In short, gaseous catalyst-assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) fundamentally benefits graphene production by enabling the direct growth of high-quality, device-ready graphene on insulating substrates. This bypasses the conventional, damage-inducing transfer step required when growing graphene on metal foils, solving a major bottleneck for advanced electronics.
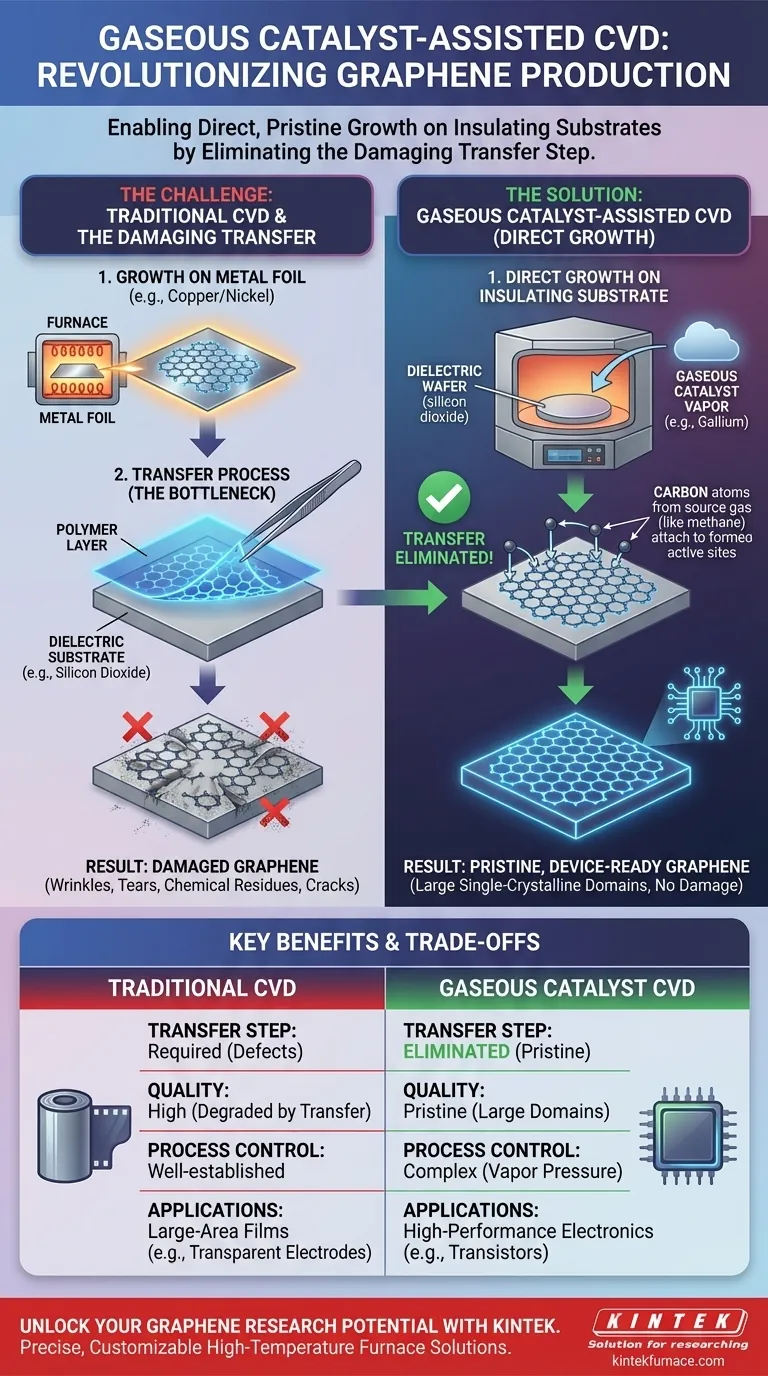
The core problem with traditional graphene synthesis is not the growth, but the subsequent transfer from a metal catalyst to a useful substrate—a process that introduces defects and impurities. Gaseous catalyst-assisted CVD solves this by changing the environment to allow direct, pristine growth on the final substrate itself.
The Challenge with Traditional Graphene Production
The Standard Method: Growth on Metal
In conventional CVD, methane and hydrogen gases are heated in a furnace to decompose over a metal catalyst, typically a thin foil of copper or nickel. Carbon atoms arrange themselves on the metal surface, forming a high-quality graphene sheet.
