At its core, indirect gas heating improves vacuum furnace efficiency not by changing the physics of heat transfer within the vacuum, but by strategically replacing a high-cost energy source (electricity) with a more economical one (natural gas). This shift primarily drives economic efficiency and provides significant advantages in overall plant energy management, leading to a faster return on investment.
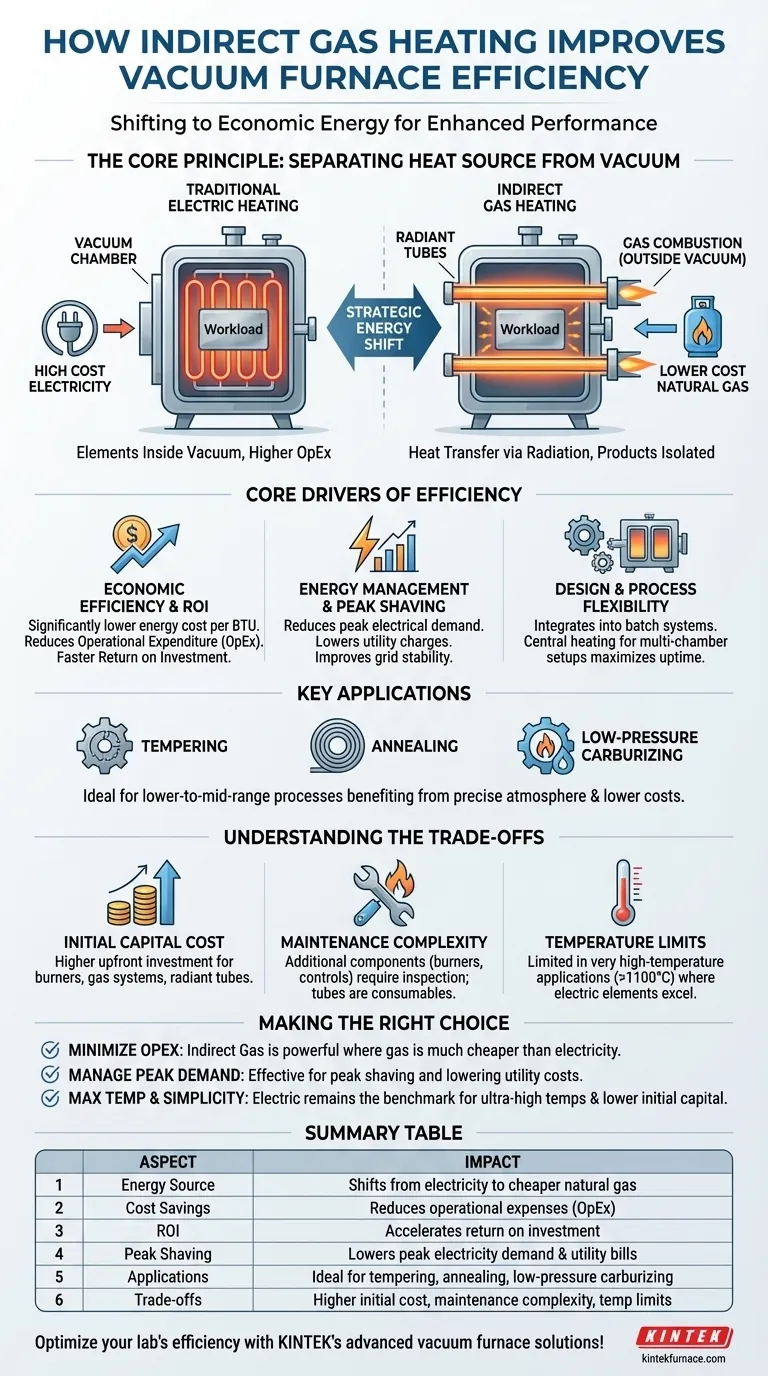
While a traditional electric furnace and an indirect gas furnace both heat parts effectively under vacuum, the key difference lies in the source of the energy. Indirect gas heating leverages the cost-effectiveness of natural gas to lower operational expenses and reduce strain on the electrical grid.
