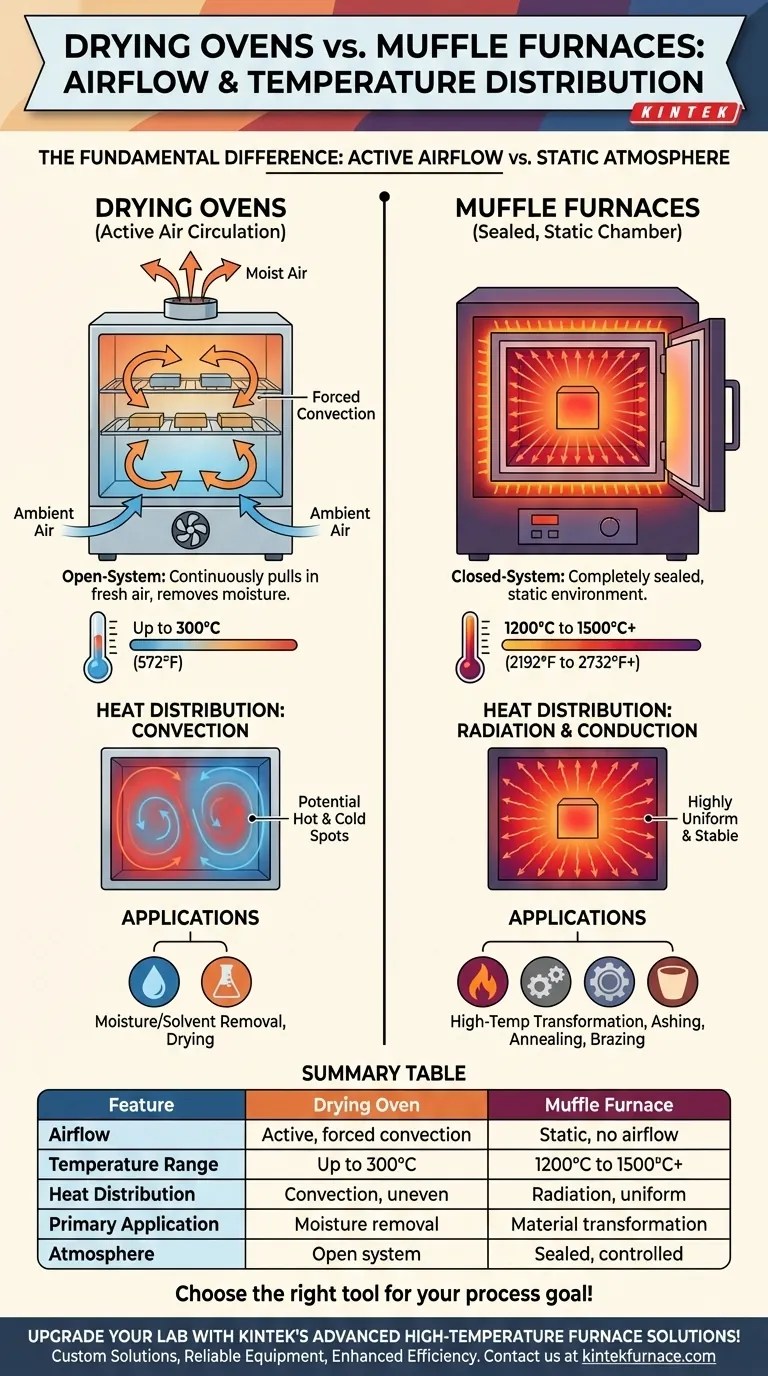
At their core, a drying oven uses active airflow to remove moisture at moderate temperatures, while a muffle furnace uses a sealed, static atmosphere to achieve highly uniform, extreme temperatures. The presence or absence of airflow is the fundamental design difference that dictates their function, temperature distribution, and ideal applications.
The choice between them is not about which is "better," but which is correct for the task. A drying oven's purpose is to carry moisture away with moving air. A muffle furnace's purpose is to transform materials using intense, uniform heat in a controlled, static environment.

The Fundamental Difference: Airflow vs. a Static Atmosphere
The most critical distinction lies in how each piece of equipment manages its internal atmosphere. This single factor influences everything from temperature range to heat uniformity.
