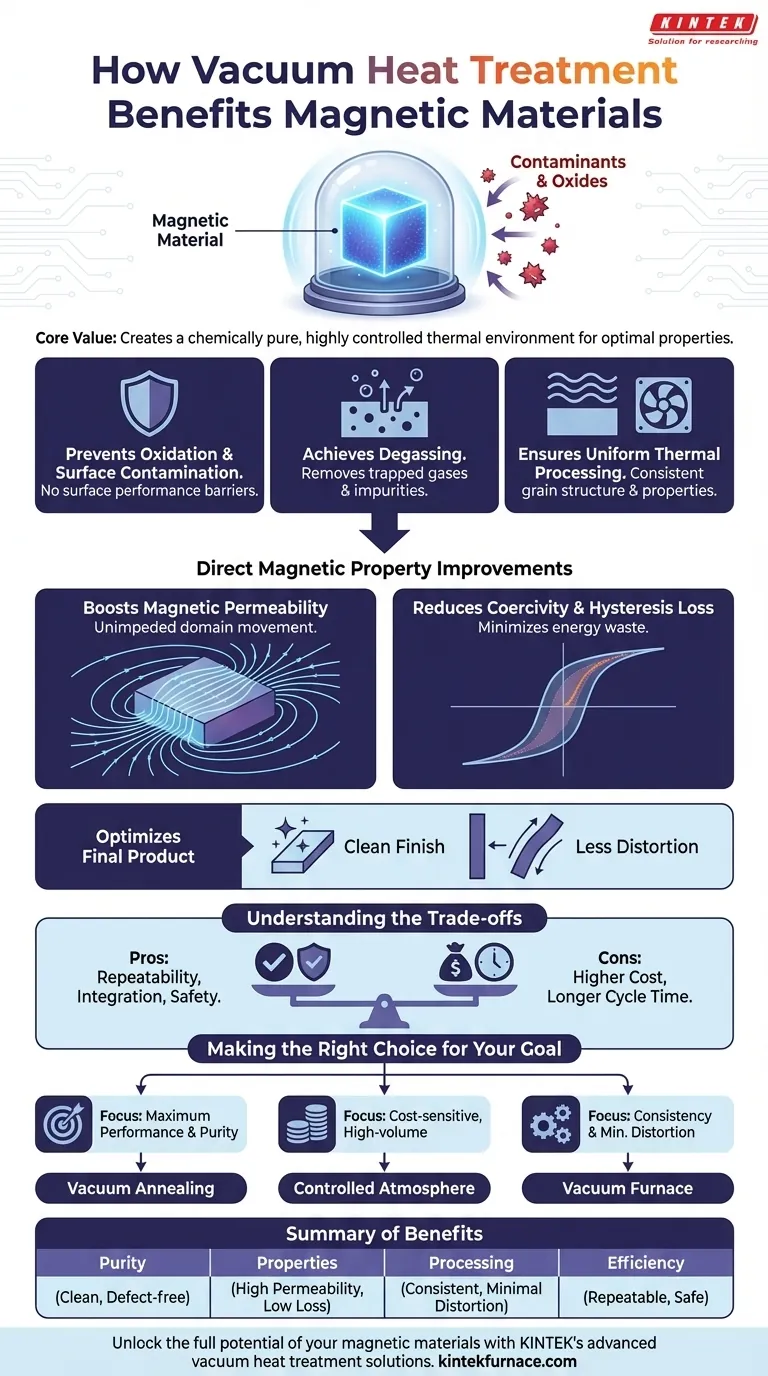
Fundamentally, vacuum heat treatment enhances magnetic materials by creating a chemically pure and highly controlled thermal environment. This process prevents the formation of performance-degrading oxides and other contaminants, allowing for precise metallurgical changes that unlock the material's optimal magnetic and mechanical properties.
The core value of vacuum heat treatment is not simply avoiding surface oxidation. It is about enabling precise control over the material's atomic structure and purity, which is the key to achieving superior magnetic permeability, lower energy loss, and consistent, reliable performance in demanding applications.

Why Purity and Control Are Non-Negotiable
The magnetic behavior of a material is dictated by its microscopic structure—its grain size, chemical purity, and the absence of internal stress. A vacuum environment provides the ultimate level of control over these factors.
Preventing Oxidation and Surface Contamination
Even a microscopic layer of oxide on a material's surface or at its internal grain boundaries can severely impede magnetic performance. Oxides act as physical barriers that disrupt the alignment of magnetic domains.
