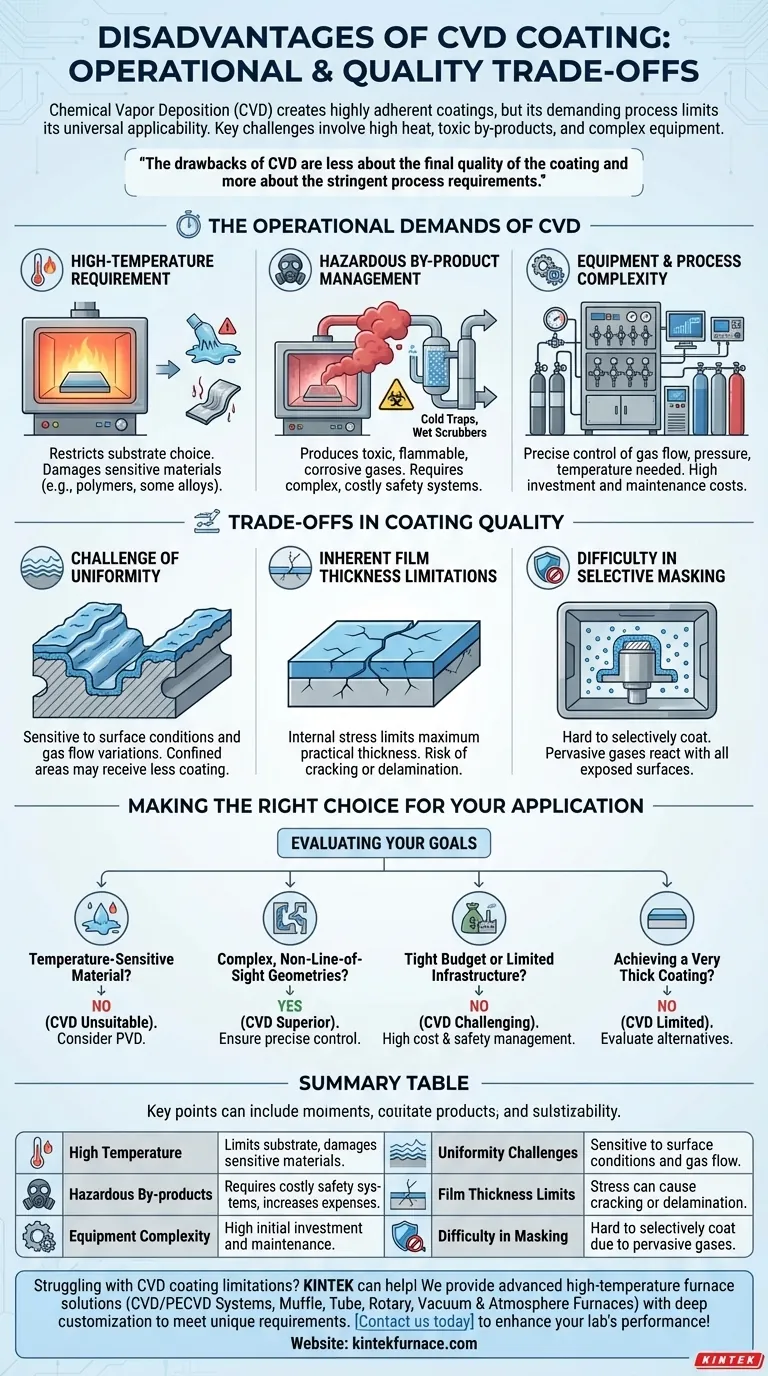
While Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is renowned for creating highly adherent and uniform coatings, it is not a universally applicable solution. Its primary disadvantages stem from the demanding nature of the process itself, specifically its reliance on high temperatures, the creation of hazardous by-products, and the inherent complexity and cost of the required equipment. These factors can significantly limit its use for certain materials and applications.
The drawbacks of CVD are less about the final quality of the coating and more about the stringent process requirements. Its high heat, toxic by-products, and sensitivity to process variables create significant constraints on substrate choice, operational safety, and overall cost.
