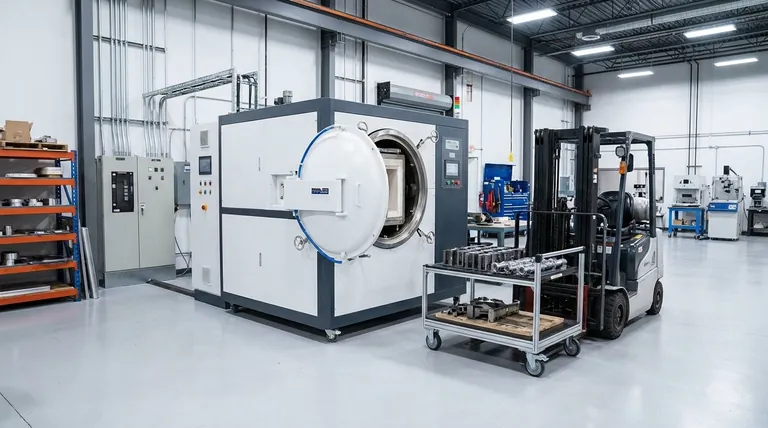
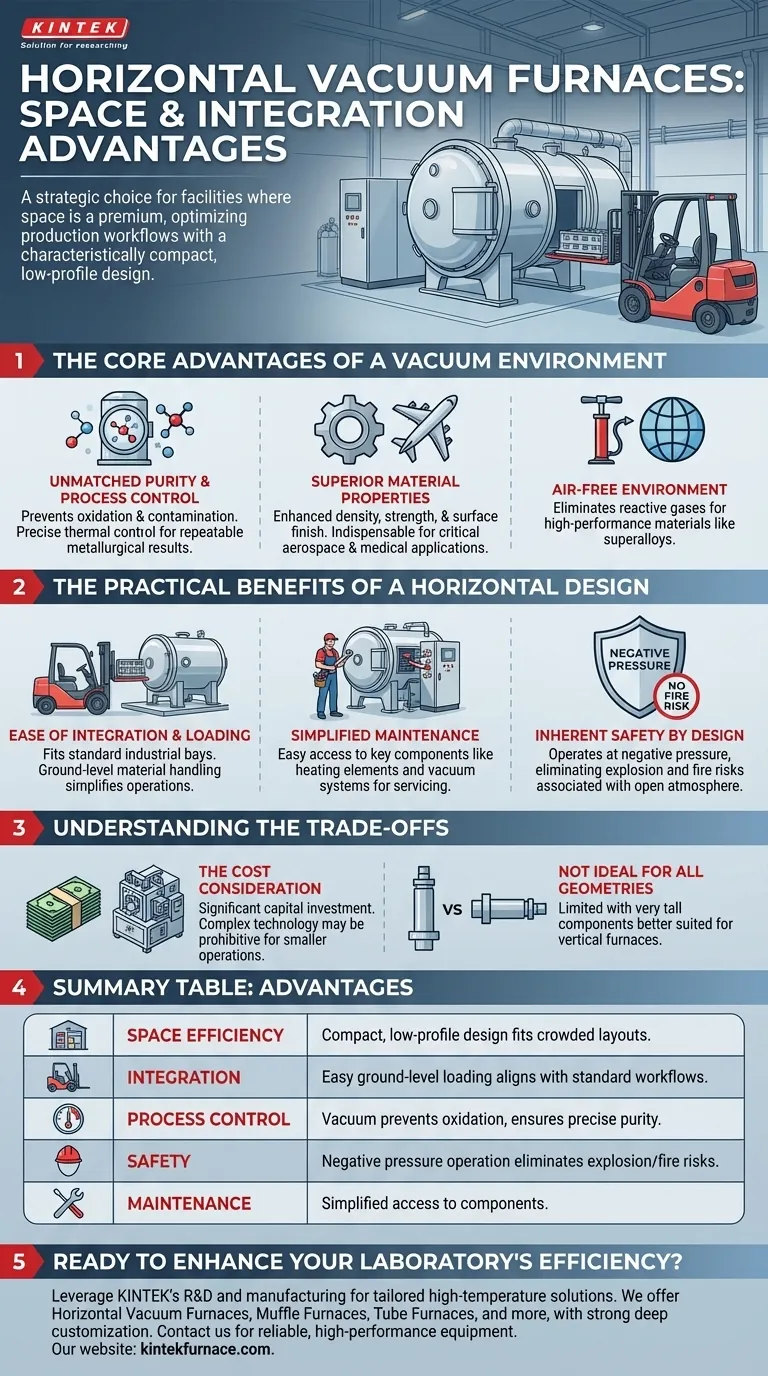
For facilities where space is a premium, a horizontal vacuum furnace is an excellent choice due to its characteristically compact design. Its low-profile configuration allows for straightforward integration into existing, often crowded, manufacturing layouts without requiring significant vertical clearance, making it a pragmatic solution for optimizing production workflows.
