While valued for their atmospheric control, gas kilns present significant disadvantages primarily related to cost, safety, and infrastructure. Unlike their electric counterparts, they require a substantial initial investment for professional installation, dedicated gas lines, and specialized ventilation systems to manage harmful emissions, making them far less portable and more complex to operate safely.
The core trade-off of a gas kiln is not one of artistic capability, but of logistical commitment. Its disadvantages stem from the infrastructure, safety protocols, and hands-on skill required to operate it, which must be weighed against its unique ability to create reduction atmospheres.

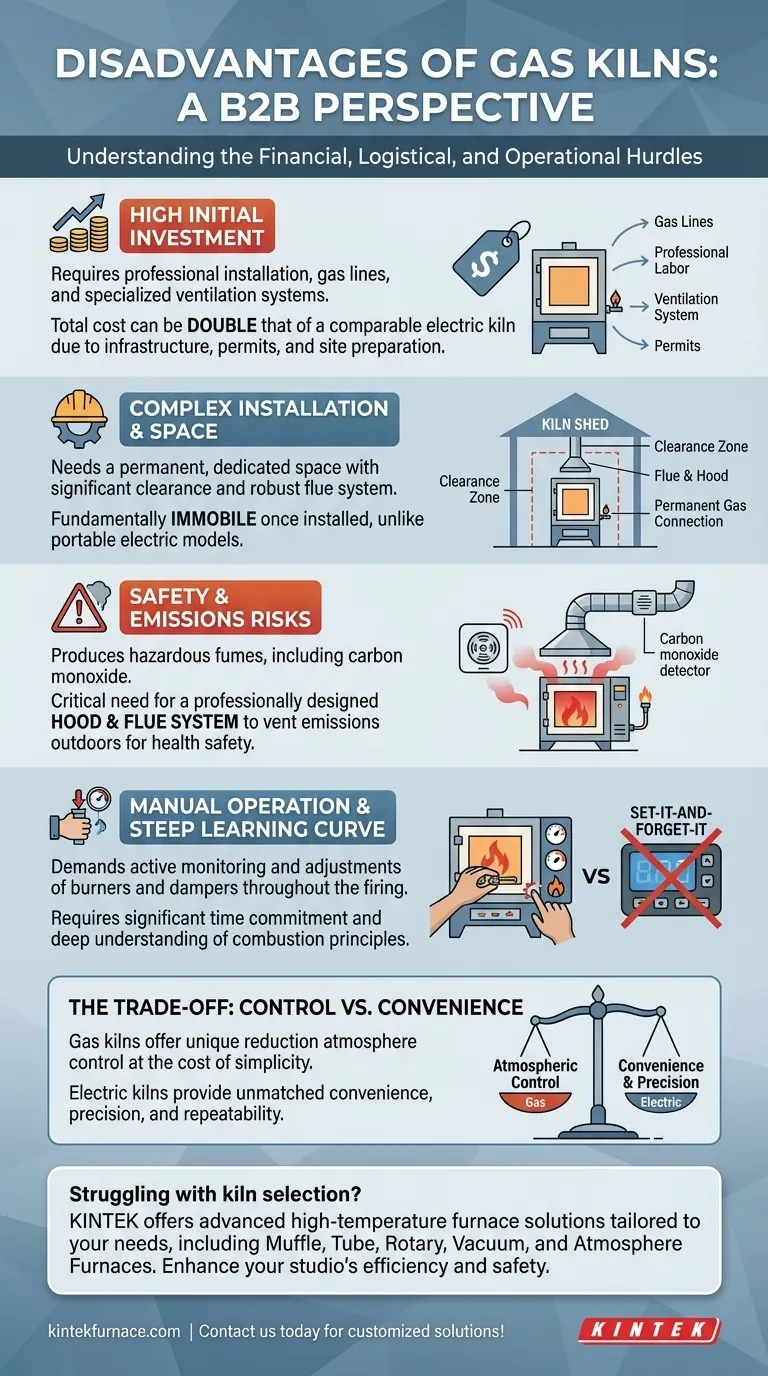
The Financial and Logistical Hurdles
The primary drawbacks of a gas kiln are often encountered before you ever fire a single piece. They involve significant upfront planning and investment that go far beyond the cost of the kiln itself.
