In short, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are essential in high-temperature industrial furnaces used for metal processing, semiconductor fabrication, and the production of glass and ceramics. Their value comes from a unique combination of high-heat tolerance, durability in harsh environments, and the ability to deliver precise, uniform heat, making them a workhorse technology for demanding thermal processes.
The decision to use SiC heating elements is not just about reaching high temperatures. It is about achieving operational reliability, process consistency, and a favorable total cost of ownership in industrial environments where lesser materials would quickly fail.
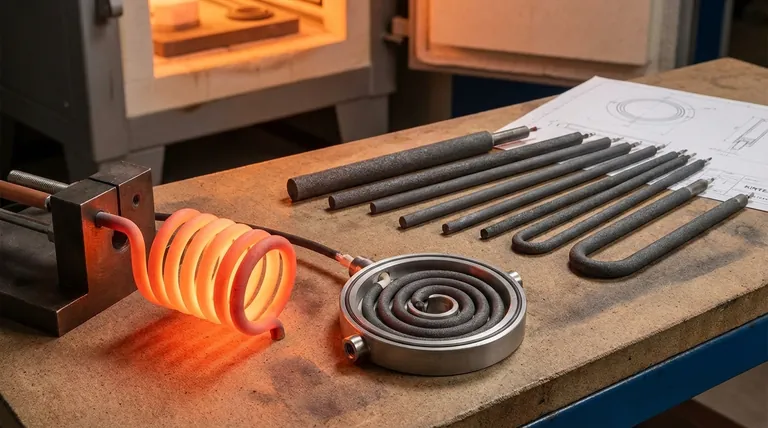

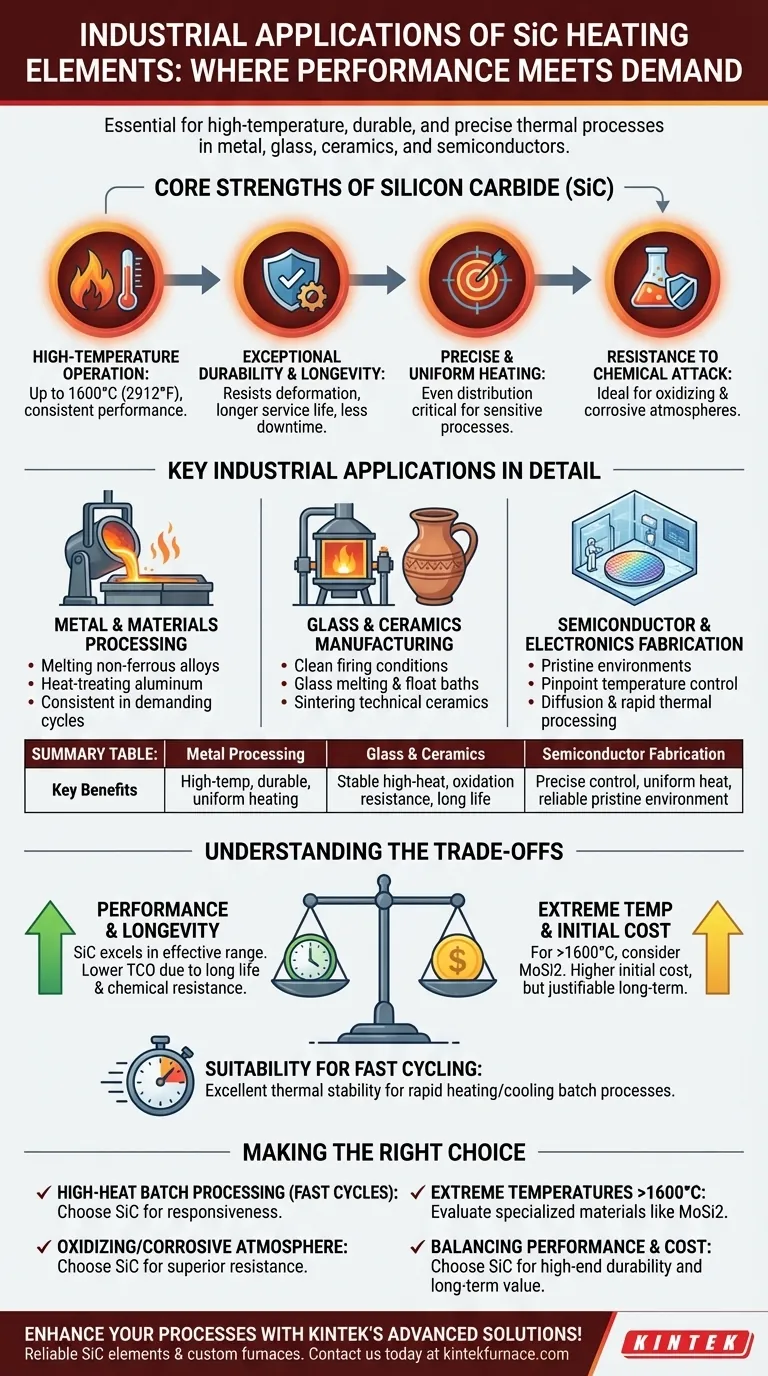
The Core Strengths of Silicon Carbide
To understand where SiC elements excel, you must first understand their fundamental properties. They are not chosen simply because they get hot, but because of how they behave under the stress of industrial production.
