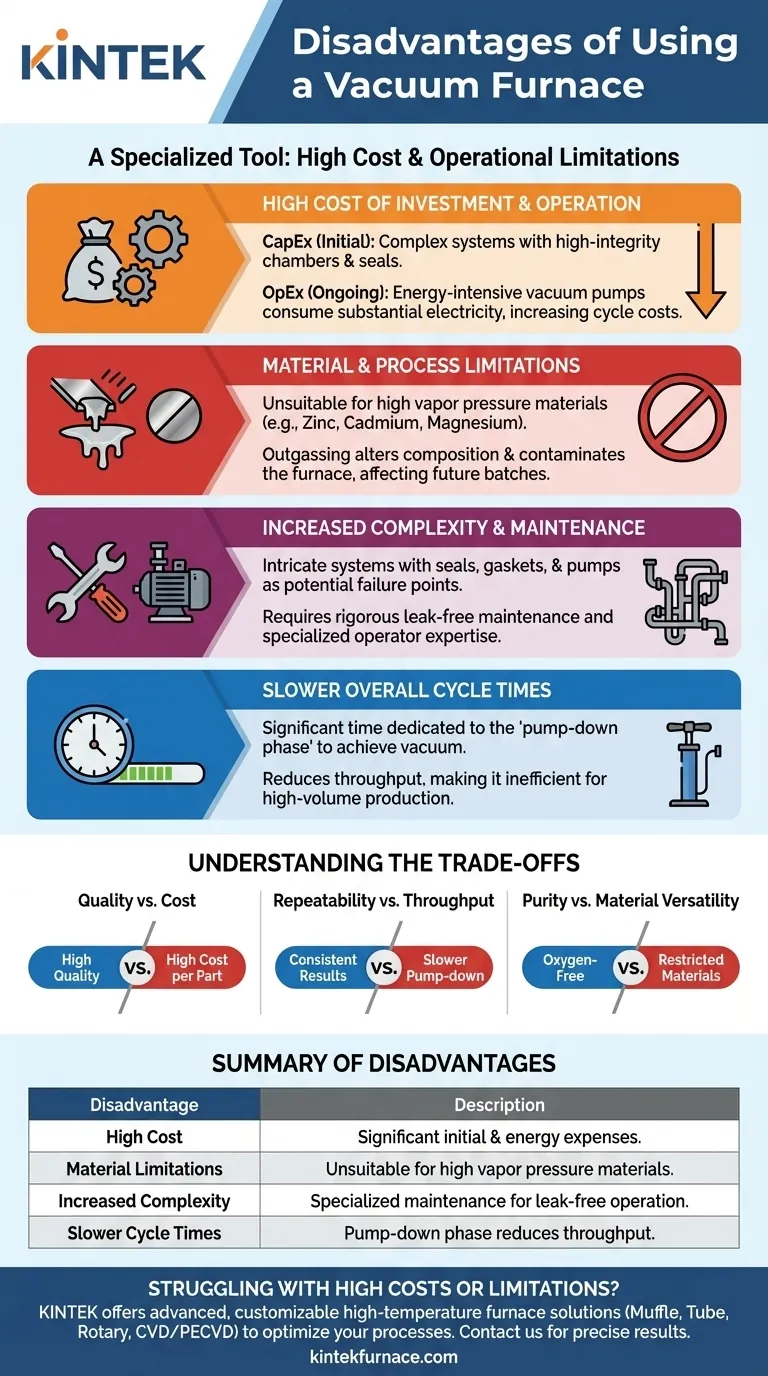
At its core, a vacuum furnace is not universally superior; it is a specialized tool designed for specific outcomes. Its primary disadvantages are significant financial investment and operational limitations that make it unsuitable for certain materials and high-volume, low-margin production. While it excels at creating parts with exceptional purity and material properties, these benefits come at a steep price.
A vacuum furnace trades cost and complexity for control. The decision to use one hinges on a simple question: Does the value of preventing oxidation and contamination outweigh the higher initial investment, increased operating costs, and specific material constraints?