High Initial Investment
A gas kiln's sticker price is only the beginning. The total cost includes hiring licensed professionals to run gas lines and ensure the installation meets strict local building and fire codes.
This additional infrastructure—including plumbing, permits, and potentially constructing a dedicated kiln shed—can easily double the initial cost compared to a comparably sized electric kiln.
Complex Installation and Space Requirements
Gas kilns cannot simply be placed and plugged in. They require a permanent, dedicated space with significant clearance from combustible materials and a robust ventilation system.
This necessity for a fixed gas connection and flue makes them fundamentally immobile. Once installed, moving a gas kiln is a major undertaking, unlike the relative portability of many electric models.
Operational and Safety Considerations
Beyond the setup, the day-to-day operation of a gas kiln demands a higher level of user engagement and safety awareness.
Managing Emissions and Ventilation
Gas kilns produce carbon monoxide and other hazardous fumes during firing. Proper ventilation is not optional; it is a critical safety requirement to prevent serious health risks.
This necessitates a professionally designed hood and flue system that effectively captures and vents all emissions outdoors. This system requires its own budget, installation, and regular maintenance.
The Manual Firing Process
Unlike the "set-it-and-forget-it" nature of modern electric kilns with digital controllers, gas kilns are manually operated. The potter must actively monitor and adjust the burners and dampers throughout the firing.
This process demands a steep learning curve, a significant time commitment during the firing cycle, and a deep understanding of combustion principles to achieve consistent results. What one potter sees as artistic control, another may see as a major operational burden.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of a gas kiln are directly linked to its greatest strengths. Choosing one is a matter of understanding which compromises you are willing to make.
Control vs. Convenience
The manual adjustments that make gas firing difficult are the very same actions that allow a potter to manipulate the kiln's atmosphere. This control is essential for creating the unique colors and effects of a reduction firing, which is impossible in a standard electric kiln.
An electric kiln offers unmatched convenience, precision, and repeatability. A gas kiln offers a broader, more dynamic artistic palette at the cost of that simplicity.
Fuel Costs and Availability
While installation costs are high, the operational cost of natural gas or propane can sometimes be lower than electricity, depending on local utility rates. However, this can be offset by a dependence on fuel deliveries or a reliable utility connection.
Electric kilns, by contrast, only require a common utility that is available nearly everywhere, offering more predictable access to power.
Making the Right Choice for Your Studio
Choosing a kiln is about aligning the tool's characteristics with your specific goals, resources, and environment.
- If your primary focus is predictable results and ease of use: The operational simplicity and automated nature of an electric kiln make it the superior choice, avoiding the logistical hurdles of gas.
- If your primary focus is achieving reduction effects and unique glazes: The disadvantages of a gas kiln are a necessary trade-off for gaining complete control over the firing atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is budget and space limitations: The high installation costs and extensive ventilation requirements of a gas kiln make an electric model a more practical and accessible option.
By understanding these fundamental disadvantages, you can confidently select the kiln that best serves not just your art, but your entire studio practice.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Initial Investment | Requires professional installation, gas lines, and ventilation, doubling costs vs. electric kilns. |
| Complex Installation | Needs permanent space, dedicated gas connection, and robust flue systems, limiting portability. |
| Safety and Emissions | Produces carbon monoxide, demanding proper ventilation and ongoing safety monitoring. |
| Manual Operation | Involves hands-on firing with a steep learning curve, requiring time and skill for consistent results. |
| Fuel Dependence | Relies on natural gas or propane, which may have availability issues and variable costs. |
Struggling with kiln selection for your lab? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Enhance your studio's efficiency and safety—contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















