At its core, a "CVD material" is not a single substance but a category of high-performance solids—typically thin films or coatings—created through a process called Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This technique deposits exceptionally pure and durable layers of materials like ceramics (e.g., aluminum oxide), carbides (e.g., titanium carbide), or advanced carbons (e.g., diamond films and nanotubes) onto a surface. The defining characteristic is the process itself, which builds the material atom-by-atom from a gas.
The crucial insight is that CVD is a manufacturing process, not an ingredient. It enables the creation of highly engineered surfaces and advanced materials with properties—like extreme hardness, purity, or specific electronic capabilities—that are often impossible to achieve through conventional means.
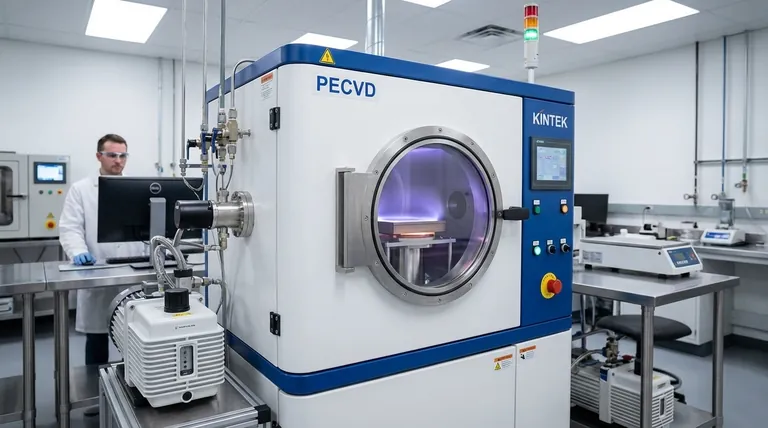

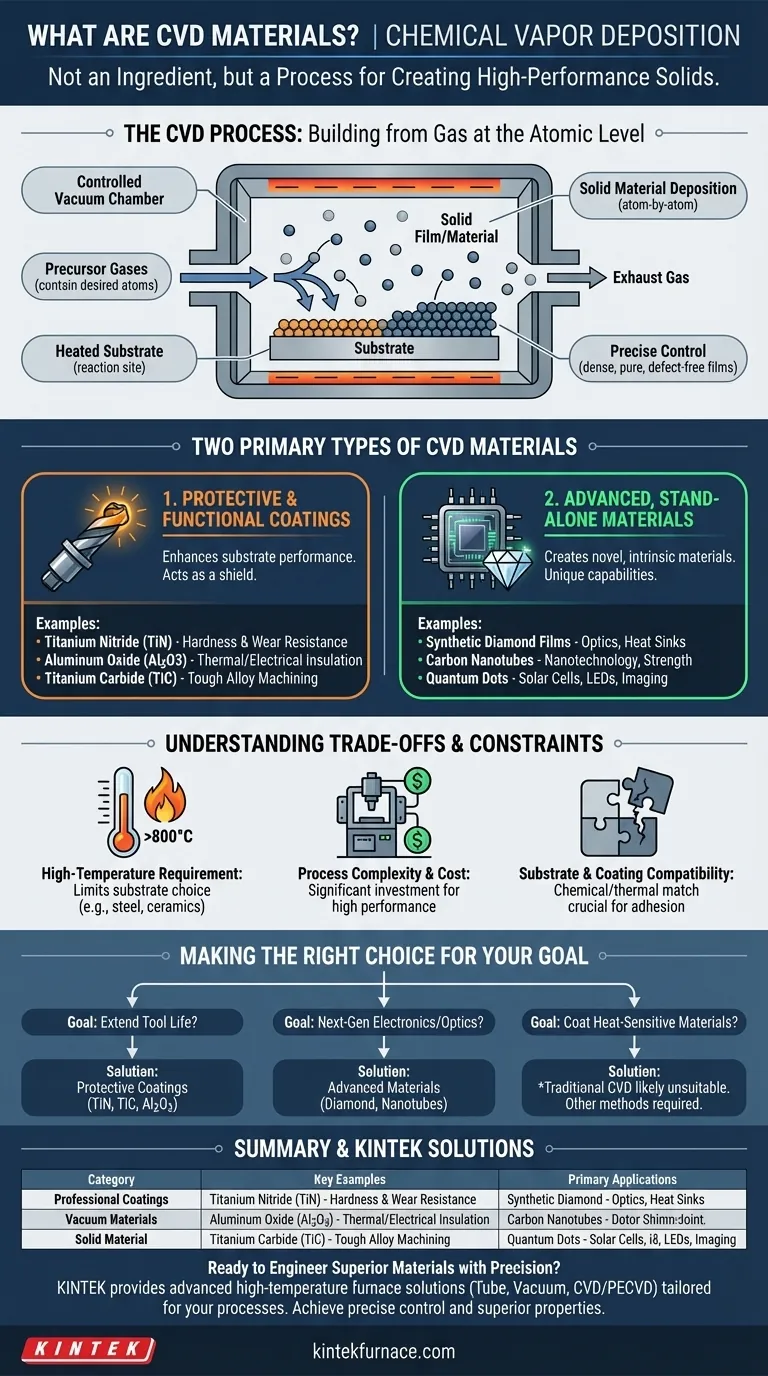
How the CVD Process Defines the Material
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a method for building a solid material from the gas phase. Understanding this process is key to understanding the material's unique properties.
