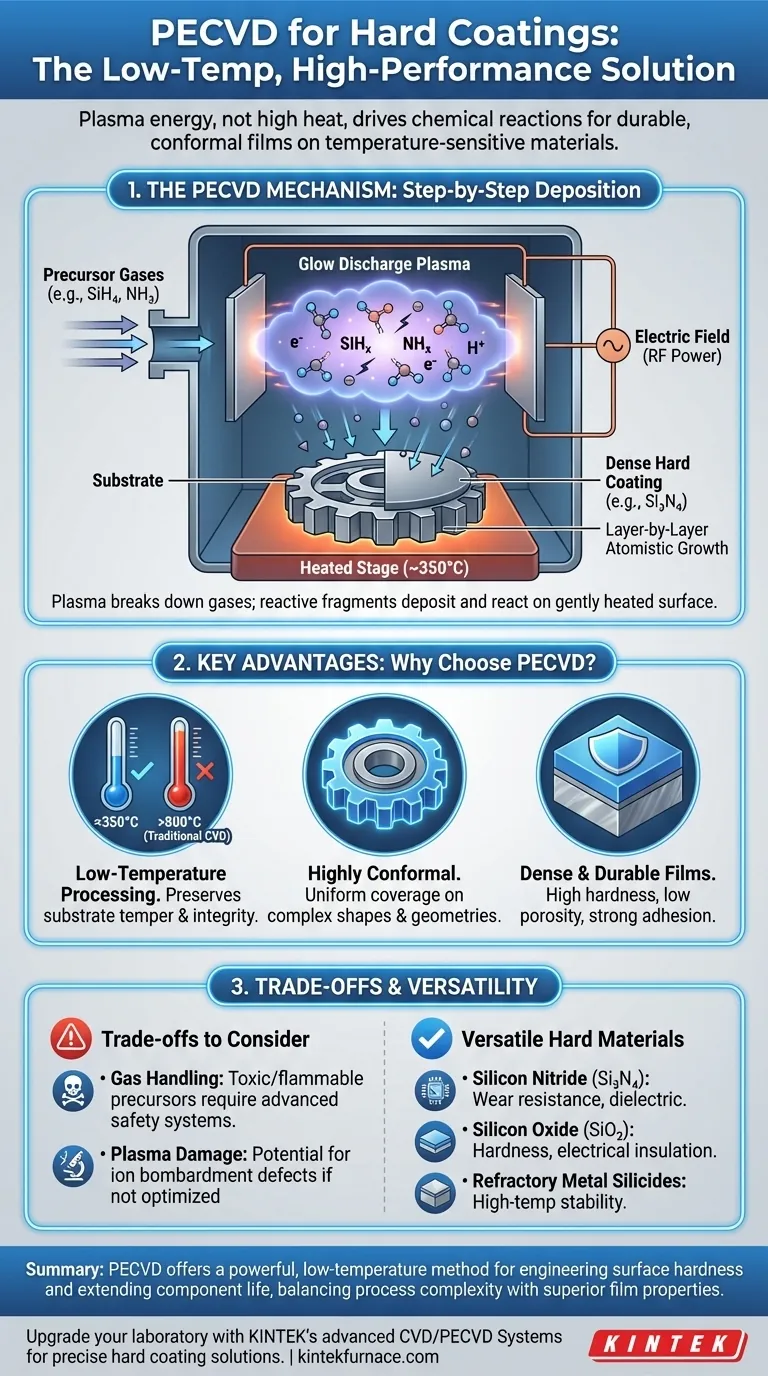
To deposit a hard coating using PECVD, precursor gases are introduced into a low-pressure chamber where an electric field ignites them into a plasma. This plasma chemically breaks down the gases into reactive fragments, which then deposit onto a component's surface as a dense, hard, and wear-resistant film, such as silicon nitride. The entire process occurs at a relatively low temperature, preserving the integrity of the underlying material.
The core value of PECVD for hard coatings lies in its use of plasma energy, rather than high heat, to drive the chemical reactions. This enables the formation of highly durable surfaces on temperature-sensitive materials that would be damaged or distorted by conventional high-temperature deposition methods.
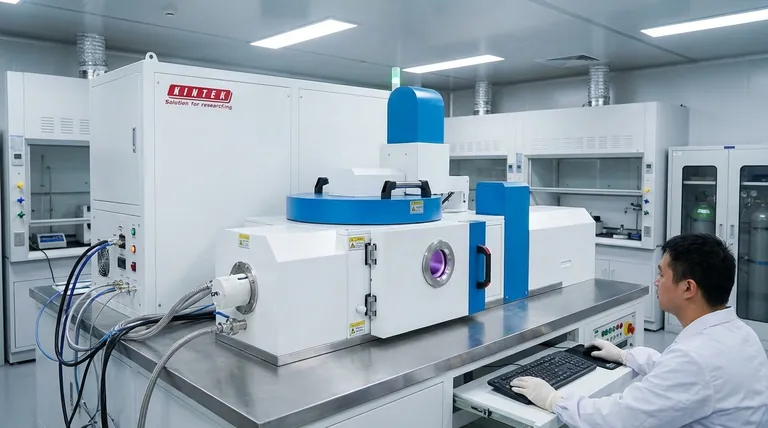

The PECVD Mechanism for Hard Coatings
PECVD, or Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition, is a process that builds a solid film atom by atom from a gaseous state. For hard coatings, the goal is to create a layer that is significantly harder and more wear-resistant than the substrate material itself.
