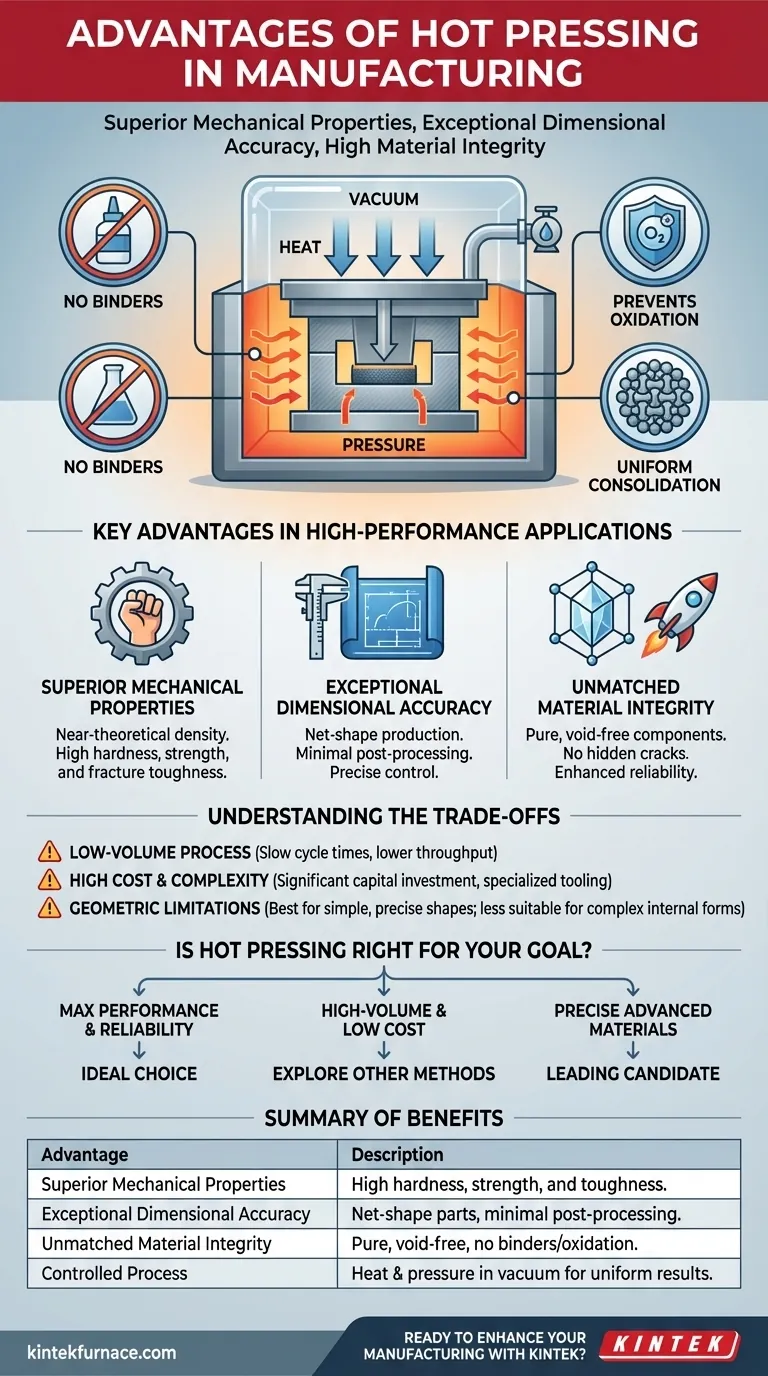
In manufacturing, the primary advantages of hot pressing are the ability to produce components with superior mechanical properties, exceptional dimensional accuracy, and high material integrity. This process uniquely combines heat and pressure, often in a vacuum, to fully consolidate materials and create strong, pure bonds without the need for chemical binders.
By simultaneously applying controlled heat and pressure, hot pressing achieves a level of material density and purity that is often unattainable with other methods, making it the definitive choice for applications where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.