The Basic Principle: Building from Gas
The process occurs inside a controlled vacuum chamber. Precursor gases, which contain the atoms of the desired material, are introduced into the chamber. These gases react on or near a heated surface, known as the substrate.
This chemical reaction causes a solid material to deposit onto the substrate, forming a thin, uniform film. The leftover gaseous byproducts are then pumped out of the chamber.
Why This Process Matters
The CVD process allows for precise control over the material's structure at the atomic level. This results in films that are extremely dense, pure, and free from the defects often found in materials formed by melting and casting. The final material is intrinsically bonded to the substrate.
The Two Primary Types of CVD Materials
While the term covers many substances, they generally fall into two distinct functional categories based on their application.
1. Protective and Functional Coatings
This is the most common industrial application. Here, a thin layer of a CVD material is applied to enhance the performance of a base component or substrate.
Common examples include:
- Titanium Nitride (TiN): A gold-colored ceramic coating used on cutting tools and drills to dramatically increase hardness and wear resistance.
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3): A highly stable ceramic used for thermal and electrical insulation and to protect against high-temperature corrosion.
- Titanium Carbide (TiC): An extremely hard material applied to tooling inserts for machining tough alloys.
In these cases, the CVD material serves as a shield, giving an ordinary object extraordinary surface properties.
2. Advanced, Stand-Alone Materials
In more advanced applications, the CVD process is used not just to coat something, but to create the primary material itself.
Key examples are:
- Synthetic Diamond Films: Used for durable optical windows, high-performance electronic heat sinks, and industrial cutting tools that can machine non-ferrous metals and composites.
- Carbon Nanotubes: Microscopic tubes of carbon with exceptional strength and electrical properties, foundational to nanotechnology and next-generation electronics.
- Quantum Dots: Semiconductor nanocrystals produced via CVD for use in advanced solar cells, high-efficiency LEDs, and medical imaging agents.
Here, the value is not in enhancing a substrate but in fabricating a novel material with unique, intrinsic capabilities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
CVD is a powerful technique, but its application is governed by significant practical constraints. Understanding these limitations is critical for its proper use.
The High-Temperature Requirement
Most CVD processes operate at very high temperatures (often >800°C). This means the substrate material must be able to withstand this heat without melting, warping, or losing its structural integrity. This limits the application to materials like tool steels, carbides, ceramics, and graphite.
Process Complexity and Cost
CVD systems are complex, requiring vacuum chambers, precise gas handling, and high-temperature control. This makes the initial investment and operational costs significant, reserving the process for applications where high performance justifies the expense.
Substrate and Coating Compatibility
A successful coating requires strong chemical and thermal compatibility between the film and the substrate. A mismatch can lead to poor adhesion, cracking, or failure of the component under stress. Not every material can be coated on every substrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a CVD material depends entirely on the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is extending the life of tools or components: You should investigate CVD protective coatings like TiN, TiC, or Al2O3 to enhance wear resistance and durability.
- If your primary focus is developing next-generation electronics or optics: You should explore CVD as a method for fabricating advanced materials like synthetic diamond films or carbon nanotubes.
- If your primary focus is on coating heat-sensitive materials like polymers or aluminum: You should recognize that traditional high-temperature CVD is likely unsuitable and other deposition methods may be required.
Ultimately, leveraging CVD is about applying a precision engineering process to create materials with precisely controlled, superior properties.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Examples | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Protective & Functional Coatings | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3), Titanium Carbide (TiC) | Cutting tools, wear resistance, thermal/electrical insulation |
| Advanced Stand-Alone Materials | Synthetic Diamond Films, Carbon Nanotubes, Quantum Dots | Electronics, optics, nanotechnology, heat sinks |
Ready to Engineer Superior Materials with Precision?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for CVD processes. Our product line—including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and specialized CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're developing next-generation electronics with diamond films or enhancing tool life with durable coatings, our expertise ensures you achieve the precise control and superior material properties your research demands.
Contact us today to discuss how our CVD solutions can accelerate your innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