This method offers excellent control over film properties and uniformity.
The Problem: A Damaging Transfer
The graphene grown on metal is not immediately useful for most electronic applications, such as transistors. It must be moved onto a dielectric (electrically insulating) substrate, like silicon dioxide.
This transfer process is the primary weakness of the traditional method. It involves coating the graphene with a polymer, etching away the metal foil, and carefully moving the fragile, one-atom-thick sheet to the new substrate.
This step is notorious for introducing wrinkles, tears, cracks, and chemical residues, which severely degrade the graphene's exceptional electronic properties.
The Gaseous Catalyst Solution: Direct Growth
Gaseous catalyst-assisted CVD re-engineers the process to eliminate this destructive transfer step entirely.
How It Works: A Vaproized Catalyst
Instead of a solid metal foil, this method introduces a catalyst in a gaseous form, such as gallium vapor, into the CVD chamber.
These catalyst atoms temporarily adsorb onto the surface of a non-reactive dielectric substrate. They provide active sites for carbon atoms from the methane source to attach and form graphene, but without permanently bonding to the substrate itself.
The Key Benefit: Eliminating the Transfer Process
Because the graphene is grown directly on the final insulating substrate, the entire polymer coating, metal etching, and transfer procedure is completely avoided.
The result is graphene that remains in its pristine, as-grown state, free from the mechanical damage and contamination inherent to the transfer process.
The Result: Superior Graphene for Electronics
This direct-growth method produces exceptionally high-quality graphene with large single-crystalline domains.
For electronics, this translates to higher carrier mobility and more reliable device performance. It bridges the gap between lab-scale material synthesis and practical, high-performance electronic and optoelectronic device fabrication.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this advanced method introduces its own set of complexities that must be managed.
Process Control
Gaseous catalyst-assisted CVD requires more sophisticated control than traditional methods. Managing the precise vapor pressure of the catalyst and ensuring its uniform distribution within the reaction chamber is critical and adds a layer of complexity.
Catalyst Choice
The choice of gaseous catalyst is limited. While gallium has proven effective, its interaction with different substrates and growth conditions is an active area of research. The purity of the catalyst source is also paramount.
Scalability vs. Application
This method is ideal for producing ultra-high-quality graphene on wafers for high-end electronics. However, for applications requiring very large areas of conductive film where minor defects are tolerable (e.g., some transparent electrodes), traditional roll-to-roll CVD on copper may still be more cost-effective to scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best synthesis method depends entirely on your end-use application and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics (e.g., transistors, high-frequency devices): Gaseous catalyst-assisted CVD is the ideal choice because it yields pristine graphene directly on the required substrate.
- If your primary focus is large-area conductive films (e.g., transparent electrodes, heating elements): Traditional CVD on copper foil followed by a transfer process may be more economical and scalable, provided the application can tolerate minor defects.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Gaseous catalyst-assisted CVD provides a cleaner platform for studying intrinsic graphene properties without the confounding variables introduced by a transfer process.
Ultimately, mastering the synthesis process is the critical first step in unlocking the true potential of graphene-based technologies.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Traditional CVD | Gaseous Catalyst-Assisted CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst | Solid metal (e.g., copper, nickel) | Gaseous (e.g., gallium vapor) |
| Substrate | Metal foil | Directly on insulating substrate |
| Transfer Step | Required, introduces defects | Eliminated, avoids damage |
| Graphene Quality | High, but degraded by transfer | Pristine, large single-crystalline domains |
| Ideal Applications | Large-area films, transparent electrodes | High-performance electronics, transistors |
Unlock the full potential of your graphene research with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide precise, customizable systems like Tube Furnaces, CVD/PECVD Systems, and more to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and drive innovation in electronics and materials science!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are gas barrier films, and how is PECVD involved in their creation? Discover Advanced Packaging Solutions
- What is the role of temperature in PECVD? Optimize Film Quality and Substrate Protection
- What is the difference between PVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Coating Technology
- How does a CVD system ensure the quality of carbon layers? Achieving Nanometer Precision with KINTEK
- What are the drawbacks of CVD compared to PECVD? Key Limitations for Your Lab



















