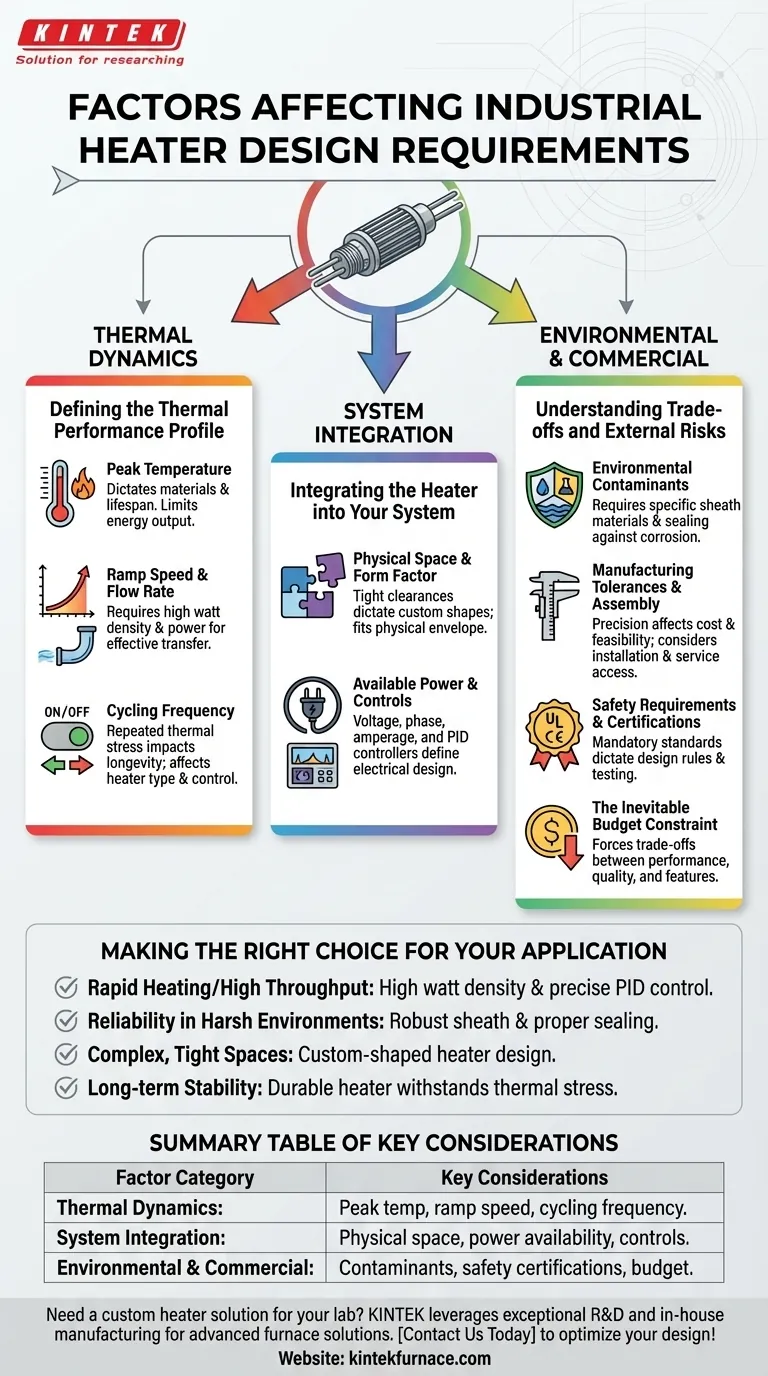
Beyond the target temperature, designing an effective industrial heater requires a holistic analysis of its operational context and physical constraints. Key additional factors fall into three main categories: the thermal dynamics of the process (how fast and how often it must heat), the system integration requirements (power, controls, and physical space), and the environmental and commercial limitations (contaminants, safety, and budget).
The most common cause of premature heater failure or poor performance is not a miscalculation of the core heating load, but a failure to account for the secondary operational, environmental, and system constraints that define the heater's real-world working conditions.

Defining the Thermal Performance Profile
The primary function of a heater is to deliver thermal energy, but how it delivers that energy is just as critical as how much. This thermal profile dictates the heater’s core construction and power requirements.
Start, Finish, and Peak Temperatures
The total temperature range the heater must produce determines the required energy output. More importantly, the peak temperature dictates the necessary materials for the heater's sheath and internal components to prevent degradation and ensure a safe operational lifespan.
Ramp Speed and Flow Rate
Ramp speed is the rate at which the temperature must climb (e.g., degrees per minute). A fast ramp-up requires a heater with a high watt density (more power in a smaller area). Similarly, heating a substance with a high flow rate (like air or water) requires significantly more power to transfer heat effectively to the moving medium.
Cycling Frequency
How often the heater cycles on and off has a major impact on its longevity. High-frequency cycling causes repeated thermal expansion and contraction, which can stress components and lead to premature failure. This factor influences the choice of heater type and the sophistication of the required control system.
Integrating the Heater into Your System
A heater does not operate in a vacuum. It must fit physically and electrically within the constraints of the larger machine or process it serves.
Physical Space and Form Factor
Often, the most challenging constraint is the physical space available. Tight clearances or complex geometries may rule out standard heater types and necessitate a custom-designed cartridge, band, or flexible heater to fit the available envelope.
Available Power and Controls
The heater's design is fundamentally limited by the facility's available electrical service. Voltage, phase, and total amperage are non-negotiable starting points for the design. Furthermore, the heater must be compatible with the thermal control system, whether it's a simple on/off thermostat or a sophisticated PID controller that manages ramp rates and prevents temperature overshoots.
Understanding the Trade-offs and External Risks
The final design is a balance between ideal performance and real-world constraints, including the environment, safety, and budget.
Environmental Contaminants
The presence of moisture, oil, chemicals, or abrasive particles in the operating environment is a leading cause of heater failure. The design must incorporate appropriate sheath materials (e.g., stainless steel, Incoloy) and sealed terminations to protect against corrosion, short-circuiting, and physical damage.
Manufacturing Tolerances and Assembly
The required precision of the heater's dimensions affects its cost and feasibility. Extremely tight tolerances increase manufacturing complexity and price. The design must also consider how the heater will be installed and serviced in the factory, as a component that is difficult to access or replace increases downtime and maintenance costs.
Safety Requirements and Certifications
Heaters must comply with relevant safety standards (like UL or CE) for the application and region. These requirements dictate specific design rules, material choices, and testing protocols that are mandatory, not optional.
The Inevitable Budget Constraint
The budget is not just a limit; it is a critical design parameter. It forces a series of trade-offs between performance, material quality, lifespan, and features. A clear budget helps prioritize which design factors are "must-haves" versus "nice-to-haves."
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To ensure success, you must provide your heater design partner with a complete picture of the application. Use this framework to guide your specification process.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating or high throughput: Prioritize a high watt density design and pair it with a precise PID control system.
- If your primary focus is reliability in a harsh environment: Emphasize robust sheath materials and proper sealing against specific contaminants.
- If your primary focus is fitting into a complex, tight space: The physical form factor will be your main constraint, likely leading to a custom-shaped heater.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational stability: Pay close attention to cycling frequency and select a durable heater designed to withstand thermal stress.
Ultimately, a successful heater design is one that is specified holistically, considering every aspect of its life inside your system.
Summary Table:
| Factor Category | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Thermal Dynamics | Peak temperature, ramp speed, cycling frequency |
| System Integration | Physical space, power availability, control systems |
| Environmental & Commercial | Contaminants, safety certifications, budget constraints |
Need a custom heater solution for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heater design!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