Drying Ovens: Active Air Circulation
A drying oven is an open-system device. It is engineered to pull in fresh, ambient air.
This air is passed over heating elements and circulated throughout the chamber, typically via a fan (forced convection). The warm, moving air absorbs moisture from the sample, and this now-moist air is then exhausted from the oven. This continuous exchange is essential for efficient drying.
Muffle Furnaces: A Sealed, Static Chamber
A muffle furnace is a closed-system device. During operation, it is completely sealed from the outside environment.
There is no active airflow. Heat is generated by electric elements that surround an inner chamber (the "muffle") and is transferred to the sample primarily through radiation and conduction. The atmosphere inside remains static, which is critical for preventing oxidation and ensuring temperature stability.
How This Impacts Temperature and Heat Distribution
The difference in airflow directly creates different thermal environments, making each tool suited for very different tasks.
Temperature Range: Moderate vs. Extreme Heat
A drying oven's continuous intake of cool, fresh air inherently limits its maximum temperature. They typically operate at lower temperatures, usually up to 300°C (572°F).
A muffle furnace's sealed, heavily insulated chamber is designed to contain extreme energy. It can easily reach much higher temperatures, often 1200°C to 1500°C (2192°F to 2732°F) or more, for processes like melting metals or creating ceramics.
Heat Distribution: Convection vs. Radiation
Drying ovens rely on convection—moving air—to distribute heat. While this is effective for drying, it can create an uneven temperature profile, with hot and cold spots depending on airflow patterns and how the oven is loaded.
Muffle furnaces provide superior temperature uniformity. The heat radiating from all sides of the internal chamber onto a static object in a sealed atmosphere creates an exceptionally even and stable thermal environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Design and Application
The functional differences lead to practical trade-offs in design, cost, and use cases.
Insulation and Construction
Drying ovens have moderate insulation, as their goal is not extreme heat retention. Muffle furnaces, by contrast, feature thick, heavy-duty insulation to safely contain extreme temperatures and maintain stability for long periods.
Process Atmosphere Control
The purpose of a drying oven is to use ambient air to remove moisture. A muffle furnace is designed to control the atmosphere, protecting samples from the oxygen in the air, which is crucial for high-temperature chemical analyses (ashing) or materials science (annealing).
Cost and Complexity
Due to their robust construction, advanced insulation, and ability to reach extreme temperatures, muffle furnaces are generally more specialized and represent a significantly higher investment than standard laboratory drying ovens.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the primary goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture or solvents: Choose a drying oven. Its active airflow is specifically designed to carry away volatiles efficiently.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material transformation: Choose a muffle furnace. It is the only option for processes like ashing, annealing, brazing, or heat-treating metals that require extreme, uniform heat.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity: Choose a muffle furnace. Its static, radiative heating provides a more stable and homogenous thermal environment than the convective airflow of an oven.
Ultimately, selecting the correct equipment begins with understanding that airflow is not just a feature, but the defining principle of its operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Drying Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Airflow Type | Active, forced convection | Static, no airflow |
| Temperature Range | Up to 300°C | 1200°C to 1500°C+ |
| Heat Distribution | Convection, potential hot/cold spots | Radiation, highly uniform |
| Primary Application | Moisture/solvent removal | High-temperature material transformation |
| Atmosphere Control | Open system, uses ambient air | Sealed system, controlled atmosphere |
Upgrade your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your thermal processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does temperature control work in modern muffle furnaces? Achieve Unmatched Precision and Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a laboratory blast oven during clay powder devolatilization? Protect Your Material.
- What is the function of a high-temp muffle furnace in zirconia debinding? Ensure Crack-Free Ceramic Processing
- How did the introduction of electrical heating elements change muffle furnaces? Revolutionizing Clean Heat for Modern Labs
- What is the primary function of a Muffle Furnace in the heat treatment of beryl? Master Gemstone Color Modification
- What temperature range can muffle furnaces reach? Find Your Ideal Lab Furnace Temperature
- What makes muffle furnaces particularly useful for sensitive materials? Ensure Precision, Purity & Protection
- How does a high-temperature electric furnace contribute to the melting process of radiation shielding glass?



















