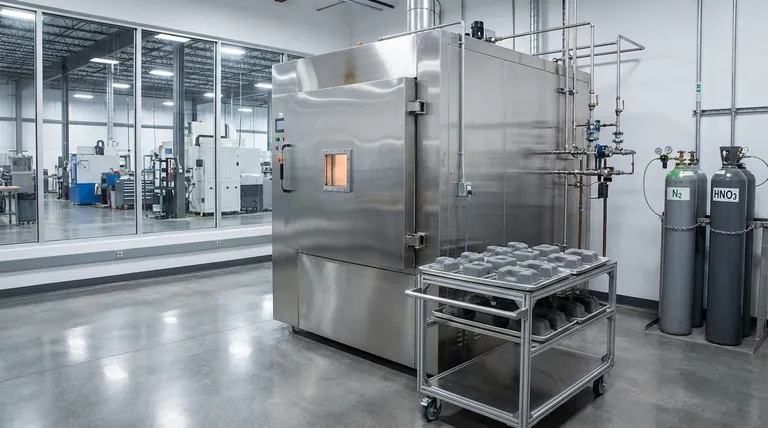
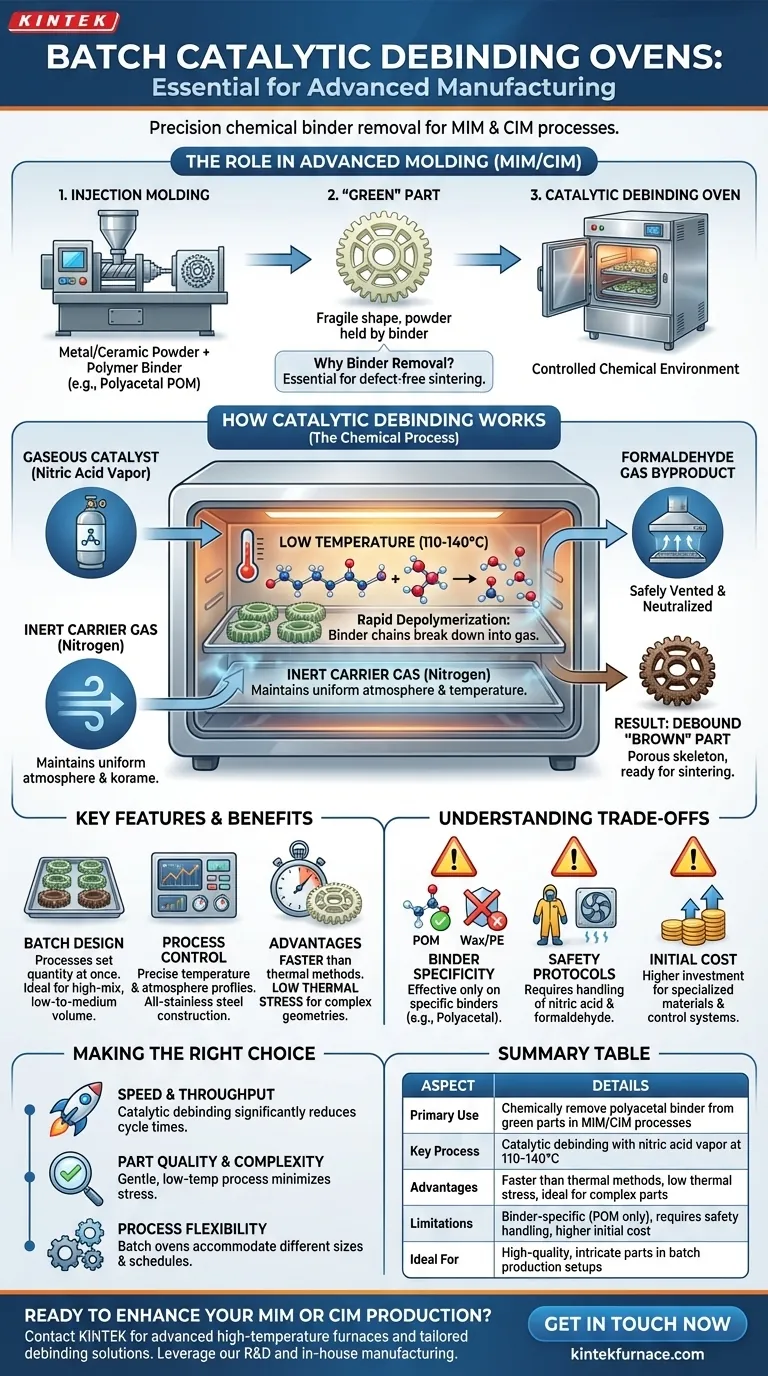
In advanced manufacturing, batch catalytic debinding ovens serve a very specific and critical function. They are engineered to chemically remove a polyacetal-based binder from "green" parts—components freshly molded from a mixture of metal or ceramic powder and a polymer. This process, known as debinding, is an essential intermediate step that prepares the fragile parts for the final high-temperature sintering that fuses them into a solid, dense final product.
The core purpose of a catalytic debinding oven is not just to heat a part, but to create a precisely controlled chemical environment. It uses a gaseous catalyst to rapidly and gently break down a specific polymer binder at low temperatures, a crucial step for producing complex and defect-free metal or ceramic components.

