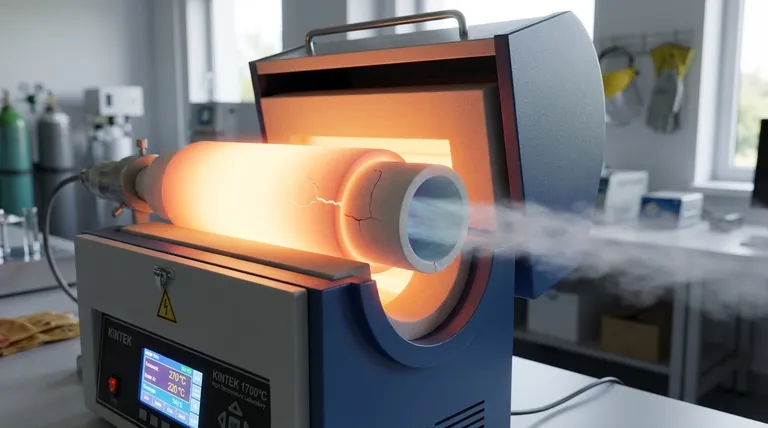
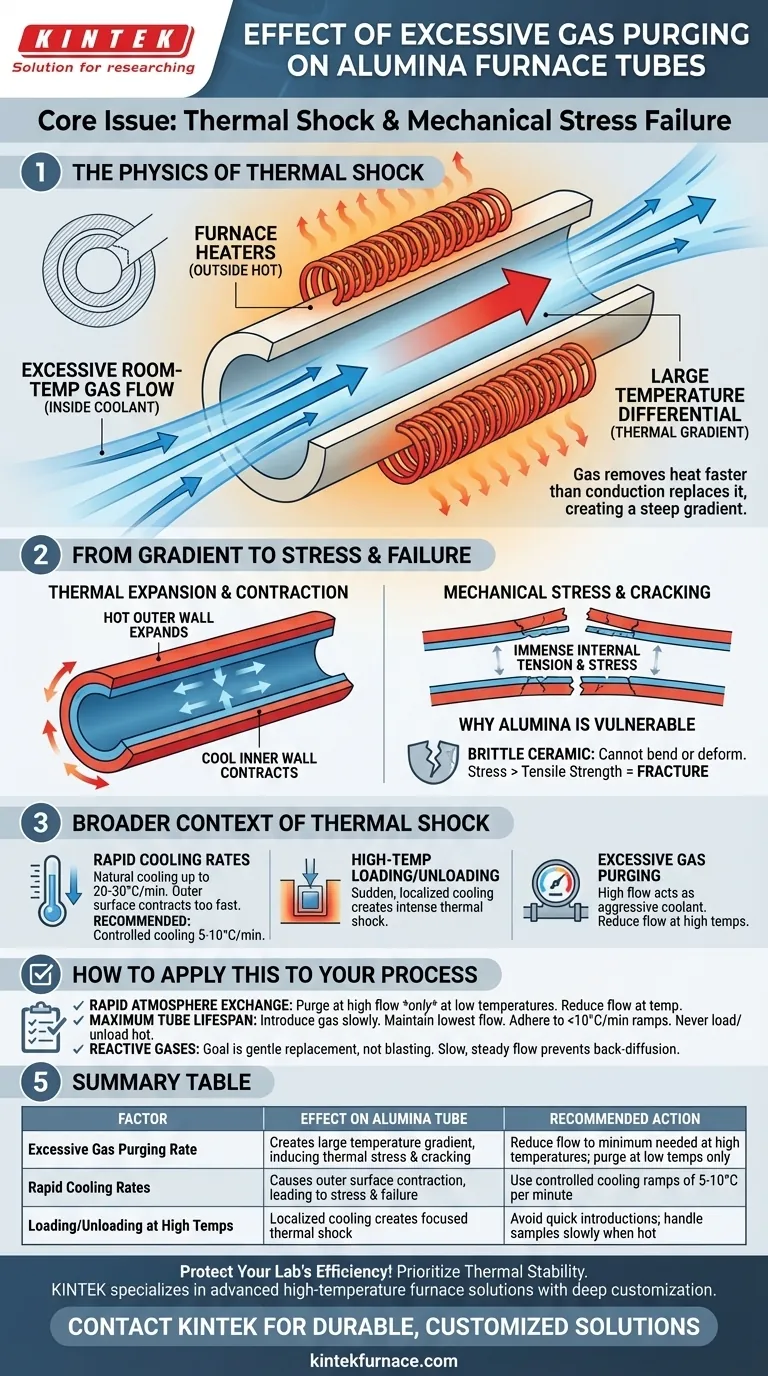
In short, an excessive gas purging rate will create a large temperature difference between the inner and outer surfaces of your alumina furnace tube. This differential, known as a thermal gradient, generates significant mechanical stress. Because alumina is a brittle ceramic, this thermal stress can easily cause the tube to crack and ultimately fail.
