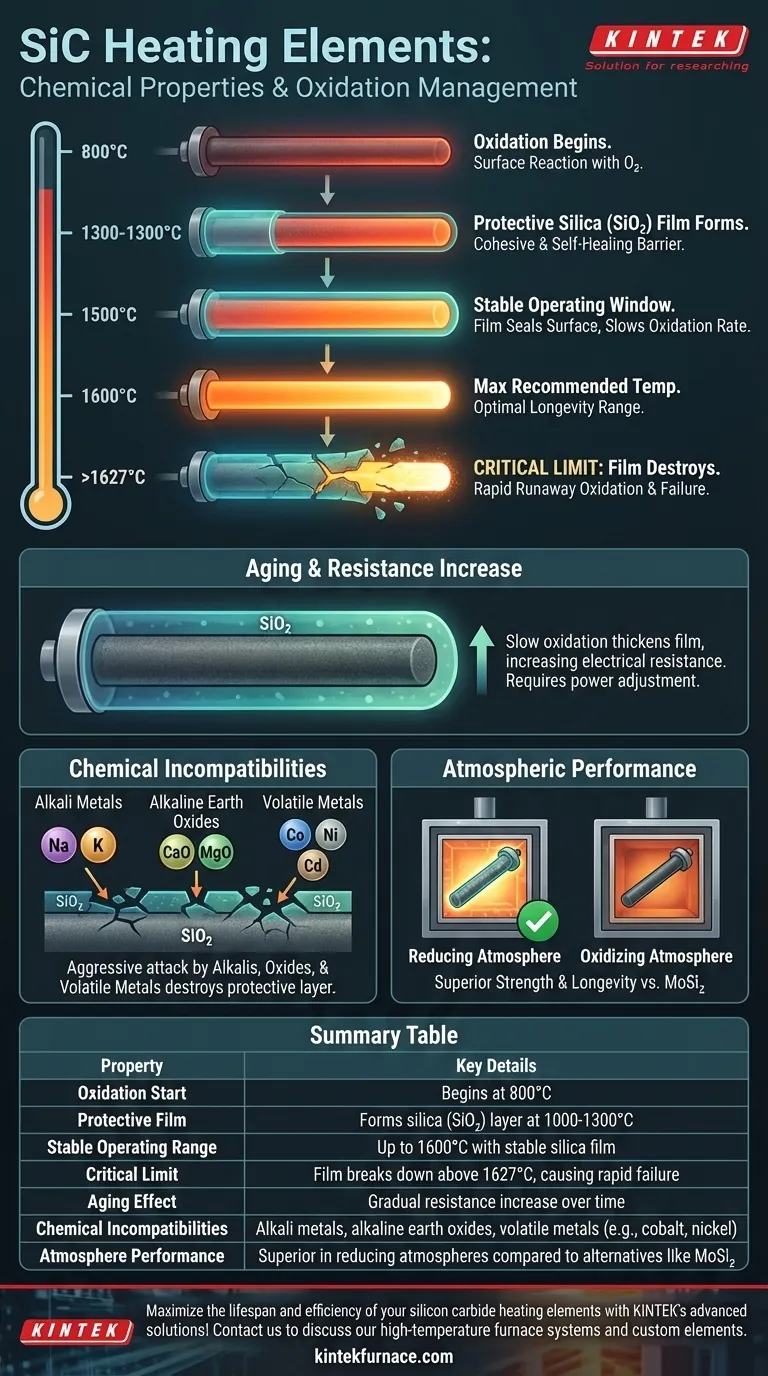
Regarding their chemical properties, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are defined by a managed oxidation process that is both protective and, ultimately, their primary failure mechanism. Oxidation begins at 800°C, forming a protective silica (SiO₂) layer that stabilizes around 1500°C. However, this protective film is destroyed above 1627°C, leading to rapid degradation and a drastically shortened operational life.
The longevity of a silicon carbide heating element is not determined by its ability to resist heat, but by its ability to maintain a protective silica film on its surface. Understanding the temperature and chemical thresholds that preserve this film is the key to maximizing its lifespan.

