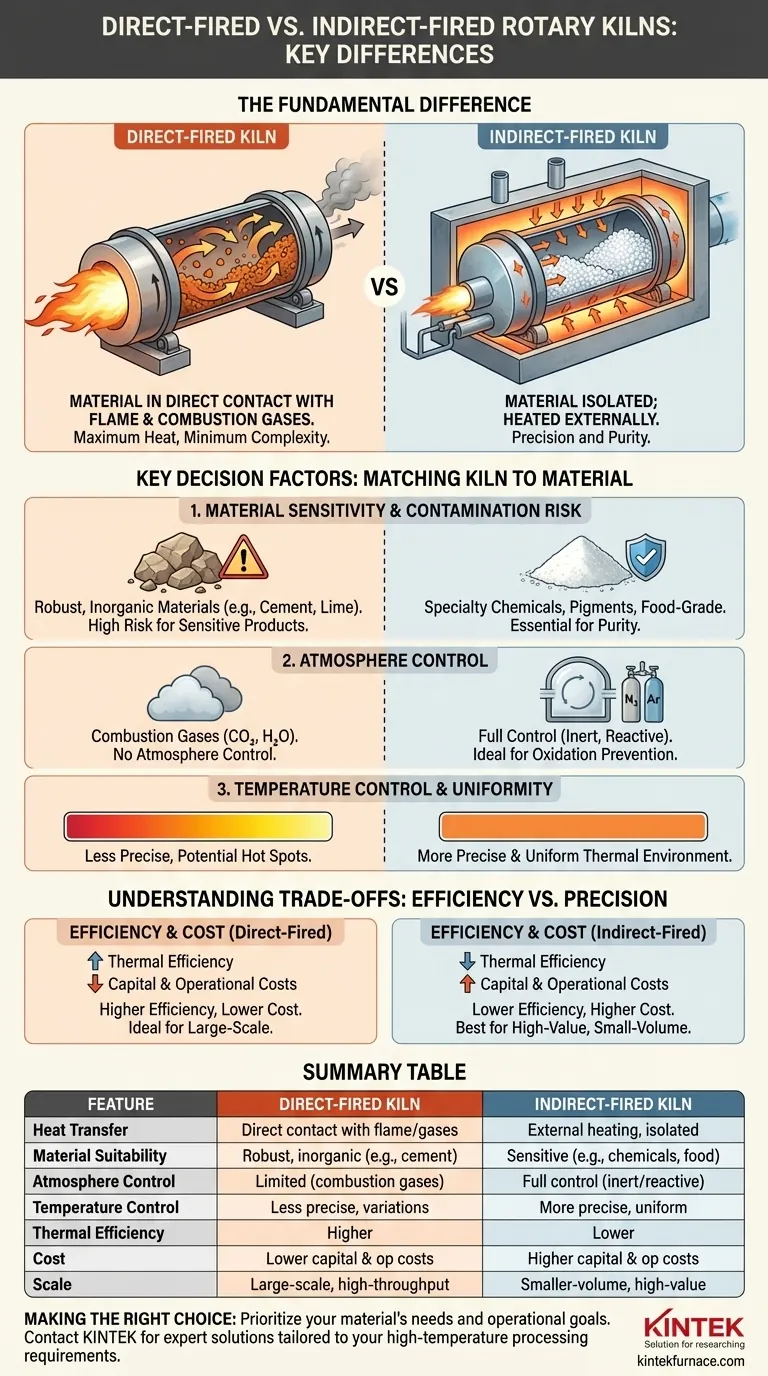
The fundamental difference between direct-fired and indirect-fired rotary kilns lies entirely in how heat is delivered to the material being processed. In a direct-fired kiln, the material is in direct contact with the flame and combustion gases. In an indirect-fired kiln, the material is isolated within a rotating drum that is heated externally, preventing any contact with combustion byproducts. This single distinction dictates each kiln's suitability for different materials, process atmospheres, and operational budgets.
The choice between a direct and indirect-fired kiln is not a question of which is superior, but which is appropriate. The decision hinges on one critical factor: whether your material can tolerate direct contact with combustion gases.

The Core Mechanism: How Heat is Transferred
To select the right technology, you must first understand how each system functions. The method of heat transfer is the central design principle that creates all other differences.
Direct-Fired Kilns: Maximum Heat, Minimum Complexity
In a direct-fired system, a burner injects a flame directly into the rotating kiln drum.
The hot combustion gases flow through the length of the kiln, tumbling with the material and transferring heat via direct contact. This is the most straightforward method of heating.