The Core Mechanism: How Hot Pressing Achieves Superior Quality
To understand the advantages, you must first understand the fundamental principles at work. Hot pressing is not simply about shaping; it is about fundamentally re-engineering a material at the microscopic level.
Combining Heat and Pressure
The process uses high temperatures to soften the material, making it more plastic and allowing it to flow. Simultaneously, immense pressure is applied to force the material particles together, eliminating voids and ensuring uniform density throughout the component.
This controlled, uniform flow results in parts with minimal internal stress and deformation, a key factor in its reliability.
Eliminating Binders for Purity
Many other consolidation processes, particularly for powders, rely on binders or sintering aids to help "glue" particles together. These binders remain in the final product as impurities, creating weak points.
Hot pressing eliminates the need for binders. The heat and pressure are sufficient to cause the material particles to bond directly to each other, resulting in a monolithic structure with significantly higher purity and strength.
The Role of Vacuum Environments
Hot pressing is often performed in a vacuum or inert gas environment. This is a critical step that prevents the material from reacting with oxygen at high temperatures.
By preventing oxidation, the process preserves the material's intrinsic properties and ensures maximum integrity, which is especially vital for reactive metals and advanced ceramics.
Key Advantages in High-Performance Applications
The unique mechanism of hot pressing directly translates into tangible benefits, making it a preferred method for industries like aerospace, defense, and medical manufacturing.
Superior Mechanical Properties
Because hot pressing creates a nearly fully dense and pure material, the final component exhibits mechanical properties—such as hardness, strength, and fracture toughness—that approach the theoretical maximum for that material.
Exceptional Dimensional Accuracy
The precise control over temperature and pressure, combined with rigid, specialized molds, allows for the production of net-shape or near-net-shape parts. This means the component comes out of the press with high dimensional accuracy and requires minimal post-processing.
Unmatched Material Integrity
The combination of complete particle bonding, zero binders, and no oxidation results in a final product with outstanding integrity. The part is free from the hidden voids, cracks, or impurities that can lead to premature failure in demanding environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is not a universal solution. Its advantages come with specific limitations that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Cycle Time and Throughput
The process of heating the mold, applying pressure for a sustained period (dwell time), and then cooling it down is inherently slow. This makes hot pressing a low-volume manufacturing process compared to methods like injection molding or stamping.
Cost and Complexity
Hot pressing equipment, including vacuum furnaces and high-tonnage presses, represents a significant capital investment. Furthermore, the specialized molds must be made from materials that can withstand extreme heat and pressure, adding to the operational cost.
Geometric Limitations
While excellent for producing precise shapes, hot pressing is less suitable for creating parts with highly complex internal geometries or undercuts. The reliance on direct, top-down pressure limits the complexity of the forms that can be achieved in a single operation.
Is Hot Pressing the Right Choice for Your Goal?
Deciding on hot pressing requires weighing its unparalleled quality against its practical constraints. Your choice should be driven by the final application's requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and reliability: Hot pressing is an ideal choice, as it delivers superior mechanical properties and material integrity for mission-critical components.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and low cost: You should explore other methods, as the slow cycle times and high operational costs of hot pressing will be prohibitive.
- If your primary focus is creating precise parts from advanced materials: Hot pressing is a leading candidate, especially for ceramics, composites, and powder metals where achieving full density is critical.
Ultimately, choosing hot pressing is a strategic decision to prioritize absolute material quality over production speed and cost.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Mechanical Properties | Achieves high hardness, strength, and toughness with near-theoretical density. |
| Exceptional Dimensional Accuracy | Produces net-shape parts with minimal post-processing. |
| Unmatched Material Integrity | Eliminates binders and oxidation for pure, void-free components. |
| Controlled Process | Combines heat and pressure in vacuum environments for uniform results. |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing with high-performance hot pressing solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can deliver superior quality and reliability for your aerospace, defense, or medical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory hot press for F-MWCNT films? Boost Power Factor by 400%
- Why are precision molds and laboratory presses critical for niobium-doped TiO2 ceramics? Achieve 94% Theoretical Density



















