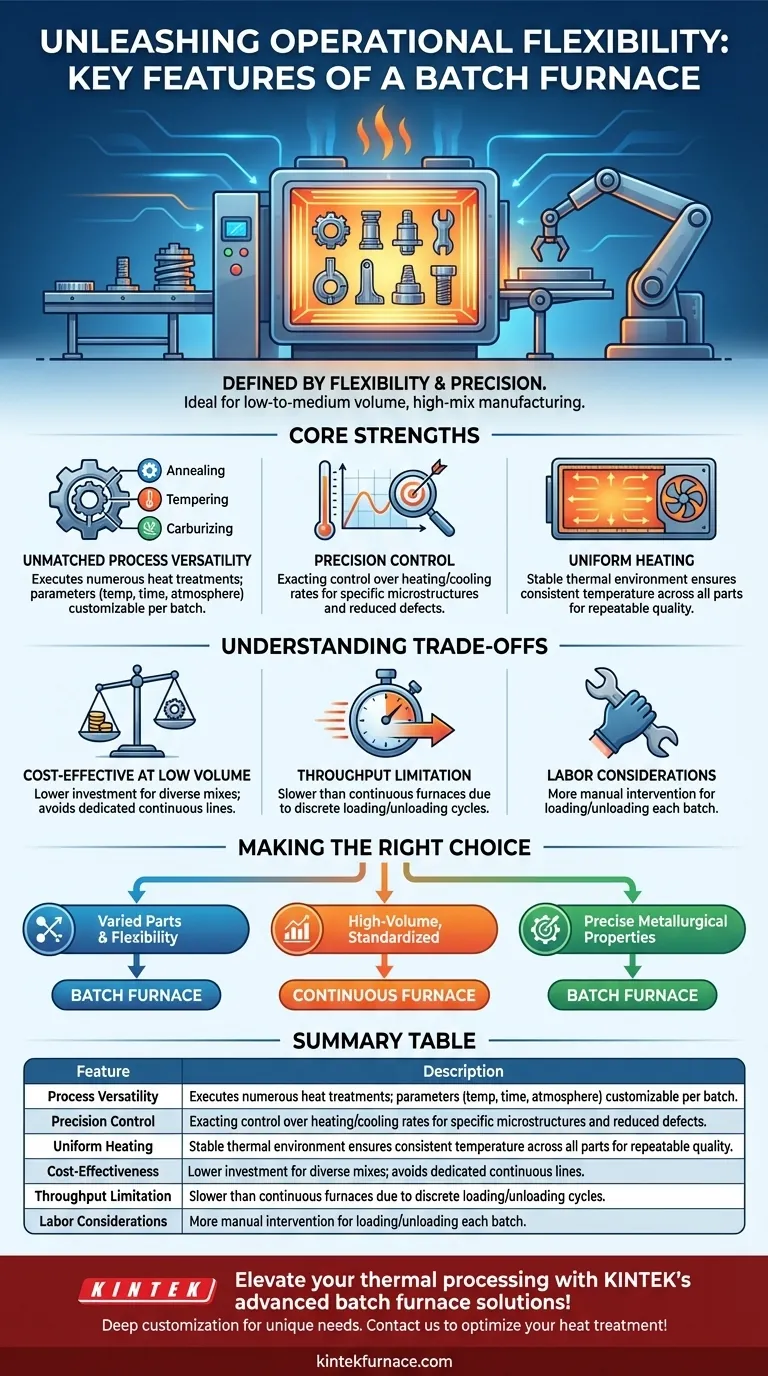
In essence, a batch furnace is defined by its operational flexibility and precision. It processes materials in distinct, separate loads, allowing for highly customized heat treatment cycles tailored to varying part sizes, weights, and metallurgical requirements. This contrasts with continuous furnaces, which are designed for high-volume, standardized production.
The core value of a batch furnace is its ability to deliver precise, repeatable, and highly customized thermal processing for a diverse range of products, making it the superior choice for low-to-medium volume and high-mix manufacturing environments.