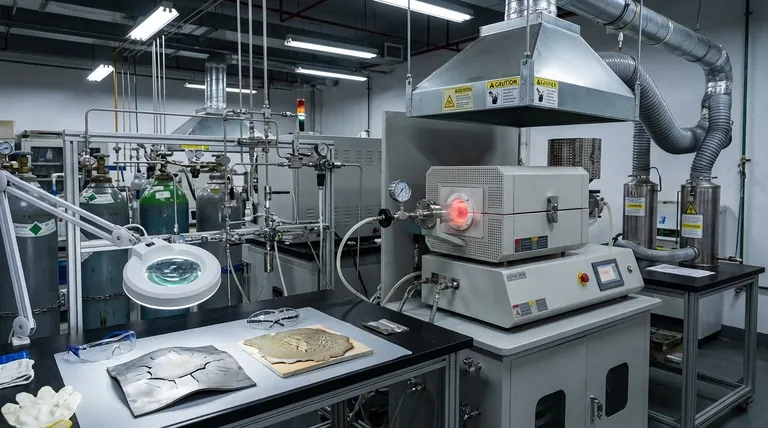

The Operational Demands of CVD
The core challenges of CVD are directly tied to the chemical reactions it uses to create a coating. Understanding these operational demands is key to identifying if it's the right process for your project.
The High-Temperature Requirement
CVD processes rely on elevated temperatures, often inside a vacuum chamber, to drive the chemical reaction between precursor gases and the substrate surface.
This heat is fundamental to the process but immediately restricts the types of materials that can be coated. Substrates sensitive to high temperatures, such as many polymers or certain metal alloys, can be damaged, warped, or otherwise compromised.
Hazardous By-product Management
The chemical reactions that form the coating also produce by-products. These gases are often toxic, flammable, or corrosive, posing significant safety and environmental risks.
Managing these by-products is non-negotiable. It necessitates complex and costly systems like cold traps, wet scrubbers, or chemical traps to neutralize the waste stream, adding to both the initial investment and ongoing operational expenses.
Equipment and Process Complexity
A CVD system is more than just a heated chamber. It requires precise control over precursor gas flow, pressure, and temperature, making the equipment inherently complex and expensive to operate and maintain compared to some alternatives like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Understanding the Trade-offs in Coating Quality
While CVD can produce exceptional coatings, achieving ideal results is a balancing act. The process is sensitive to several variables that can impact the final product.
The Challenge of Achieving Uniformity
CVD's key advantage is its ability to coat complex, non-line-of-sight geometries uniformly. However, this is not automatic.
Variations in the part's surface condition, such as the difference between a rough and a polished surface, can affect the outcome. Furthermore, confined areas like the inside of a narrow bore may receive less coating if the gas flow and reaction rate are not perfectly optimized.
Inherent Film Thickness Limitations
The process of building up the coating layer creates internal stresses within the film. This coating stress limits the maximum thickness that can be practically applied. Attempting to create an overly thick coating can lead to cracking or delamination.
Difficulty in Selective Masking
Because CVD relies on a reactive gas that fills the entire chamber, it is difficult to mask specific areas of a component that you do not want to be coated. The pervasive nature of the gas means it will react with any exposed surface that reaches the required temperature, making selective coating a significant challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Evaluating these disadvantages against CVD's benefits is critical for selecting the correct coating technology. Your primary goal will determine whether its drawbacks are acceptable trade-offs.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: CVD is likely unsuitable due to its high processing temperatures, and a lower-temperature process like PVD should be considered.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-line-of-sight internal geometries: CVD is a superior choice, provided you can precisely control the process variables to ensure uniformity.
- If your primary focus is managing a tight budget or limited facility infrastructure: The high capital cost and need for hazardous waste management make CVD a more challenging and expensive option.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very thick coating: The inherent stress in CVD films may be a limiting factor, and alternative deposition methods should be evaluated.
By understanding these fundamental limitations, you can accurately determine if CVD's powerful capabilities align with the specific constraints of your project.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Temperature | Limits substrate choice, can damage sensitive materials |
| Hazardous By-products | Requires costly safety systems, increases operational expenses |
| Equipment Complexity | High initial investment and maintenance costs |
| Uniformity Challenges | Sensitive to surface conditions and gas flow variations |
| Film Thickness Limits | Coating stress can cause cracking or delamination |
| Difficulty in Masking | Hard to selectively coat specific areas due to pervasive gases |
Struggling with CVD coating limitations? KINTEK can help! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, overcoming challenges with tailored, efficient setups. Contact us today to enhance your lab's performance and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More



















