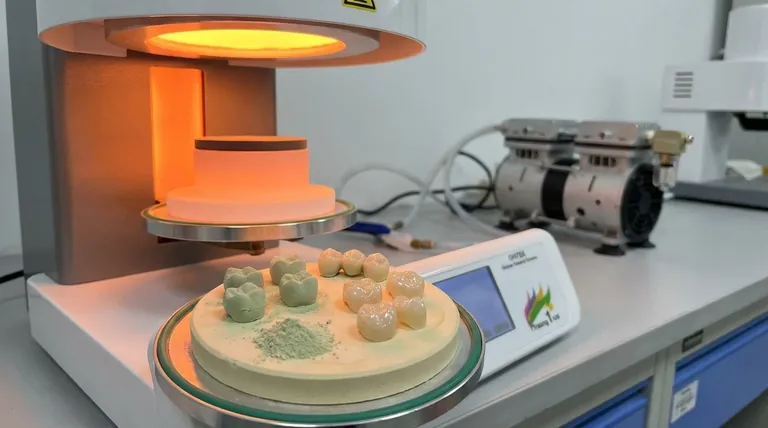
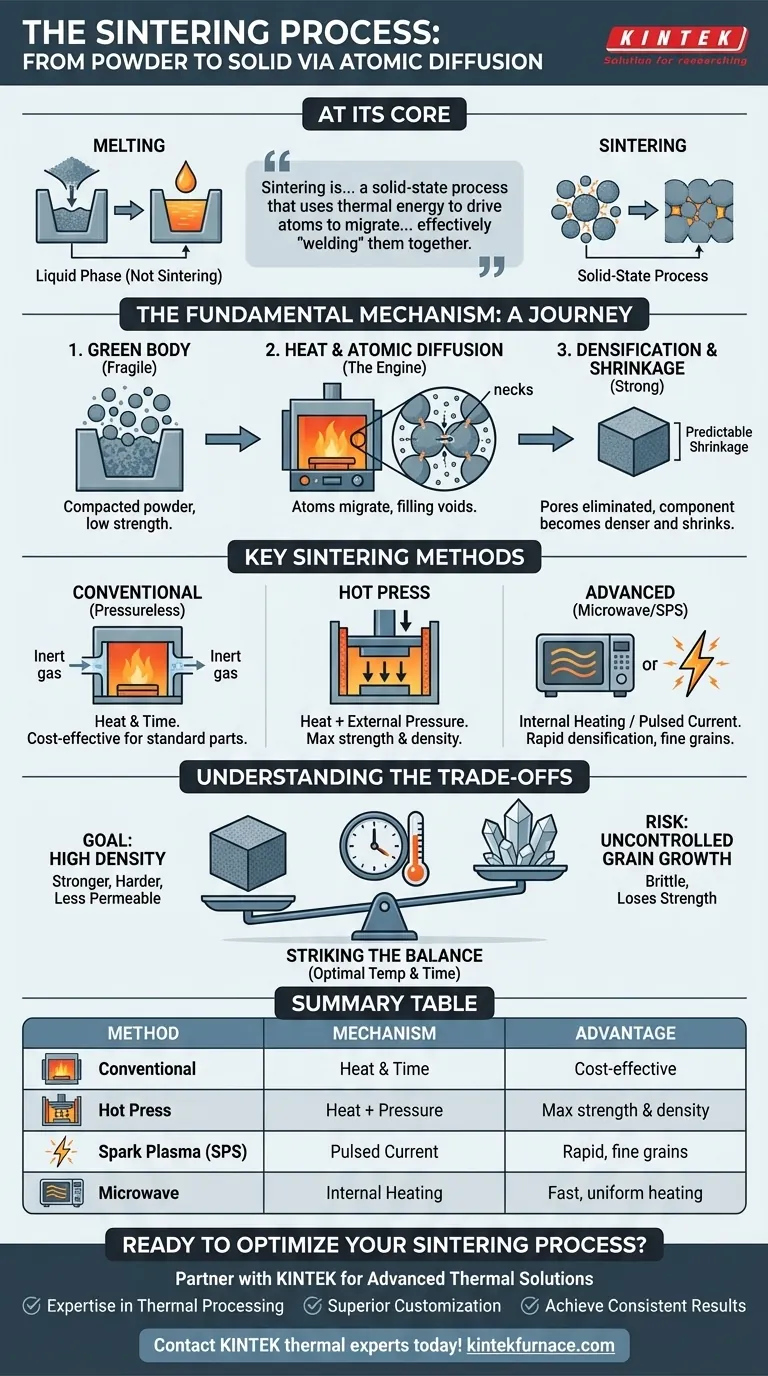
At its core, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms a powder into a solid, dense object using high heat. Unlike melting, the material is heated to a temperature below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together through atomic diffusion, resulting in a strong, coherent mass.