The Oxidation Process: A Protective Double-Edged Sword
Silicon carbide's exceptional performance at high temperatures is not due to an immunity to oxidation, but rather a controlled reaction with it.
Initial Oxidation and Film Formation
At temperatures above 800°C, the surface of the silicon carbide element begins to react with oxygen in the atmosphere. This is the start of the oxidation process.
Between 1000°C and 1300°C, this reaction forms a cohesive, self-healing layer of silica (SiO₂) glass. This film acts as a protective barrier, preventing further, more aggressive oxidation of the underlying SiC material.
The Stable Operating Window
At approximately 1500°C, the protective silica film becomes highly stable. It effectively seals the element's surface, slowing the rate of oxidation to a manageable crawl. This is why SiC elements can operate reliably for thousands of hours at high temperatures.
The maximum recommended operating temperature is typically around 1600°C, which operates within this stable regime.
The Critical Temperature Limit
Above 1627°C (2960°F), the protective silica film breaks down and is destroyed.
Without this barrier, the raw silicon carbide is exposed directly to the atmosphere. This results in accelerated, runaway oxidation that rapidly damages the element, causing premature failure.
Consequences of Long-Term Use and Aging
Even under ideal conditions, slow oxidation occurs over the element's life, leading to predictable changes in its properties.
The Inevitable Increase in Resistance
This slow, continuous oxidation gradually thickens the silica layer and alters the element's crystalline structure. The primary consequence is a gradual increase in electrical resistance over time.
This phenomenon, known as aging, is a normal part of the element's lifecycle. It requires a power supply capable of providing increased voltage to maintain the desired heat output.
Understanding Chemical Incompatibilities
Beyond temperature, certain chemicals can aggressively attack the silicon carbide element or its protective film, drastically reducing its lifespan.
The Threat of Alkali Contamination
Alkali metals and alkaline earth oxides are extremely corrosive to SiC elements. At temperatures around 1300°C, these compounds react with the silica film to form silicates.
This chemical attack destroys the protective layer and can significantly reduce the heating efficiency and structural integrity of the element.
Corrosion from Metals
Certain molten metals and their vapors can also cause severe corrosion. Process atmospheres containing volatile metals like cobalt, nickel, and cadmium will attack the elements at high temperatures, leading to rapid deterioration.
Performance in Different Atmospheres
Compared to other high-temperature elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂), SiC elements demonstrate superior strength and longevity in reducing atmospheres. This makes them a better choice for specific chemical processes where oxygen is intentionally limited.
Operating Your Elements for Maximum Lifespan
Translating these chemical properties into practice allows you to control the aging process and prevent premature failure.
- If your primary focus is longevity and stability: Operate consistently below 1500°C to maintain the integrity and protective quality of the silica film.
- If you must operate at peak temperatures: Be aware that any excursion above 1600°C significantly accelerates aging and any operation above 1627°C risks catastrophic failure.
- If your process involves chemical agents: Ensure your furnace atmosphere is meticulously clean and free from alkali compounds or volatile metals to prevent chemical corrosion.
By understanding and respecting these chemical boundaries, you can ensure the reliable, long-term performance of your silicon carbide heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Oxidation Start | Begins at 800°C |
| Protective Film | Forms silica (SiO₂) layer at 1000-1300°C |
| Stable Operating Range | Up to 1600°C with stable silica film |
| Critical Limit | Film breaks down above 1627°C, causing rapid failure |
| Aging Effect | Gradual resistance increase over time |
| Chemical Incompatibilities | Alkali metals, alkaline earth oxides, volatile metals (e.g., cobalt, nickel) |
| Atmosphere Performance | Superior in reducing atmospheres compared to alternatives like MoSi₂ |
Maximize the lifespan and efficiency of your silicon carbide heating elements with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you avoid oxidation pitfalls and chemical incompatibilities. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored heating elements can enhance your lab's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















