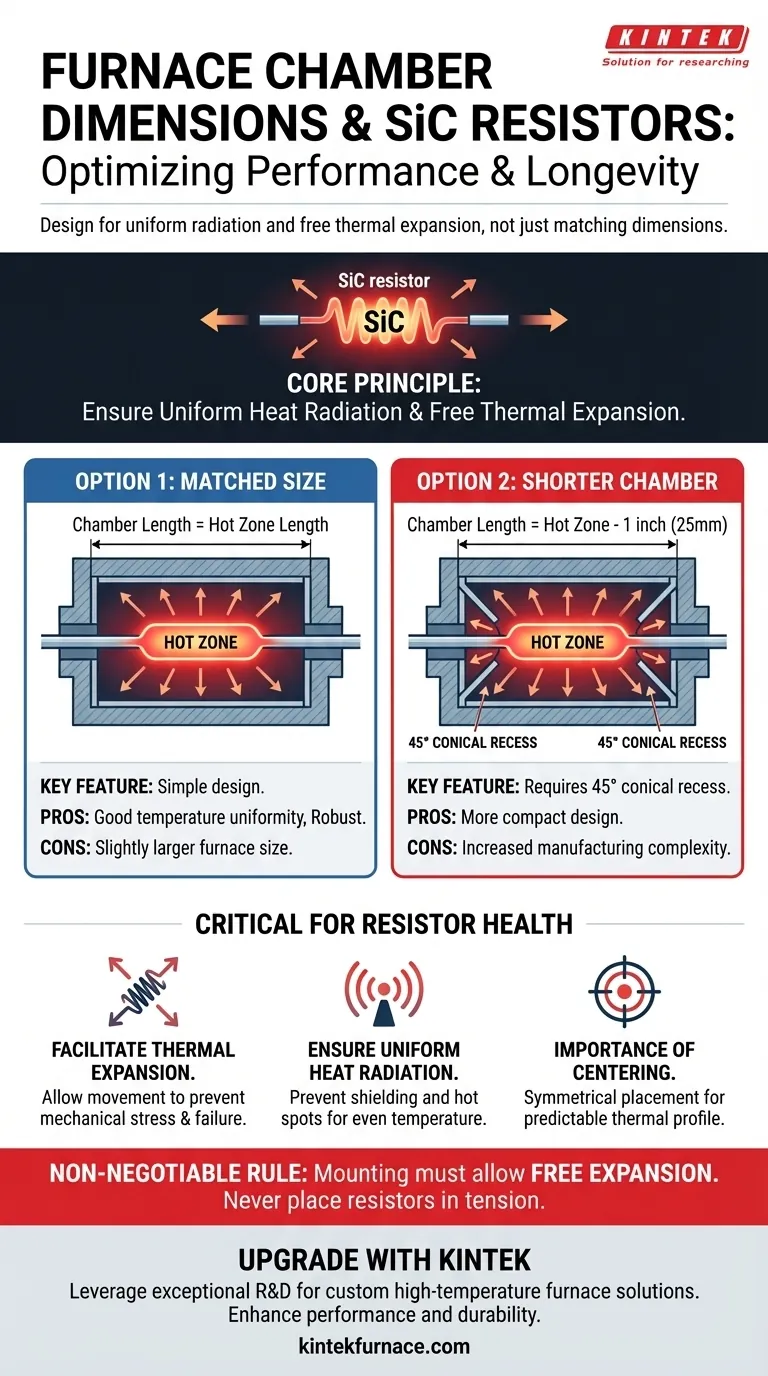
For optimal performance and longevity, your furnace heating chamber dimensions must be specified with careful consideration of the SiC resistor's hot zone. You have two primary design options: make the chamber length equal to the resistor's hot zone length, or make it one inch (25mm) shorter, provided you incorporate a specific design feature to manage heat radiation.
The central principle is not just about matching dimensions, but about ensuring the SiC heating element can radiate heat uniformly and expand freely without mechanical stress. The chamber design must facilitate these two critical functions.