Vacuum furnaces remove virtually all oxygen and other reactive gases. This ensures the material remains chemically pure throughout the heating and cooling cycle, resulting in a bright, clean surface and, more importantly, unimpeded internal magnetic pathways.
Achieving Purity Through Degassing
Many raw materials contain trapped impurities like hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon. When heated, these elements can react with the alloy or form internal voids.
The vacuum actively pulls these trapped gases out of the material—a process known as degassing. This purification step reduces internal defects, prevents issues like hydrogen embrittlement, and leads to a denser, more metallurgically sound component.
Ensuring Uniform Thermal Processing
Achieving a specific magnetic property often requires holding a material at a precise temperature and then cooling it at a controlled rate. This process, known as annealing, allows the material's grain structure to grow and internal stresses to be relieved.
Vacuum furnaces provide exceptionally uniform heating (often through radiation in the absence of air) and controlled cooling (using inert gas quenching). This precision ensures that the entire component acquires the same desired grain structure and consistent magnetic properties throughout.
How Vacuum Treatment Directly Improves Magnetic Properties
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace translates directly into measurable improvements in the characteristics that matter most for magnetic components.
Enhancing Magnetic Permeability
Permeability is a measure of how easily a material can support the formation of a magnetic field. For soft magnetic materials used in transformers and inductors, high permeability is critical.
By eliminating impurities and enabling the growth of large, uniform grains, vacuum annealing allows magnetic domain walls to move freely. This dramatically increases the material's permeability.
Reducing Coercivity and Hysteresis Loss
Coercivity is the energy required to demagnetize a material. In applications like motors and transformers where the magnetic field is constantly cycling, low coercivity is essential to minimize energy wasted as heat (hysteresis loss).
Impurities and internal stresses act as "pinning sites" that obstruct the movement of magnetic domain walls, increasing coercivity. The pure, stress-relieved structure achieved in a vacuum furnace minimizes these pinning sites, leading to significantly lower energy loss.
Optimizing the Final Product
Because vacuum processing prevents scaling and discoloration, parts emerge from the furnace with a clean, often bright finish. This can reduce or eliminate the need for secondary cleaning or machining operations.
Furthermore, the slow, uniform heating and cooling cycles minimize thermal stress, resulting in less distortion and warping compared to conventional atmospheric heat treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum heat treatment offers superior technical results, it's essential to understand its practical implications.
Advantage: Process Repeatability and Integration
Modern vacuum furnaces are highly automated systems that can perform multiple processes—like hardening, annealing, and tempering—in a single, sealed cycle. This provides exceptional control and repeatability, leading to a high pass rate for finished products.
Advantage: Safety and Environmental Impact
The process is inherently safe and clean. It eliminates the need to handle and store flammable or costly gases like hydrogen and argon, and it produces no harmful emissions.
The Primary Trade-off: Cost and Cycle Time
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The process of pumping down to a deep vacuum also adds to the overall cycle time compared to atmospheric furnaces. Therefore, the decision to use vacuum treatment is a trade-off between the higher cost and the superior performance required for the application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment process depends entirely on the performance requirements and cost constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum magnetic performance and purity: Vacuum annealing is the definitive choice, especially for high-permeability materials where even trace impurities can degrade performance.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, high-volume production: A controlled atmosphere furnace (using nitrogen or hydrogen) can be a viable alternative, provided you can accept minor surface imperfections and slightly lower magnetic performance.
- If your goal is minimizing component distortion and ensuring batch-to-batch consistency: The precise thermal control and uniform quenching of a vacuum furnace offer significant advantages over less controlled methods.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum heat treatment is an investment in achieving the highest possible quality and unlocking the true performance potential of your magnetic materials.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Purity | Prevents oxidation and removes trapped gases (degassing) for clean, defect-free materials. |
| Improved Magnetic Properties | Increases permeability and reduces coercivity for lower energy loss and better performance. |
| Uniform Thermal Processing | Ensures consistent grain structure and minimal distortion through controlled heating and cooling. |
| Process Efficiency | Offers repeatability, safety, and integration in a single cycle, reducing need for secondary operations. |
Unlock the full potential of your magnetic materials with KINTEK's advanced vacuum heat treatment solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance purity, performance, and efficiency in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















