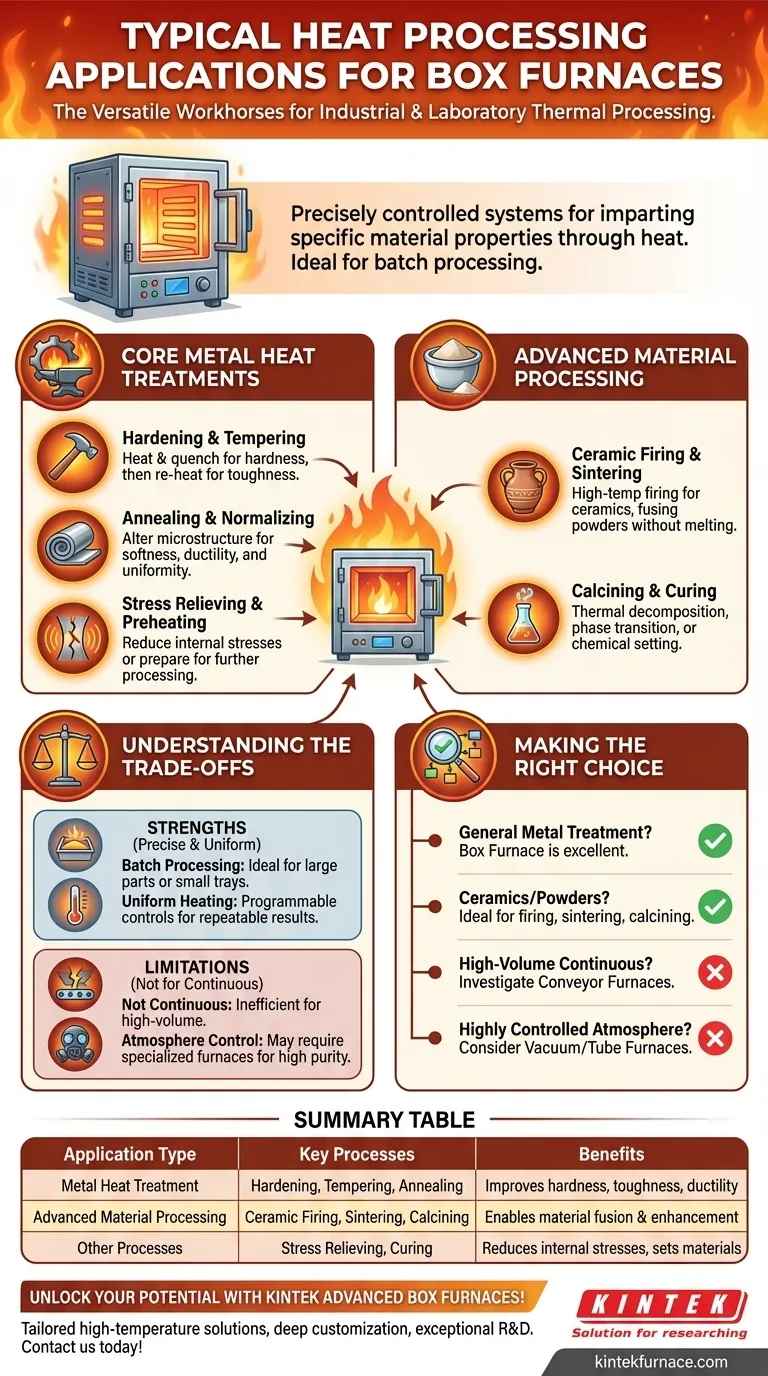
Box furnaces are the versatile workhorses of industrial and laboratory thermal processing, renowned for their ability to handle a wide array of applications. Their core functions include heat-treating metals through processes like hardening, annealing, and tempering, as well as advanced material processing such as ceramic firing, sintering, and calcining.
The key to understanding a box furnace is to see it not just as an oven, but as a highly controlled system for imparting specific material properties through heat. Its value lies in its ability to deliver precise, uniform high temperatures to a batch of parts, making it a foundational tool in metallurgy, materials science, and manufacturing.

Core Heat Treatment Processes for Metals
A primary role of the box furnace is the precise modification of metal properties. These furnaces are engineered for the high temperatures and controlled heating/cooling cycles that these metallurgical processes demand.
Hardening and Tempering
Hardening involves heating steel to a critical temperature and then rapidly cooling (quenching) it to increase its hardness and wear resistance.