The Two Core Sizing Strategies
The relationship between the chamber and the resistor's hot zone directly impacts temperature uniformity and the lifespan of the heating element. Choosing the right strategy depends on your design priorities.
Option 1: Matching Chamber to Hot Zone Length
This is the most straightforward and common approach. By making the internal furnace chamber length equal to the hot zone length of the SiC resistor, you provide ample space.
This design ensures the entire heating section of the resistor can radiate energy freely and symmetrically into the chamber. It is the simplest path to achieving good temperature uniformity.
Option 2: Chamber 1 Inch (25mm) Shorter
A more compact furnace can be achieved by making the chamber slightly shorter than the element's hot zone. However, this requires a critical modification to the furnace wall.
You must incorporate a 45° conical recess into the refractory wall at each end of the element. This tapered opening prevents the ends of the hot zone from being "shielded" by a flat wall, which would cause poor heat transfer and potential hot spots on the element. The conical shape allows the heat to radiate properly into the main chamber.
Why This Dimension is Critical for Resistor Health
The correct chamber design is not merely an efficiency concern; it is fundamental to preventing premature failure of your SiC heating elements. The goal is to create a stable environment where the element can function as intended.
Facilitating Unrestricted Thermal Expansion
SiC resistors expand when heated. The furnace chamber and mounting system must allow for this movement.
If the element is constrained, mechanical stress will build up, leading to cracks and catastrophic failure. Both sizing strategies, when implemented correctly, provide the necessary clearance for this thermal expansion and contraction.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Radiation
The primary function of the heating element is to radiate heat. If any part of the hot zone is too close to a surface or shielded, it cannot radiate effectively.
This creates non-uniform temperatures both on the element and within the furnace. These imbalances reduce resistor lifespan and compromise the quality of the process being run in the furnace.
The Importance of Centering
Regardless of the length dimension, the SiC resistors must be centered within the chamber. This applies to both horizontal and vertical orientations.
Centering ensures heat radiates symmetrically toward the furnace walls and the workload, which is essential for achieving a predictable and uniform thermal profile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each design strategy comes with its own set of considerations. Your choice depends on balancing simplicity against other design constraints.
Matched Size: Simplicity vs. Space
The primary advantage of matching the chamber to the hot zone is design simplicity. It is a robust, forgiving approach that is less prone to manufacturing error.
The trade-off is a slightly larger, and therefore potentially less insulated, furnace design for a given hot zone.
Shorter Chamber: Compactness vs. Complexity
Making the chamber shorter allows for a more compact furnace design. This can be beneficial where space is a premium or for optimizing insulation.
The clear downside is increased complexity. The 45° conical recess must be manufactured correctly. An improperly formed recess can worsen temperature uniformity, defeating the purpose of the design.
Mounting Freedom is Non-Negotiable
Remember that resistors should never be placed in tension. The mounting hardware must support the element securely while allowing it to expand and contract independently. This principle is paramount and applies to all sizing and orientation choices.
Making the Right Choice for Your Furnace Design
Your final decision should be guided by your project's specific priorities, whether they are ease of manufacturing, performance guarantees, or physical constraints.
- If your primary focus is design simplicity and guaranteed uniformity: Match the furnace chamber dimension directly to the resistor's hot zone length.
- If your primary focus is creating the most compact furnace possible: You may design the chamber to be one inch (25mm) shorter, but you must include a properly-formed 45° conical recess at each end.
- Regardless of your choice: Always ensure the mounting system supports the element without restriction, allowing for free thermal expansion to prevent mechanical failure.
Proper chamber dimensioning is the foundation for a reliable and efficient high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Strategy | Chamber Length Relative to Hot Zone | Key Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Option 1 | Equal to hot zone length | No additional features | Simple design, good temperature uniformity | Slightly larger furnace size |
| Option 2 | 1 inch (25mm) shorter | 45° conical recess at each end | More compact design | Increased manufacturing complexity |
Upgrade your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your furnace design!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