The decision to use a horizontal vacuum furnace extends beyond its convenient footprint. It represents a strategic choice for achieving superior material purity and process control, balanced against the practicalities of facility integration and workflow efficiency.

The Core Advantages of a Vacuum Environment
Before focusing on the horizontal design, it's crucial to understand why vacuum furnaces are used. The benefits stem from performing heat treatment in a controlled, air-free environment.
Unmatched Purity and Process Control
A vacuum furnace operates by removing the atmosphere, which prevents oxidation, decarburization, and other forms of contamination at elevated temperatures. This is essential for processing high-performance materials like superalloys, advanced ceramics, and reactive metals.
This air-free environment allows for incredibly precise thermal control, ensuring temperature uniformity and repeatable metallurgical results. Processes are often computer-controlled, guaranteeing that each batch meets identical, high-quality standards.
Superior Material Properties
The result of this controlled process is enhanced material quality. Components treated in a vacuum furnace exhibit superior density, strength, and surface finish.
This makes the technology indispensable for critical applications in aerospace, medical, and advanced manufacturing where material integrity is non-negotiable.
The Practical Benefits of a Horizontal Design
While the vacuum provides the chemical and metallurgical benefits, the horizontal orientation provides distinct logistical advantages.
Ease of Integration and Loading
The primary advantage of a horizontal furnace is its ease of integration. Unlike vertical furnaces that require significant overhead height for loading and crane access, horizontal units fit into standard industrial bays.
Loading and unloading are typically accomplished with forklifts or dedicated charging carts, aligning perfectly with common ground-level material handling workflows. This simplifies operations and can increase throughput.
Simplified Maintenance
Maintenance access is often more straightforward in a horizontal furnace. Key components like heating elements, insulation packs, and vacuum systems are frequently located along the sides or rear of the vessel, making them easier for technicians to reach and service.
Inherent Safety by Design
All vacuum furnaces offer a high degree of safety. By operating at negative pressure, they eliminate the risk of explosion associated with pressurized vessels.
Furthermore, the low-oxygen environment virtually eliminates the risk of fire, making them fundamentally safer than conventional heating furnaces that operate in an open atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. A balanced evaluation requires acknowledging the limitations.
The Cost Consideration
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The technology is complex, and the cost can be prohibitive for some applications or smaller operations.
The necessity of this investment must be weighed against the specific requirements of your materials and the quality standards you need to achieve.
Not Ideal for All Part Geometries
The key trade-off of a horizontal design is its limitation with certain part shapes. Very tall or long components that must be oriented vertically during treatment are better suited for a top-loading or bottom-loading vertical furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by your specific operational and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is processing high-performance or reactive materials: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable, and a horizontal model provides a highly efficient layout for most standard part sizes.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput on a production line: The simple, ground-level loading and workflow integration of a horizontal furnace is a decisive advantage.
- If your primary focus is cost and you are processing less sensitive materials: You must carefully evaluate if the quality benefits of a vacuum environment justify the investment over a more conventional atmosphere furnace.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about aligning the equipment's physical design and technical capabilities with your unique production and quality objectives.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Space Efficiency | Compact, low-profile design fits into crowded layouts without vertical clearance needs. |
| Integration | Easy ground-level loading with forklifts or carts, aligning with standard workflows. |
| Process Control | Vacuum environment prevents oxidation, ensures precise temperature and material purity. |
| Safety | Negative pressure operation eliminates explosion and fire risks. |
| Maintenance | Simplified access to components like heating elements and insulation. |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's efficiency with a tailored high-temperature furnace solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced options like Horizontal Vacuum Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for material purity, space optimization, and workflow integration. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals with reliable, high-performance equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