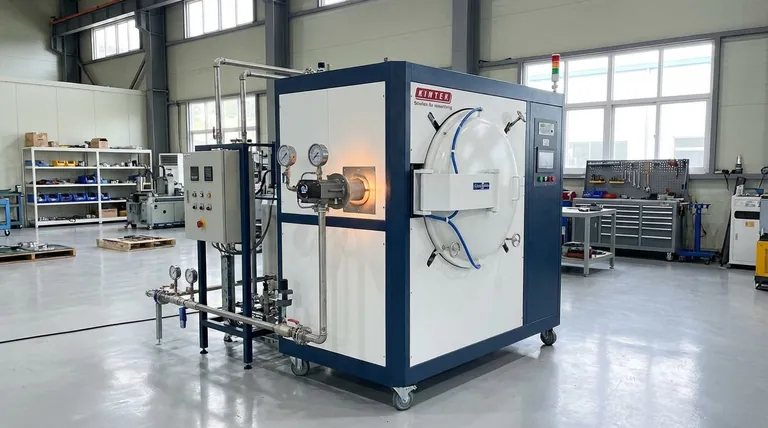

The Principle: Separating the Heat Source from the Vacuum
To understand the efficiency gains, it's crucial to grasp how this technology works. It decouples the combustion process from the controlled vacuum environment.
What Is Indirect Heating?
In a standard electric vacuum furnace, heating elements are located directly inside the vacuum chamber.
Indirect gas heating works differently. The combustion of natural gas occurs outside the vacuum chamber in a sealed component, typically a radiant tube.
The Role of Radiant Tubes
These gas-fired burners heat radiant tubes to a very high temperature. The tubes, which pass through the furnace chamber, then glow and radiate thermal energy inward, heating the workload.
This design cleverly transfers heat into the chamber while keeping all products of combustion completely isolated from the vacuum and the parts being processed.
Where It Excels: Key Applications
This method is particularly effective for lower-to-mid-range temperature processes where electricity costs can be a significant burden.
Common applications include tempering, annealing, and low-pressure carburizing, which benefit from the precise atmospheric control of a vacuum furnace combined with lower energy costs.
Core Drivers of Efficiency
The term "efficiency" here refers to a combination of economic, energy, and operational advantages. It’s a holistic improvement, not just a thermodynamic one.
Economic Efficiency and ROI
The primary driver for adopting indirect gas heating is cost. In most industrial regions, natural gas is a significantly cheaper source of energy per BTU than electricity.
This cost differential directly reduces the furnace's operational expenditure (OpEx), leading to a faster return on investment (ROI) for the equipment.
Energy Management and Peak Shaving
Large electric furnaces represent a massive electrical load. Running them contributes to a facility's "peak demand," which often incurs steep charges from utility providers.
By shifting this thermal load to natural gas, a plant can reduce its peak electricity consumption. This practice, known as peak shaving, lowers utility bills and improves the stability of the plant's electrical grid.
Design and Process Flexibility
Indirect gas heating can be integrated into various furnace designs, including single-chamber and multi-chamber batch systems.
In multi-chamber furnaces, this can be especially efficient. A central heating chamber with indirect gas firing can serve multiple process or cooling chambers, maximizing the uptime and throughput of the entire system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the potential downsides and considerations.
Initial Capital Cost
A vacuum furnace equipped with indirect gas heating may have a higher upfront capital cost than its all-electric counterpart due to the need for burners, gas plumbing, exhaust systems, and specialized radiant tubes.
Maintenance Complexity
Gas-fired systems introduce additional components that require inspection and maintenance, such as burners, ignition systems, and flame safety controls. The radiant tubes themselves are also consumables that will eventually require replacement.
Temperature Uniformity and Limits
Achieving excellent temperature uniformity with radiant tubes requires careful engineering in their placement and design. While modern systems are highly effective, they may face limitations in very high-temperature applications (above ~2000°F or ~1100°C) where materials like graphite or molybdenum electric elements excel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on a clear-eyed assessment of your plant's specific operational and financial priorities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational expenditure (OpEx): Indirect gas heating is a powerful tool, especially in regions with a large price gap between natural gas and electricity.
- If your primary focus is managing high peak electrical demand: This technology offers a direct and effective strategy for peak shaving and lowering your overall utility costs.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature range and process simplicity: A traditional, all-electric vacuum furnace remains the benchmark for simplicity, ultra-high-temperature work, and a lower initial capital investment.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating technology is about aligning the equipment's strengths with your facility's long-term energy strategy and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Energy Source | Shifts from electricity to cheaper natural gas |
| Cost Savings | Reduces operational expenses (OpEx) |
| ROI | Accelerates return on investment |
| Peak Shaving | Lowers peak electricity demand and utility bills |
| Applications | Ideal for tempering, annealing, low-pressure carburizing |
| Trade-offs | Higher initial cost, maintenance complexity, temperature limits (~1100°C) |
Optimize your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, helping you reduce costs and enhance performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor our products for your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