Sintering is not about melting a material into a liquid mold. Instead, it is a solid-state process that uses thermal energy to drive atoms to migrate across particle boundaries, effectively "welding" them together and eliminating the empty spaces between them.

The Fundamental Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
To understand sintering, you must visualize what happens at the microscopic level. The process is a journey from a fragile, loosely packed powder to a dense, engineered component.
The Starting Point: The "Green Body"
The process begins with a compacted powder, often held together by a binder. This initial, fragile form is known as a green body. While it has the desired shape, it lacks the strength, hardness, and density required for its final application.
Activating the Process: Heat and Atomic Diffusion
When the green body is heated in a furnace, the atoms at the contact points of the particles gain enough energy to move. This movement, called atomic diffusion, is the engine of sintering. Atoms migrate from the bulk of the particles to the "necks" forming between them and into the pores (empty spaces).
The Result: Densification and Shrinkage
As atoms fill the voids, the pores shrink and are eventually eliminated. This causes the entire component to become denser and shrink in size. This sintering shrinkage is predictable and must be accounted for; parts are intentionally made larger in their green state to ensure they shrink to the correct final dimensions.
Key Sintering Methods and Their Purpose
The specific method used depends on the material, the desired properties, and economic factors. Each variation manipulates temperature, pressure, and heating method to achieve a specific outcome.
Conventional (Pressureless) Sintering
This is the most common form. The green body is simply heated in a furnace with a controlled atmosphere (often a vacuum or inert gas) to prevent oxidation. It relies solely on temperature and time to drive densification.
Hot Press Sintering
In this method, external pressure is applied simultaneously with heat. The pressure physically forces the particles together, which accelerates densification and helps achieve higher final densities, especially for materials that are difficult to sinter conventionally.
Advanced Methods: Microwave and Plasma Sintering
These techniques use alternative energy sources. Microwave sintering uses microwave radiation to heat the material internally, which can be faster and more uniform. Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) passes a pulsed electric current through the powder, generating intense localized heat at particle contacts, allowing for extremely rapid densification at lower overall temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Successful sintering is not just about heating a material. It is a precise balancing act between achieving high density and controlling the material's microstructure.
The Goal: High Density
The primary objective of sintering is to eliminate porosity. A high-density part is generally stronger, harder, and less permeable, which are critical properties for high-performance applications from dental implants to jet engine turbines.
The Risk: Uncontrolled Grain Growth
As particles fuse and densify, the microscopic crystals that make up the material, known as grains, tend to grow larger. If grains grow too large, the material can become brittle and lose strength, negating the benefits of high density.
Striking the Balance
The core challenge for engineers is to optimize the sintering cycle—specifically the temperature and hold time. The goal is to hold the part at a high enough temperature for long enough to achieve maximum density, but to cool it down before the grains can grow to a detrimental size.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your choice of sintering process and parameters is determined entirely by the final properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of standard parts: Conventional pressureless sintering is typically the most economical and straightforward approach.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and performance: Hot press or spark plasma sintering are superior choices for achieving the highest possible density with fine grain structure.
- If your primary focus is speed and process efficiency: Microwave and spark plasma sintering can dramatically reduce cycle times compared to conventional methods.
Understanding these principles transforms sintering from a simple heating step into a precise tool for engineering material properties from the atomic level up.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Method | Key Mechanism | Primary Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional (Pressureless) | Heat & Time | Cost-effective for standard parts |
| Hot Press | Heat + External Pressure | Maximum strength & density |
| Spark Plasma (SPS) | Pulsed Electric Current | Rapid densification, fine grains |
| Microwave | Internal Microwave Heating | Fast, uniform heating |
Ready to Optimize Your Sintering Process?
Choosing the right sintering furnace is critical to achieving the perfect balance of density, strength, and microstructure for your materials. KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions are engineered to deliver the precise thermal control your R&D or production demands.
Why Partner with KINTEK?
- Expertise in Thermal Processing: Leverage our deep knowledge to select the ideal furnace—from Muffle and Tube Furnaces to sophisticated Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces.
- Superior Customization: Our strong in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities allow us to tailor furnace systems—including specialized CVD/PECVD Systems—to your unique experimental or production requirements.
- Achieve Consistent Results: Ensure predictable sintering shrinkage and controlled grain growth with our reliable, high-performance equipment.
Don't let furnace limitations compromise your material's properties. Whether you are developing new ceramics, metal alloys, or advanced composites, KINTEK provides the robust sintering solutions you need for success.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss how we can help you master your sintering process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Quality and Efficiency for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of dental sintering furnaces? Transform Zirconia into Durable, High-Quality Dental Restorations
- What are the effects of overloading a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Predictable, High-Quality Zirconia Restorations
- What factors determine the quality of sintered zirconia restorations? Master Material, Equipment, and Technique
- Why is proper ventilation important in dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Quality and Safety in Your Lab



















