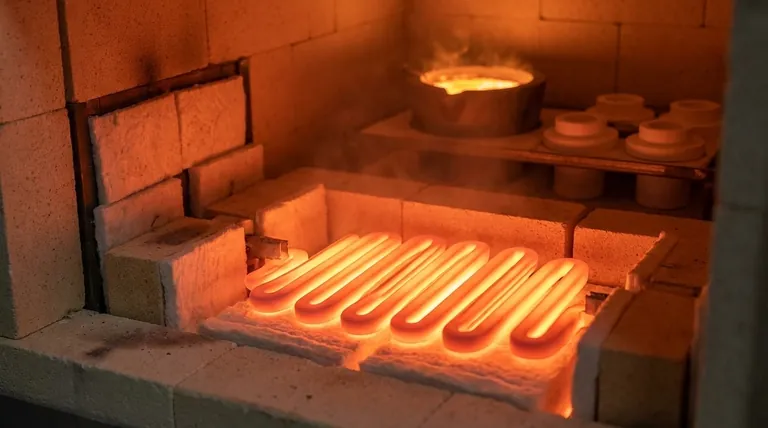
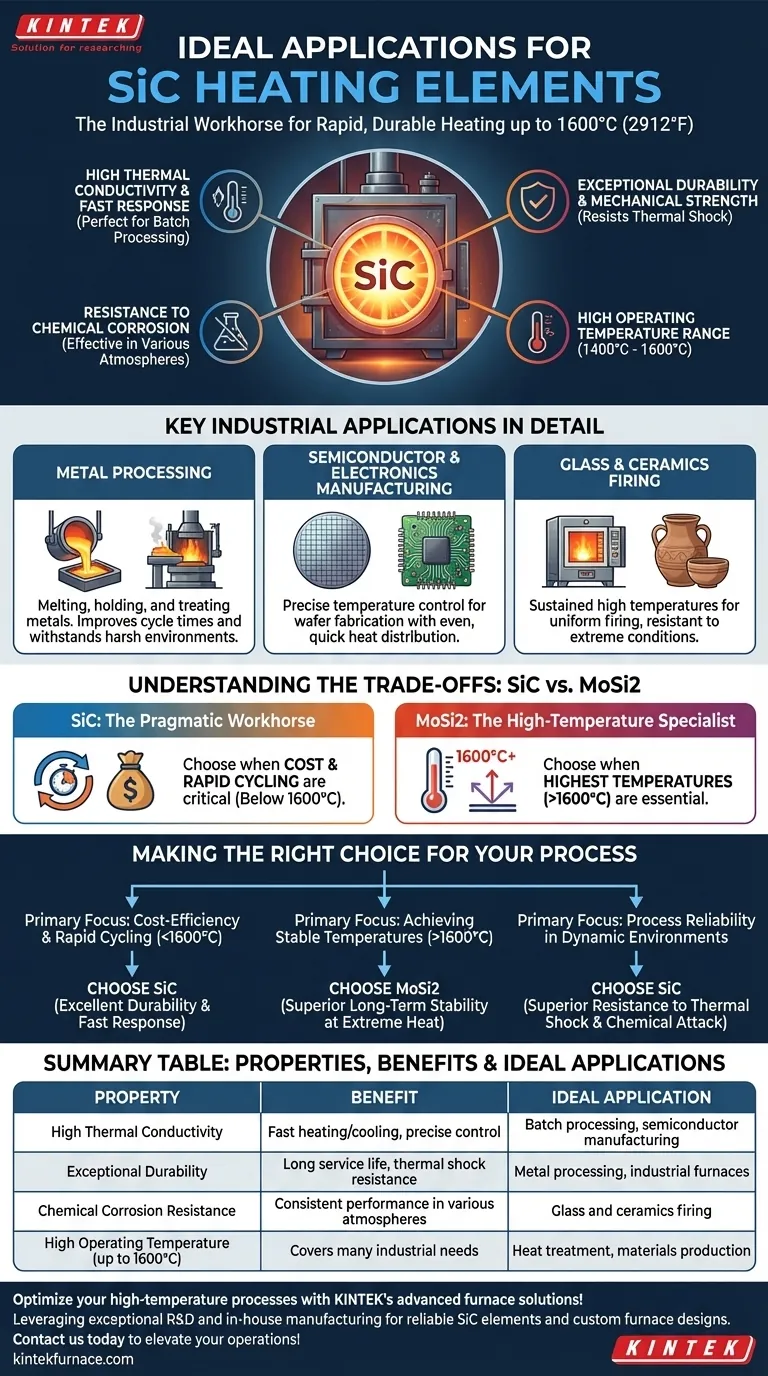
In short, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are the workhorses of industrial furnaces where rapid heating, durability, and operational efficiency are paramount. They are ideally suited for processes in metal treatment, semiconductor manufacturing, and the production of glass and ceramics, especially when operating temperatures do not need to exceed 1600°C (2912°F).