A Closer Look at the Primary Disadvantages
While offering unparalleled environmental control, the technology behind vacuum furnaces introduces several critical drawbacks that must be factored into any process engineering decision.
The High Cost of Investment and Operation
The most significant barrier is financial. This cost is twofold: the initial purchase (CapEx) and the ongoing running costs (OpEx).
Vacuum furnace systems are mechanically complex, requiring high-integrity chambers, sophisticated seals, and powerful pumping systems. This advanced engineering leads to a much higher initial purchase price compared to standard atmospheric furnaces.
Operationally, the primary cost driver is energy. While the furnace chamber itself can be very thermally efficient, the vacuum pumps required to achieve and maintain low pressure consume a substantial amount of electricity. This often negates any energy savings from better insulation, resulting in a higher overall energy cost per cycle.
Material and Process Limitations
A vacuum environment is not suitable for all materials. The low-pressure conditions can cause elements with high vapor pressures (like zinc, cadmium, magnesium, or lead) to "outgas" or vaporize from the alloy.
This vaporization can have two negative effects: it can alter the chemical composition and properties of the workpiece, and the vaporized material can contaminate the furnace's interior, affecting future batches. This makes vacuum furnaces ill-suited for processing certain brasses, bronzes, or other specific alloys.
Increased Complexity and Maintenance
The addition of a vacuum system introduces significant mechanical complexity. Seals, gaskets, valves, and pumps are all potential points of failure that require specialized knowledge for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Achieving and holding a deep vacuum requires a pristine, leak-free system. This demands rigorous maintenance schedules and a higher level of operator skill compared to the relative simplicity of an atmospheric furnace.
Slower Overall Cycle Times
While the heating and cooling rates within a vacuum furnace can be very fast, the total cycle time can be longer. A significant portion of each cycle is dedicated to the pump-down phase—the time it takes for the pumps to remove air from the chamber and reach the target vacuum level.
For applications requiring high throughput, this non-productive pump-down time can be a major bottleneck, reducing the number of batches that can be processed in a day.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use a vacuum furnace is an exercise in weighing its distinct benefits against its clear disadvantages. The "right" choice is entirely dependent on the specific requirements of the final product.
Quality vs. Cost
This is the central trade-off. A vacuum furnace produces exceptionally clean, bright parts with no surface oxidation and superior metallurgical properties. This is non-negotiable for critical applications like aerospace turbine blades or medical implants. However, this premium quality comes at a higher cost per part due to the equipment and energy expenses.
Repeatability vs. Throughput
The tightly controlled digital environment of a vacuum furnace ensures that every cycle is virtually identical, leading to highly repeatable results. This consistency is a major advantage for quality control. However, it often comes at the expense of throughput due to the pump-down time required for each batch.
Purity vs. Material Versatility
The primary benefit of a vacuum is the elimination of oxygen and other reactive gases. This guarantees a pure processing environment. The trade-off is that you are restricted from processing materials that are volatile under vacuum, limiting the furnace's universal applicability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision must be driven by the end goal. A vacuum furnace is an excellent tool, but only when applied to the right problem.
- If your primary focus is maximum material integrity and purity: The high costs and complexity are necessary investments to achieve the required quality for critical components in aerospace, medical, or advanced electronics.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: An atmospheric or controlled-atmosphere furnace is almost always the more economical choice, especially if slight surface oxidation is acceptable or can be removed later.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The precise control and repeatability of a vacuum furnace make it an invaluable tool for developing new alloys and heat-treatment processes, justifying the investment.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace technology requires a clear understanding of your product's non-negotiable requirements.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Cost | Significant initial investment and ongoing energy expenses for vacuum pumps. |
| Material Limitations | Unsuitable for high vapor pressure materials like zinc, leading to contamination. |
| Increased Complexity | Requires specialized maintenance for seals, pumps, and leak-free operation. |
| Slower Cycle Times | Pump-down phase reduces throughput, making it inefficient for high-volume production. |
Struggling with high costs or material limitations in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems with deep customization to overcome challenges like those of vacuum furnaces. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or R&D, our expertise ensures precise, efficient results. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and deliver value!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