This process, however, often leaves the metal brittle. Tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature heat treatment that reduces this brittleness and improves toughness, making the part durable for its end-use.
Annealing and Normalizing
Annealing is a process that alters a material's microstructure to make it softer and more ductile. This is crucial for relieving internal stresses from previous operations (like cold working or welding), improving machinability, and refining the grain structure.
Normalizing is a similar process applied to ferrous alloys to refine the grain size and create a more uniform, desirable microstructure after operations like forging or rolling.
Stress Relieving and Preheating
Stress relieving is a lower-temperature process used to reduce internal stresses in parts, particularly welded fabrications and complex machined components, without significantly changing their core material properties.
Preheating is the application of heat to a part before further processing, such as welding or forging. For example, large forging dies are often preheated in a box furnace to prevent thermal shock and extend their operational life.
Advanced Material and Component Processing
Beyond traditional metallurgy, the precise temperature control of box furnaces makes them essential for working with a variety of other materials.
Ceramic Firing and Sintering
The high-temperature capabilities of box furnaces, with some models exceeding 3000°F, make them ideal for firing ceramics and glass in laboratory, artistic, and industrial settings.
They are also used for sintering, a process that uses heat to fuse powdered materials—such as metals or ceramics—into a solid, coherent mass without melting them. This is fundamental to powder metallurgy.
Calcining and Curing
Calcining is a thermal treatment that causes decomposition, phase transition, or the removal of a volatile fraction from a material. It's a common step in the production of cement, lime, and certain catalysts.
Curing uses a box furnace to apply heat to trigger a chemical reaction to set or "cure" materials like polymers, composites, coatings, and adhesives, ensuring they achieve their final desired strength and stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A box furnace is an exceptional tool, but its effectiveness depends on correctly matching it to the operational need. Understanding its design strengths and limitations is critical.
Strength: Batch Processing
The fundamental design of a box furnace is for batch processing. You load a set of parts, run a thermal cycle, and then unload them. This is ideal for treating individual large parts (like forgings or fabrications) or trays of smaller components.
Strength: Precise and Uniform Heating
Modern box furnaces feature fully programmable controls and strategically placed heating elements to ensure highly uniform temperature throughout the chamber. This precision is what enables the repeatable, high-quality results required for applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Limitation: Not for Continuous Production
The batch nature of a box furnace makes it inefficient for high-volume, continuous manufacturing lines. For that, a conveyor furnace or continuous belt furnace, where parts move steadily through different heat zones, is the appropriate choice.
Limitation: Atmosphere Control
While some box furnaces can be equipped for modified atmospheres (e.g., inert gas purge), they are not inherently designed for the stringent, high-purity environments required for certain sensitive processes. For applications demanding strict atmospheric purity or a hard vacuum, a specialized vacuum furnace or tube furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the right thermal processing equipment, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose metal heat treatment: A box furnace is an excellent and flexible choice for batch processes like hardening, annealing, and tempering.
- If your primary focus is processing ceramics or powdered materials: The high-temperature capabilities and uniform heating of a box furnace make it ideal for firing, sintering, and calcining.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: You should investigate a conveyor or continuous belt furnace designed for your specific throughput needs.
- If your primary focus is processing in a highly controlled, pure atmosphere: A specialized vacuum furnace or tube furnace will provide the necessary environmental control that a standard box furnace cannot.
Ultimately, selecting a box furnace is a decision for robust, repeatable thermal processing for a diverse range of materials and parts.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Key Processes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Heat Treatment | Hardening, Tempering, Annealing | Improves hardness, toughness, and ductility |
| Advanced Material Processing | Ceramic Firing, Sintering, Calcining | Enables material fusion and property enhancement |
| Other Processes | Stress Relieving, Curing | Reduces internal stresses and sets materials |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced box furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental requirements are met precisely. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of laboratory high-temperature box furnaces in T6 aluminum treatment? Key to Material Strength
- How is a muffle furnace utilized for AlN crystal post-processing? Optimize Surface Purity via Staged Oxidation
- Why is immediate water-quenching required after thermal simulation? Preserve (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Alloy Microstructure
- What role does a high-temperature box resistance furnace play in sintering? Mastering Electrolyte Tube Densification
- How is a laboratory muffle furnace utilized during the debinding stage of HAp green bodies? Precision Thermal Control



