The Role of Debinding in Advanced Molding
To understand the oven's function, you must first understand the manufacturing process it supports: Metal Injection Molding (MIM) and Ceramic Injection Molding (CIM). This process allows for the mass production of complex, high-performance parts.
What is a "Green" Part?
A "green" part is the component immediately after it comes out of the injection molding machine. It has the final desired shape but is extremely fragile.
It consists of fine metal or ceramic powders held together by a polymer binder system, which typically makes up a significant portion of its volume.
The Purpose of the Binder
The binder, often a material like polyacetal (POM), is essential. It gives the powder mixture the flow characteristics of a plastic, allowing it to be injected into a complex mold.
Without the binder, it would be impossible to form these intricate shapes using an injection molding process.
Why Binder Removal is Critical
Before the part can be sintered (heated to near-melting point to fuse the powder particles), the binder must be completely removed.
If any binder remains during sintering, it will burn off at high temperatures, releasing gases that can cause cracks, voids, distortion, or contamination in the final part. The debinding step ensures the part is just a porous skeleton of metal or ceramic powder, ready for densification.
How Catalytic Debinding Works
Catalytic debinding is an elegant chemical solution to the problem of binder removal. It is significantly faster and gentler than purely thermal methods.
The Chemical Reaction
The process involves introducing a gaseous acid catalyst, typically nitric acid vapor, into the heated oven chamber.
This catalyst causes the polyacetal (POM) binder to rapidly depolymerize—breaking down its long polymer chains directly into a gas (formaldehyde). This occurs at a relatively low temperature, often around 110-140°C.
The Role of the Oven
The oven's primary job is to manage this reaction with extreme precision. It maintains a uniform temperature across all parts and controls the flow of an inert carrier gas, like nitrogen, which is saturated with the catalyst.
It must also be equipped with a system to safely vent and neutralize the resulting formaldehyde gas byproduct.
Advantages Over Other Methods
Compared to traditional thermal debinding, which slowly burns the binder out over many hours, the catalytic process can be completed in a fraction of the time.
This speed, combined with the low processing temperature, dramatically reduces thermal stress on the parts, making it ideal for delicate and complex geometries that might warp or crack during a slower thermal cycle.
Understanding the "Batch" Oven Design
The term "batch" refers to how parts are processed, which has implications for flexibility and control.
Processing in Batches
A batch oven processes a set quantity of parts at one time. Parts are loaded onto trays or fixtures, placed inside the chamber, and the door is sealed. The entire cycle—heating, catalytic exposure, and cooling—is run on that single "batch."
This contrasts with continuous furnaces, where parts move through different temperature zones on a conveyor belt.
Key Features for Process Control
These ovens are built with specific features mentioned in technical datasheets for a reason. All-stainless steel construction is necessary to resist the corrosive acidic catalyst.
Complete control of atmosphere and temperature profiles is non-negotiable. This ensures that every part in the batch, and every batch run, experiences the exact same conditions, leading to highly repeatable and predictable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, catalytic debinding is not a universal solution. It involves specific requirements and limitations that are critical to understand.
Binder Specificity
The primary limitation is that catalytic debinding is only effective on specific binder systems, with polyacetal (POM) being the most common. It will not work on parts molded with other binders like wax or polyethylene.
Chemical Handling and Safety
The process requires the use of a strong acid (nitric acid) and produces a hazardous gas (formaldehyde). This necessitates robust safety protocols, specialized chemical handling equipment, and effective ventilation and exhaust treatment systems.
Initial Equipment Cost
The specialized materials and precise control systems required for catalytic debinding ovens generally result in a higher initial investment compared to simpler thermal debinding furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a debinding process depends entirely on your manufacturing priorities.
- If your primary focus is speed and throughput: Catalytic debinding is one of the fastest methods available, reducing debinding cycles from days or hours to just a few hours.
- If your primary focus is part quality and complexity: The gentle, low-temperature nature of the process minimizes internal stresses, making it the superior choice for small, intricate, or fragile parts.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility: A batch oven is ideal for high-mix, low-to-medium volume production, as it can easily accommodate different part sizes and run schedules.
By understanding the core principles of catalytic debinding, you can effectively leverage its unique advantages to achieve superior quality and efficiency in your MIM or CIM operations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Chemically remove polyacetal binder from green parts in MIM/CIM processes |
| Key Process | Catalytic debinding with nitric acid vapor at 110-140°C |
| Advantages | Faster than thermal methods, low thermal stress, ideal for complex parts |
| Limitations | Binder-specific (POM only), requires safety handling, higher initial cost |
| Ideal For | High-quality, intricate parts in batch production setups |
Ready to enhance your MIM or CIM production with reliable debinding solutions? Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our advanced high-temperature furnaces, including custom Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, can be tailored to your unique needs. Leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing for precise, efficient results—get in touch now to start optimizing your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature box resistance furnace play in sintering? Mastering Electrolyte Tube Densification
- Why is a laboratory high-temperature box furnace essential for KNN ceramic powders? Mastering Solid-State Synthesis
- What is the significance of the thermal environment in calcination? Achieve Pure Ceramic Phases with KINTEK
- Why is immediate water-quenching required after thermal simulation? Preserve (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Alloy Microstructure
- How is a muffle furnace utilized for AlN crystal post-processing? Optimize Surface Purity via Staged Oxidation



