Think of it like roasting a marshmallow directly over a campfire—the heat source touches the object you are heating.
Indirect-Fired Kilns: Precision and Purity
In an indirect-fired system, the rotating drum is enclosed within an external furnace or heating chamber.
Burners heat the outside of the drum's shell, and that heat is conducted through the metal wall to the material tumbling inside. The material never touches the flame or its exhaust gases.
This is analogous to cooking food in a sealed pan on a stovetop—the heat is transferred through the pan, not from the flame itself.
Key Decision Factors: Matching the Kiln to the Material
Your material's chemical and physical properties will be the primary driver of your decision. An incorrect choice can lead to contamination, product degradation, or an inefficient process.
Material Sensitivity and Contamination Risk
Direct-fired kilns are ideal for robust, inorganic materials that will not be chemically altered by contact with combustion gases. This includes common applications like cement, lime, and certain ore processing.
Indirect-fired kilns are essential for materials where purity is critical. This includes specialty chemicals, pigments, food-grade products, or any substance that could be contaminated or discolored by combustion byproducts.
Atmosphere Control
A direct-fired kiln's internal atmosphere is, by definition, the product of combustion—typically high in carbon dioxide and water vapor. You cannot fundamentally alter this.
An indirect-fired kiln provides complete control over the internal atmosphere. Because the process is sealed off from the heat source, you can process materials in an inert environment (like nitrogen) to prevent oxidation or in a specific reactive gas atmosphere if the process requires it.
Temperature Control and Uniformity
Indirect kilns generally offer more precise and uniform temperature control. The entire shell is heated, creating a more consistent thermal environment for the material inside.
Direct-fired systems can achieve very high bulk temperatures efficiently but may have greater temperature variations and hot spots along the length of the kiln.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Efficiency vs. Precision
The advantages of one system in terms of purity and control often come at the expense of efficiency and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for a sound technical and financial decision.
Thermal Efficiency
Direct-fired kilns are generally more energy-efficient. Heat is transferred directly from the fuel source to the material, resulting in fewer thermal losses.
Indirect-fired kilns are inherently less efficient. Heat must be transferred from the flame to the furnace, then through the kiln shell, and finally to the material. Each step involves some energy loss.
Capital and Operational Costs
A direct-fired system is typically less complex in its construction. This translates to a lower initial capital cost and often simpler maintenance.
An indirect-fired system, with its external furnace, specialized seals, and more complex design, is significantly more expensive to build and maintain.
Scale and Throughput
Direct-fired kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry. Their design is well-suited for very large-scale, high-throughput continuous applications where efficiency is paramount.
Indirect-fired kilns are more commonly used for smaller-volume, higher-value materials where precision and purity justify the higher operational cost and potentially lower throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by a clear understanding of your primary process objective. Analyze your goals against the core strengths of each kiln type.
- If your primary focus is high-volume processing of robust materials: A direct-fired kiln offers the best combination of thermal efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is material purity and contamination control: An indirect-fired kiln is non-negotiable to isolate your product from combustion gases.
- If your primary focus is processing in a specific or inert atmosphere: You must use an indirect-fired kiln to maintain precise atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is minimizing capital cost for a compatible material: A direct-fired kiln is the more economical choice.
By prioritizing your material's needs and your operational goals, you can confidently select the right kiln technology for your application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct-Fired Kiln | Indirect-Fired Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer | Direct contact with flame and gases | External heating, isolated material |
| Material Suitability | Robust, inorganic materials (e.g., cement, lime) | Sensitive materials requiring purity (e.g., chemicals, food-grade) |
| Atmosphere Control | Limited, combustion gases present | Full control, inert or reactive atmospheres possible |
| Temperature Control | Less precise, potential for variations | More precise and uniform |
| Thermal Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Lower capital and operational costs | Higher capital and operational costs |
| Scale | Ideal for large-scale, high-throughput | Better for smaller-volume, high-value applications |
Struggling to choose the right kiln for your material processing? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and achieve superior results with our expert solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How do vibrational feeder specifications impact rotary kiln efficiency? Optimize Your Lab's Material Flow & Stability
- What are some common processes carried out in rotary kilns? Unlock Efficient Material Transformation Solutions
- What distinguishes direct from indirect rotary kilns? Choose the Right Kiln for Your Material
- How does customization benefit the use of rotary kilns? Boost Efficiency and Quality with Tailored Solutions



















