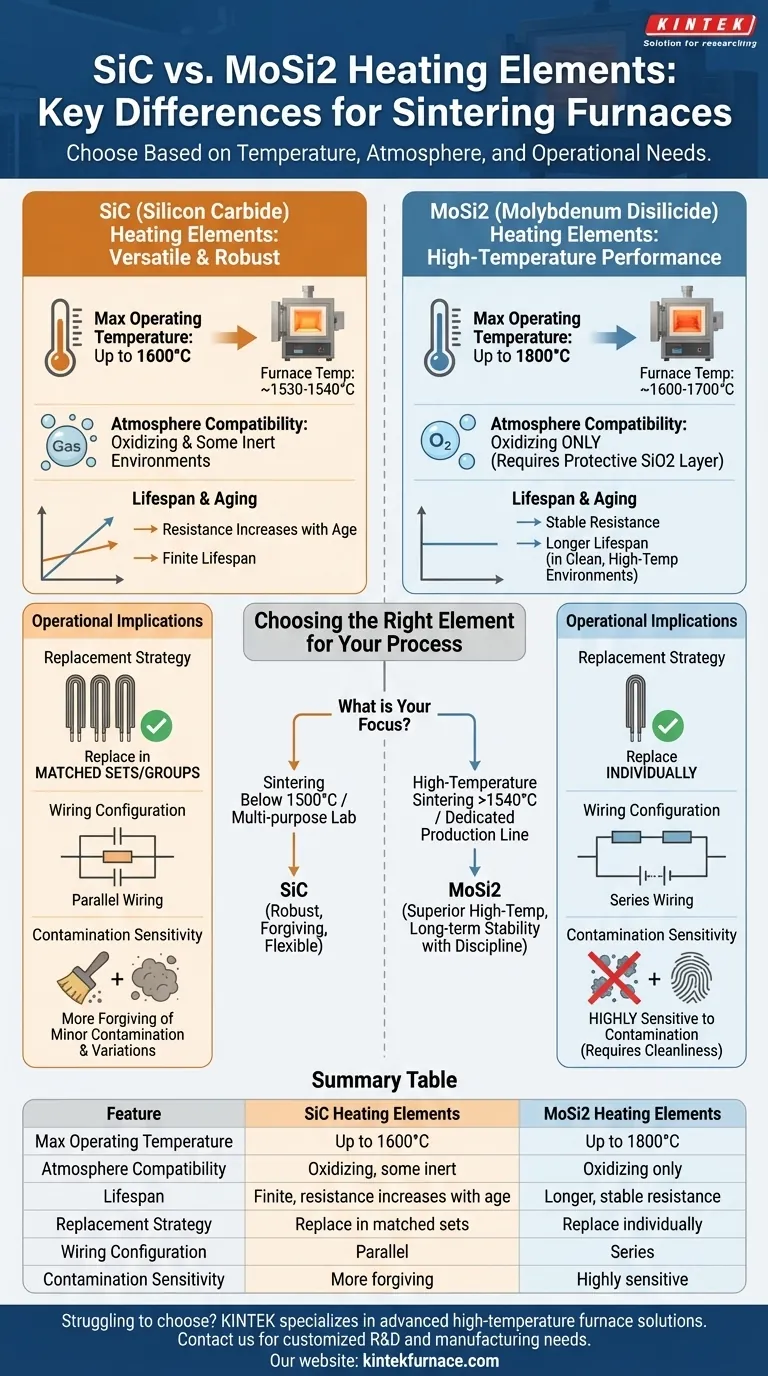
In short, the primary difference is that Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are built for higher temperatures (up to 1800°C) but require a clean, oxidizing atmosphere, while Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are more versatile and robust for processes up to 1600°C. Your choice fundamentally depends on your required sintering temperature and your operational capacity for maintenance.
The decision between SiC and MoSi2 is not about which is "better," but which is the right tool for the job. MoSi2 offers superior high-temperature performance, while SiC provides greater operational flexibility and forgiveness at slightly lower temperatures.

Core Technical Differences
Understanding the material science behind each element is the first step in making an informed decision. Their inherent properties dictate their ideal operating windows and failure modes.
Maximum Operating Temperature
MoSi2 elements are the clear choice for extreme heat. They can operate at element surface temperatures of 1800°C or even higher, allowing for furnace processing temperatures in the 1600-1700°C range.
