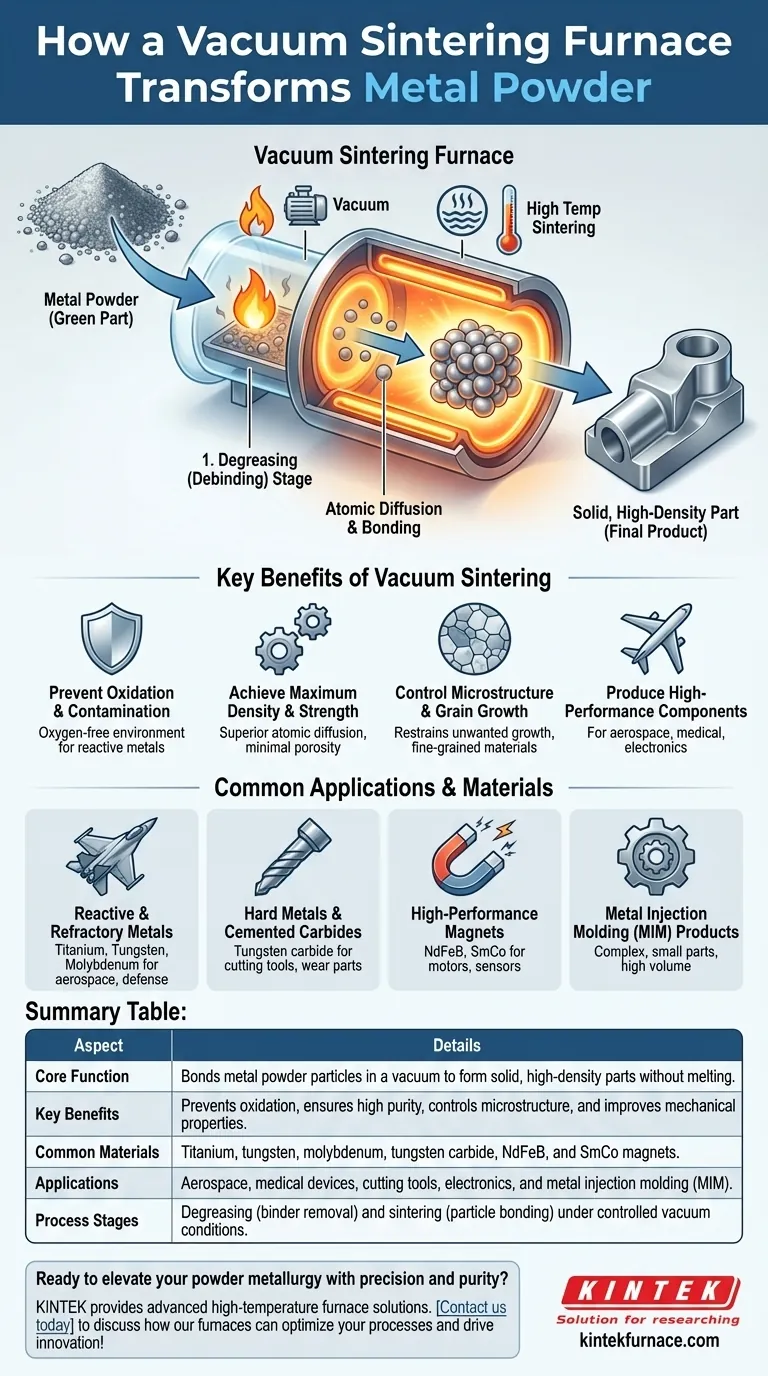
In the field of powder metallurgy, a vacuum sintering furnace is an essential tool used to transform compacted metal powders into solid, high-density parts with superior mechanical properties. By heating the material in a controlled, oxygen-free environment, it facilitates the bonding of powder particles without melting them, preventing oxidation and contamination that would degrade the final product's quality.
The core purpose of the vacuum is not merely to enable heating, but to create a chemically pure environment. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, vacuum sintering prevents the formation of oxides, allowing for cleaner particle-to-particle bonding and the creation of materials with exceptional density, strength, and purity.

The Core Function: From Powder to Solid Part
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal process that bonds powder particles together at a temperature below the material's melting point. As the material is heated, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them into a solid, coherent piece.
This process dramatically increases the density and strength of the component, turning a fragile "green" part made of pressed powder into a robust, functional metal product.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
The vacuum is the most critical element. Many advanced metals, such as titanium and refractory metals, are highly reactive with oxygen, especially at high temperatures.
