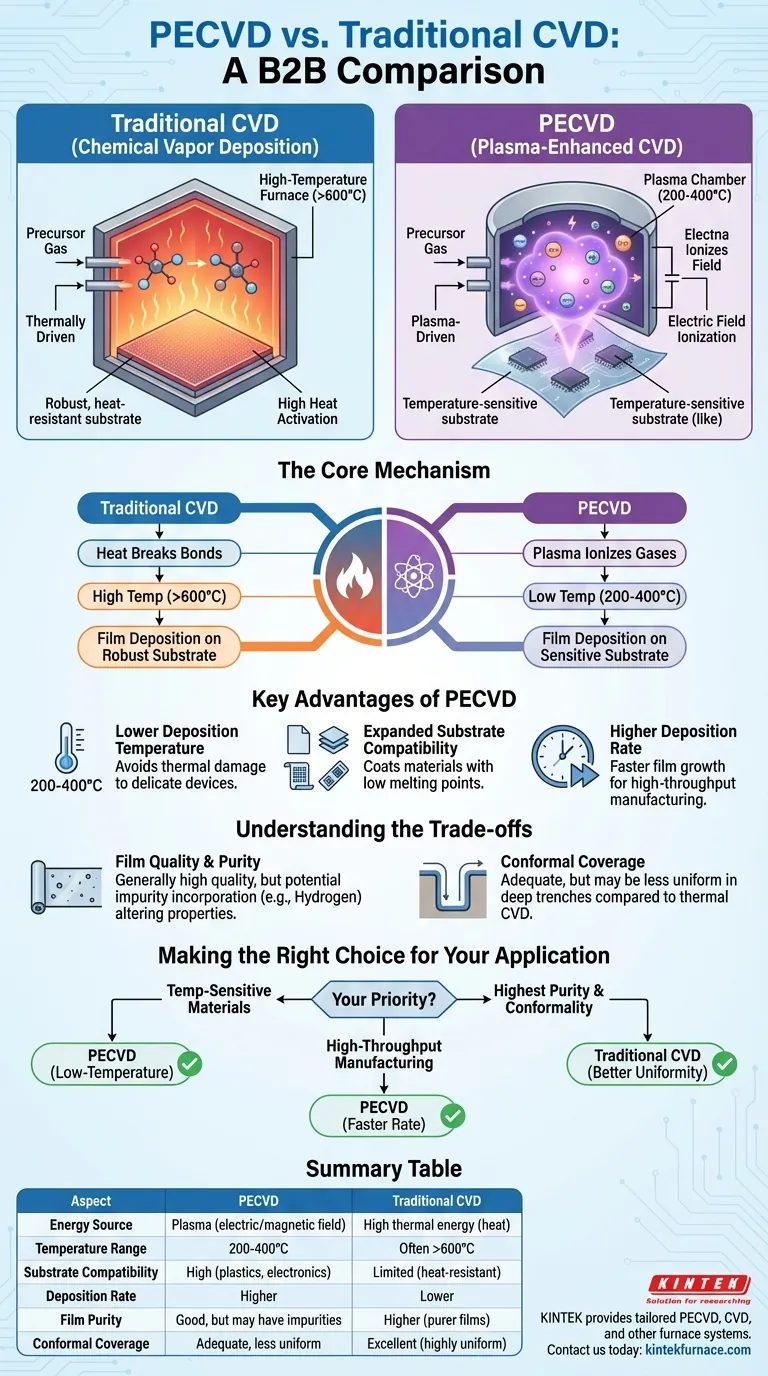
The fundamental difference between Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) and traditional, thermally-driven Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the energy source used to initiate the chemical reaction. While traditional CVD relies on high temperatures (often >600°C) to break down precursor gases, PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma, allowing the deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures (typically 200-400°C). This distinction is the primary driver behind all other differences in application, film quality, and substrate compatibility.
The core takeaway is that PECVD replaces extreme heat with plasma energy. This single change dramatically expands the range of materials that can be coated, making it possible to deposit high-quality thin films onto temperature-sensitive substrates like plastics and complex electronics that traditional CVD would damage or destroy.

The Core Mechanism: Plasma vs. Thermal Energy
To understand the practical differences, you must first grasp how each process drives the film deposition. The energy source is the defining factor.
How Traditional CVD Works
Traditional CVD processes, such as Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), are thermally driven. Precursor gases are introduced into a high-temperature furnace.
The intense heat provides the necessary activation energy to break the chemical bonds in the gases. These reactive species then diffuse and adsorb onto the hot substrate surface, forming a solid, uniform thin film.
How PECVD Works
PECVD achieves the same goal without the extreme heat. It uses a strong electric or magnetic field to ionize the precursor gases, creating a plasma.
This plasma is a high-energy soup of ions, electrons, and radicals. These highly reactive particles have enough energy to form the desired film when they contact the substrate, even though the substrate itself remains at a much lower temperature.
Key Advantages of the PECVD Process
The use of plasma instead of heat creates several significant advantages that define PECVD's role in manufacturing and research.
Lower Deposition Temperature
This is the most critical benefit. By operating at temperatures around 200-400°C, PECVD avoids thermal damage to the underlying device or material.
Expanded Substrate Compatibility
The low operating temperature directly enables the coating of materials with low melting points or thermal budgets. This includes plastics, polymers, and fully fabricated semiconductor wafers with sensitive metallic interconnects.
Higher Deposition Rate
The plasma environment is intensely reactive, which can often lead to faster film growth compared to thermally driven processes. For applications where throughput is a primary concern, PECVD can offer a significant manufacturing advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is not a universal replacement for all thermal CVD methods. The use of plasma introduces specific trade-offs that must be considered.
Film Quality and Purity
PECVD films are generally high quality, with good density and adhesion. However, the plasma process can sometimes lead to the incorporation of impurities, such as hydrogen from precursor gases, into the film.
This can alter the film's chemical, electrical, and optical properties. In contrast, high-temperature thermal CVD can sometimes produce purer films with better stoichiometry because the process is closer to thermodynamic equilibrium.
Conformal Coverage
Traditional thermal processes like LPCVD are known for their excellent conformality, meaning the film deposits with a highly uniform thickness over complex, three-dimensional surface features.
While PECVD provides adequate coverage for many applications, the deposition can have a more directional component from the plasma, sometimes resulting in less uniform coverage in deep trenches or complex topographies compared to LPCVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on your substrate, the required film properties, and your manufacturing goals.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials: PECVD is unequivocally the correct choice due to its low-temperature processing window.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput manufacturing: PECVD's typically higher deposition rate makes it an extremely attractive option, assuming the film properties meet your requirements.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest film purity and conformality on a robust substrate: A traditional thermal process like LPCVD may be a better choice, particularly for critical electronic layers.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between heat, plasma, and film formation empowers you to select the precise tool for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PECVD | Traditional CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Plasma (electric/magnetic field) | High thermal energy (heat) |
| Temperature Range | 200-400°C | Often >600°C |
| Substrate Compatibility | High (plastics, electronics) | Limited (heat-resistant materials) |
| Deposition Rate | Higher | Lower |
| Film Purity | Good, but may have impurities | Higher (purer films) |
| Conformal Coverage | Adequate, less uniform in complex topographies | Excellent (highly uniform) |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored PECVD, CVD, and other furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our deep customization ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs—whether you're working with temperature-sensitive substrates or demanding high throughput. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thin film deposition processes and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment



