High-Temperature Operation
SiC elements are engineered to operate consistently at very high temperatures, often up to 1600°C (2912°F). This capability is critical for processes like melting non-ferrous metals or firing advanced ceramics.
Exceptional Durability and Longevity
Unlike many metallic heating elements, SiC is a ceramic material with high mechanical strength. It resists sagging and deformation at high temperatures, leading to a significantly longer service life and reducing costly downtime for element replacement.
Precise and Uniform Heating
These elements can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, allowing for furnace designs that provide extremely uniform heat distribution. This precision is non-negotiable in applications like semiconductor wafer processing, where temperature gradients can ruin entire batches.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
SiC has excellent resistance to oxidation and chemical corrosion. This makes it ideal for use in furnaces with oxidizing atmospheres or where process byproducts could corrode and destroy metallic elements.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The properties of SiC directly translate to its widespread use in several key industries.
Metal and Materials Processing
In foundries and heat-treating facilities, SiC elements are used for melting, holding, and heat-treating aluminum and other non-ferrous alloys. Their durability ensures consistent performance despite the demanding thermal cycles.
Glass and Ceramics Manufacturing
The production of glass and ceramics requires sustained high temperatures and clean firing conditions. SiC elements provide the stable, high-heat environment needed for glass melting, float glass baths, and the sintering of technical ceramics.
Semiconductor and Electronics Fabrication
The manufacturing of semiconductors and electronic components demands pristine environments and pinpoint temperature control. SiC elements are used in diffusion furnaces and rapid thermal processing systems where their precise heating capabilities are essential for producing high-quality wafers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technology is a universal solution. Choosing SiC involves understanding its position relative to other heating element materials.
Performance vs. Maximum Temperature
SiC provides outstanding performance in its effective temperature range. However, for the absolute highest temperatures (above 1600°C), more specialized and often more expensive elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) may be required.
Cost vs. Service Life
The initial procurement cost of SiC elements can be higher than for standard metallic elements (like Kanthal). However, their significantly longer service life and resistance to failure often result in a lower total cost of ownership, especially in aggressive environments.
Suitability for Fast Cycling
SiC's thermal stability makes it well-suited for batch processes that require rapid heating and cooling. This ability to withstand thermal shock gives it an advantage in applications where furnaces are not running continuously.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your industrial application.
- If your primary focus is high-heat batch processing with fast cycles: SiC is an excellent choice due to its thermal stability and responsiveness.
- If your primary focus is longevity in an oxidizing or corrosive atmosphere: SiC's inherent chemical resistance makes it a superior and more reliable option than most metallic elements.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures above 1600°C: You should evaluate more specialized materials like MoSi2, which are designed for that upper range.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance with operational cost: SiC offers a compelling middle ground, providing high-end durability and precision for a justifiable long-term investment.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element is about matching the material's proven capabilities to your specific process requirements.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Metal Processing | High-temperature operation, durability, and uniform heating for melting and heat-treating non-ferrous metals. |
| Glass & Ceramics | Stable high-heat environments, resistance to oxidation, and long service life for clean firing conditions. |
| Semiconductor Fabrication | Precise temperature control, uniform heat distribution, and reliability in pristine environments for wafer processing. |
Enhance your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable SiC heating elements and custom furnace designs, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to optimize your thermal applications and achieve superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