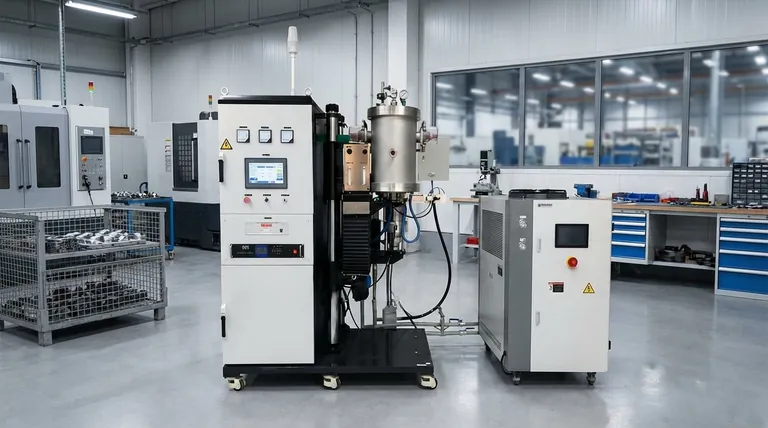

The Core Strengths of a Batch Furnace
A batch furnace's design philosophy prioritizes control and adaptability over sheer volume. This manifests in several key operational advantages.
Unmatched Process Versatility
A single batch furnace can execute numerous different heat treatments, such as annealing, tempering, carburizing, or nitriding.
Because each load is a discrete event, operators can change the process parameters—like temperature, time, and atmosphere—for each new batch. This makes it ideal for handling different grades of steel or components with unique specifications.
Precision Control Over Thermal Cycles
Batch furnaces offer exacting control over heating and cooling rates. This precision is critical for achieving specific microstructures and mechanical properties in the final product.
This level of control ensures that complex or sensitive parts receive the exact thermal profile required, minimizing the risk of distortion or defects.
Uniform Heating and Consistency
By design, a batch furnace is engineered to create a stable and uniform thermal environment. Fans and strategically placed heating elements ensure that all parts within the load, regardless of their position, experience the same temperature.
This uniformity is fundamental to achieving consistent quality and repeatable results from one batch to the next.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a batch furnace is not the universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision. The primary alternative is a continuous furnace, which processes parts on a moving conveyor.
Cost-Effectiveness at Low Volume
For job shops, prototyping, or manufacturing lines with diverse product mixes, the batch furnace is highly cost-effective. Its flexibility avoids the need for multiple, dedicated continuous lines.
The initial capital investment and operational costs are generally lower for smaller-scale operations compared to a large continuous system.
The Throughput Limitation
The primary trade-off is production speed. Loading, processing, and unloading discrete batches is inherently slower than the non-stop flow of a continuous furnace.
For mass production of identical parts where throughput is the main driver, a continuous furnace will almost always be more efficient.
Labor and Handling Considerations
Batch processing typically involves more manual intervention for loading and unloading each cycle. This can lead to higher labor costs per part compared to the more automated nature of continuous systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing between a batch system and an alternative depends entirely on your production goals and product mix.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility for varied parts: The batch furnace is the definitive choice for its ability to handle different sizes, materials, and heat treatment cycles on demand.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: You should investigate a continuous furnace, which is engineered for maximum throughput and efficiency with uniform parts.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise, critical metallurgical properties: The superior process control and thermal uniformity of a batch furnace make it the most reliable option for high-specification components.
Ultimately, a batch furnace empowers you to prioritize quality and adaptability in your thermal processing operations.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Versatility | Handles multiple heat treatments (e.g., annealing, tempering) with customizable parameters per batch. |
| Precision Control | Exact control over heating/cooling rates for specific microstructures and reduced defects. |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures consistent temperature across all parts for repeatable quality. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower investment and operational costs for diverse, low-volume production. |
| Throughput Limitation | Slower than continuous furnaces due to batch-by-batch processing. |
| Labor Considerations | Requires more manual handling, potentially increasing labor costs. |
Elevate your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced batch furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories and manufacturers with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental and production needs, enhancing quality and efficiency in low-to-medium volume environments. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in the formation of the 'core-rim' structure in Ti(C,N)-FeCr cermets?
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing



