Heating these materials in air would cause immediate oxidation, forming a brittle, weak oxide layer that prevents proper particle bonding. A vacuum removes the oxygen, ensuring the metal surfaces remain pure and can fuse together effectively.
The Two-Stage Process: Degreasing and Sintering
Most powder metallurgy processes use a binder or lubricant to help shape the initial powder compact. This binder must be removed before the final sintering phase.
Vacuum furnaces often perform this in a preliminary degreasing (or "debinding") stage, where the part is heated to a lower temperature to burn off these organic compounds. The furnace then ramps up to the higher sintering temperature to complete the bonding process.
Key Benefits of Vacuum Sintering
Achieving Maximum Density and Strength
By preventing the formation of oxide films between particles, vacuum sintering facilitates superior atomic diffusion. This results in parts with near-theoretical density, minimal porosity, and significantly improved mechanical properties like tensile strength and hardness.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
This is the primary advantage for working with reactive or high-purity materials. The oxygen-free environment is essential for producing parts from titanium alloys, tungsten, and molybdenum for demanding applications in aerospace and medical devices.
Controlling Microstructure and Grain Growth
The precise temperature control of a vacuum furnace can restrain the unwanted growth of crystal grains during sintering. This is particularly valuable for producing nanocrystalline materials or fine-grained hard metals, which derive their unique properties from a stable and tiny microstructure.
Producing High-Performance Components
The combination of high purity, high density, and controlled microstructure enables the production of components for the most demanding industries. This includes everything from aerospace turbine blades to high-performance magnetic materials and durable medical implants.
Common Applications and Materials
Reactive and Refractory Metals
Vacuum furnaces are indispensable for sintering reactive metals like titanium and refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum. These materials are foundational to the aerospace, electronics, and defense industries.
Hard Metals and Cemented Carbides
The process is widely used to produce hard metal cutting tools and wear-resistant components from materials like tungsten carbide. The vacuum ensures a strong, void-free bond between the hard carbide particles and the metallic binder (e.g., cobalt).
High-Performance Magnets
Materials like Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) and Samarium Cobalt (SmCo) are sintered in a vacuum to achieve the specific magnetic properties and structural integrity required for high-power electric motors, sensors, and electronics.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Products
For small, complex, and high-volume parts, MIM is a popular technique. After the binder is removed, the final sintering is almost always done in a vacuum furnace to achieve the necessary density and final shape for these intricate components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
Vacuum vs. Atmosphere Sintering
A vacuum furnace is not the only option. For less reactive materials like certain stainless steels or copper alloys, atmosphere sintering can be a more cost-effective choice. This process uses a protective atmosphere of inert gases (like argon) or reactive gases (like hydrogen) to prevent oxidation.
Sintering vs. Annealing
It is critical to distinguish sintering from annealing. Sintering is a forming process that bonds powder particles into a solid mass. Vacuum annealing, in contrast, is a heat treatment process performed on an already solid part to relieve internal stresses and improve ductility, not to form it.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum sintering furnaces represent a significant capital investment and require specialized knowledge to operate and maintain. The process cycles are also typically longer than atmosphere sintering, which can impact production throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding on a thermal process for powder metallurgy, the material and the desired outcome are paramount.
- If your primary focus is producing parts from reactive metals like titanium or refractory metals: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-dense, fine-grained hard metals or magnetic materials: The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace is critical for managing microstructure and maximizing performance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of less-reactive iron or steel powders: You should evaluate whether a controlled atmosphere furnace provides a sufficient cost-benefit balance for your quality requirements.
Ultimately, the vacuum sintering furnace is a powerful tool that empowers engineers to build high-value components with precisely controlled properties that are unattainable by other means.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Bonds metal powder particles in a vacuum to form solid, high-density parts without melting. |
| Key Benefits | Prevents oxidation, ensures high purity, controls microstructure, and improves mechanical properties. |
| Common Materials | Titanium, tungsten, molybdenum, tungsten carbide, NdFeB, and SmCo magnets. |
| Applications | Aerospace, medical devices, cutting tools, electronics, and metal injection molding (MIM). |
| Process Stages | Degreasing (binder removal) and sintering (particle bonding) under controlled vacuum conditions. |
Ready to elevate your powder metallurgy with precision and purity? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with reactive metals, hard alloys, or magnetic materials, we deliver tailored solutions for superior density and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your processes and drive innovation in your industry!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What is the purpose of performing medium vacuum annealing on working ampoules? Ensure Pure High-Temp Diffusion
- What processing conditions does a vacuum furnace provide for TiCp/Fe microspheres? Sintering at 900 °C
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density



