Creating the Plasma Environment
The process begins inside a vacuum chamber containing the component to be coated, which is placed on an electrode. Precursor gases, which contain the atomic building blocks of the final coating, are introduced into the chamber at a controlled flow rate.
Energizing the Precursors with Plasma
A powerful electric field is applied between the electrodes, causing the low-pressure gas to break down and form a glow discharge plasma. This plasma is a highly energetic state of matter containing ions, electrons, and neutral radical species. It is this energy—not extreme heat—that breaks the chemical bonds in the precursor gases.
For example, to deposit a silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) hard coating, gases like silane (SiH₄) and ammonia (NH₃) are used. The plasma splits them into highly reactive SiHₓ and NHₓ fragments.
Surface Reaction and Film Growth
These reactive fragments bombard the surface of the component. The component itself is gently heated (typically around 350°C) to provide just enough thermal energy to promote surface mobility and chemical reactions. The fragments react on the surface to form a stable, dense, and solid hard coating film.
The film grows layer by layer, resulting in a highly uniform and conformal coating that can range from nanometers to micrometers in thickness, depending on the application's requirements.
Key Advantages of the PECVD Process
Engineers choose PECVD for specific reasons when other methods fall short. The benefits are directly tied to the use of plasma instead of high thermal energy.
Low-Temperature Processing
This is the most significant advantage. Traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) often requires temperatures exceeding 800°C. PECVD achieves similar or better results around 350°C. This makes it possible to coat heat-treated steels, aluminum alloys, and other materials that would lose their crucial bulk properties (like temper or hardness) at high temperatures.
High-Quality and Uniform Films
The plasma-driven process produces films that are incredibly dense, with low porosity and strong adhesion to the substrate. Because the reactive gas species fill the chamber, the deposition is highly conformal, meaning it can uniformly coat complex shapes and geometries without thinning at sharp corners.
Versatility in Hard Materials
PECVD can be used to deposit a variety of ceramic hard coatings by changing the precursor gases. Common materials include:
- Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄): Excellent for wear resistance and as a dielectric.
- Silicon Oxide (SiO₂): Provides hardness and electrical insulation.
- Refractory Metal Silicides: Offer high-temperature stability and hardness.
This versatility allows the coating's properties to be tailored to specific operational demands, such as those for cutting tools or automotive engine components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is not a universal solution. A clear understanding of its limitations is crucial for successful implementation.
Precursor Gas Handling
The gases used in PECVD, such as silane, are often toxic, flammable, or pyrophoric (igniting spontaneously in air). This necessitates sophisticated safety systems, gas handling equipment, and facility infrastructure, which can add to the initial cost and complexity.
Distinguishing from Other Applications
The same fundamental PECVD technology is used for a wide range of applications beyond hard coatings, most notably for creating optical coatings (like anti-reflective layers) and in semiconductor manufacturing. The key difference is the choice of precursors and the precise control of plasma parameters (pressure, power, gas flow) to achieve a desired refractive index or electrical property instead of maximum hardness.
Potential for Plasma-Induced Damage
While the process is low-temperature, the bombardment by energetic ions from the plasma can, if not carefully controlled, introduce stress or microscopic defects into the film or the substrate's surface. Optimizing the process parameters is critical to balance deposition rate with film quality and minimize this effect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coating technology requires matching its capabilities to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-treated or temperature-sensitive parts: PECVD is an ideal choice due to its low processing temperature, which protects the substrate's material properties.
- If your primary focus is achieving a dense, conformal coating on a complex shape: PECVD's plasma-based nature ensures excellent, uniform coverage that is difficult to achieve with line-of-sight methods.
- If your primary focus is depositing a specific ceramic like silicon nitride: PECVD provides precise control over film composition by simply adjusting the ratio and type of precursor gases.
Ultimately, PECVD provides a powerful, low-temperature method for engineering surface hardness and extending the functional life of critical components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition using precursor gases in a low-pressure chamber |
| Key Feature | Low-temperature operation (~350°C) preserves substrate integrity |
| Common Coatings | Silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), silicon oxide (SiO₂), refractory metal silicides |
| Advantages | Uniform, conformal films; high density; strong adhesion; versatility for complex shapes |
| Limitations | Requires handling of toxic gases; potential for plasma-induced damage if not optimized |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, such as optimizing PECVD processes for hard coatings. Contact us today to enhance your research and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection



