SiC elements have a lower maximum operating temperature. Their surface should not exceed 1600°C, which translates to a practical maximum furnace temperature of around 1530-1540°C.
Atmospheric Compatibility and Resistance
MoSi2 elements thrive in oxidizing atmospheres. At high temperatures, they form a protective, self-healing layer of glassy silicon dioxide (SiO2) that prevents further oxidation of the element. They are not suitable for reducing atmospheres.
SiC elements are more versatile. They can be used in a broader range of environments, including oxidizing and some inert atmospheres, making them suitable for more varied processes.
Lifespan and Aging Characteristics
SiC elements have a finite lifespan and their electrical resistance increases with age and use. This aging process is a critical operational factor.
MoSi2 elements do not exhibit the same resistance drift. When operated correctly above 1500°C and in a clean environment, they can have a significantly longer lifespan than SiC elements.
Operational and Maintenance Implications
How you run and maintain your furnace is as important as the element technology itself. These two materials demand very different operational procedures.
Element Replacement Strategy
Because the resistance of SiC elements changes over time, a failed element cannot simply be replaced with a new one. The new element's lower resistance would draw too much current. Therefore, SiC elements must be replaced in matched sets or complete furnace groups to ensure a balanced electrical load.
MoSi2 elements maintain a stable resistance, so a single failed element can be replaced individually. This can simplify maintenance and reduce the immediate cost of a single failure.
Wiring and Power Control
SiC elements are typically wired in parallel. This configuration accommodates the need to manage power to elements that are aging at different rates.
MoSi2 elements are wired in series. This simpler configuration is possible because their resistance remains stable throughout their operational life.
Contamination Sensitivity
This is a critical weakness of MoSi2. These elements are highly susceptible to contamination, which can degrade their protective SiO2 layer and lead to premature failure. Strict furnace maintenance and process cleanliness are non-negotiable.
SiC elements are generally more robust and forgiving of minor process variations and less-than-perfect furnace cleanliness, though good maintenance practices are always recommended.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element involves balancing performance against operational reality. There is no universally superior option, only the best fit for your specific context.
The Temperature Crossroads
The decision often pivots around 1500°C. For consistent sintering temperatures below 1450°C, SiC is often the more reliable and cost-effective workhorse. For processes that require temperatures above 1540°C, MoSi2 is the only viable choice.
Cost of Uptime vs. Cost of Replacement
While a full set of SiC elements can be a significant expense, their replacement is a predictable maintenance event. The ability to replace single MoSi2 elements seems cheaper, but a failure caused by contamination can lead to unexpected downtime and troubleshooting.
The Maintenance Burden
MoSi2 promises longer life, but only if you can guarantee a clean operating environment. If your process involves binders that produce contaminants or if your maintenance protocols are not rigorous, the perceived longevity of MoSi2 may never be realized. The robustness of SiC is often a safer bet in these scenarios.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Base your decision on your specific, recurring operational needs.
- If your primary focus is sintering below 1500°C: SiC elements offer a robust, forgiving, and cost-effective solution for a wide range of atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering (>1540°C): MoSi2 is your only practical option and you must commit to the rigorous maintenance it requires.
- If you run a multi-purpose lab with varied processes: The versatility and atmospheric tolerance of SiC often make it the more flexible choice.
- If you have a dedicated high-volume production line with strict protocols: The long-term stability and individual replaceability of MoSi2 can deliver superior lifetime value.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating element is about aligning the material's capabilities with your process requirements and operational discipline.
Summary Table:
| Feature | SiC Heating Elements | MoSi2 Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 1600°C | Up to 1800°C |
| Atmosphere Compatibility | Oxidizing, some inert | Oxidizing only |
| Lifespan | Finite, resistance increases with age | Longer, stable resistance |
| Replacement Strategy | Replace in matched sets | Replace individually |
| Wiring Configuration | Parallel | Series |
| Contamination Sensitivity | More forgiving | Highly sensitive |
Struggling to choose the right heating element for your sintering furnace? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you require the versatility of SiC or the high-temperature performance of MoSi2, our experts can help optimize your process for efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What is the temperature range for MoSi2 heating elements? Maximize Lifespan in High-Temp Applications
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- What types of molybdenum disilicide heating elements are available? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the primary applications of MoSi2 heating elements in research? Achieve Reliable High-Temp Control for Material Synthesis



