The core decision to use SiC hinges on finding a balance between performance and cost. SiC provides exceptional durability and fast thermal response for a wide range of applications, making it the pragmatic choice for most industrial heating needs below 1600°C.

The Core Strengths of SiC Elements
Understanding the ideal applications for SiC begins with its fundamental material properties. These characteristics define where it excels and why it is chosen over other technologies.
High Thermal Conductivity and Fast Response
SiC elements possess excellent thermal conductivity, allowing them to heat up and cool down very quickly.
This makes them perfect for batch processing, where furnaces must undergo frequent thermal cycles. This responsiveness ensures precise temperature control and efficient throughput.
Exceptional Durability and Mechanical Strength
These elements are known for their high mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock.
In demanding industrial environments, this translates to a longer service life and greater reliability, as the elements can withstand the physical stresses of rapid temperature changes without fracturing.
Resistance to Chemical Corrosion
SiC is highly resistant to chemical attack and oxidation.
This allows it to operate effectively in various furnace atmospheres, protecting the element from degradation and ensuring consistent performance over time.
High Operating Temperature Range
SiC heating elements operate effectively in a temperature range of 1400°C to 1600°C (2552°F to 2912°F).
This window covers the requirements for a vast number of industrial processes, from tempering steel to firing advanced ceramics.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The properties of SiC make it a versatile solution across several key industries that rely on high-temperature furnaces.
Metal Processing
In foundries and heat-treating facilities, SiC elements are used for melting, holding, and treating metals. Their rapid heating capabilities improve cycle times, while their durability withstands the harsh environment of metal processing.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The production of semiconductors and electronic components demands extremely precise temperature control. SiC's ability to provide even, quick heat distribution is critical for processes like wafer fabrication.
Glass and Ceramics Firing
Firing glass and ceramics requires sustained high temperatures and uniform heat. SiC's resistance to extreme conditions and its ability to deliver consistent heating make it an industry standard for kilns and furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs: SiC vs. MoSi2
To truly understand SiC's ideal applications, it is useful to compare it to its main high-temperature alternative, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
When to Choose SiC (The Pragmatic Workhorse)
SiC is the definitive choice when cost is a significant factor and processes require rapid cycling. Its robust nature makes it highly reliable for the majority of industrial applications that operate at or below 1600°C.
When to Choose MoSi2 (The High-Temperature Specialist)
MoSi2 elements are better suited for applications where achieving the highest possible temperatures (often above 1600°C) is critical. They offer superior oxidation resistance at these extreme temperatures, making them ideal for specialized laboratory furnaces, materials research, and certain sintering processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific operational goal is the most important factor in selecting the right heating element technology.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency and rapid cycling below 1600°C: SiC is the ideal choice due to its excellent durability and fast thermal response.
- If your primary focus is achieving stable temperatures above 1600°C: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is the more appropriate technology, especially for processes requiring long-term stability at extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is process reliability in a dynamic environment: SiC's superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack makes it a robust and dependable solution for batch processing.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element is about matching the material's specific strengths to your operational demands and budget.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| High Thermal Conductivity | Fast heating/cooling, precise control | Batch processing, semiconductor manufacturing |
| Exceptional Durability | Long service life, thermal shock resistance | Metal processing, industrial furnaces |
| Chemical Corrosion Resistance | Consistent performance in various atmospheres | Glass and ceramics firing |
| High Operating Temperature (up to 1600°C) | Covers many industrial needs | Heat treatment, materials production |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable SiC heating elements and custom furnace designs, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can elevate your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