The core issue is not the gas itself, but the thermal shock it induces. A high flow of room-temperature gas acts as an aggressive coolant on the inside of the tube while the furnace heaters keep the outside hot, creating a destructive tug-of-war within the material.

The Physics of Thermal Shock in Alumina Tubes
To prevent failure, it's critical to understand the mechanism at work. The damage happens because of a direct conflict between the material's properties and the thermal environment you create.
How Gas Flow Creates a Temperature Gradient
A tube furnace works by heating the outside of the alumina tube. The heat then conducts through the ceramic to heat the internal process area.
When you introduce a continuous flow of gas, it constantly removes heat from the inner surface of the tube. An excessive flow rate removes this heat much faster than it can be replaced by conduction from the outside, creating a steep temperature gradient across the tube's wall.
From Temperature Gradient to Mechanical Stress
Materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. With a steep thermal gradient, the hot outer wall of the tube is expanded, while the cool inner wall is trying to contract.
This differential expansion creates immense internal tension. The outer layer is essentially trying to stretch the inner layer, which is simultaneously trying to shrink away from it.
Why Alumina Is Vulnerable
Alumina is a ceramic, prized for its high-temperature stability and chemical inertness. However, like most ceramics, it is extremely brittle.
This means it cannot bend, stretch, or deform to relieve internal stress. Once the thermal stress exceeds the material's inherent tensile strength, it has no alternative but to fracture.
Understanding the Broader Context of Thermal Shock
Gas flow is just one potential source of damaging thermal shock. The principle remains the same for other common operational mistakes.
Rapid Cooling Rates
Allowing a furnace to cool "naturally" without a controller can be catastrophic. The initial temperature drop can be as high as 20-30°C per minute.
This rapid cooling causes the outer surface of the tube to contract much faster than the insulated inner core, creating the same type of stress as excessive gas flow, just in reverse. A controlled cooling rate of 5-10°C per minute is the recommended safe limit.
Loading and Unloading at High Temperatures
Introducing a room-temperature sample holder or pushing a sample into the hot zone too quickly is another common cause of failure. The sudden, localized cooling creates an intense, focused thermal shock that can easily crack the tube.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your operational choices should always prioritize thermal stability. Balancing process needs with the physical limitations of your equipment is key to preventing costly and time-consuming failures.
- If your primary focus is rapid atmosphere exchange: Purge the tube with a higher flow rate only at low temperatures before you begin heating. Once at temperature, reduce the flow to the minimum rate required to maintain your atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is maximum tube lifespan: Always introduce gas flow slowly and maintain the lowest possible rate that still achieves your process goals. Strictly adhere to controlled heating and cooling ramps (below 10°C/min) and never load or unload samples into a hot furnace.
- If your process involves reactive gases: Remember that the goal is to gently replace the atmosphere, not to blast it out. A slow, steady flow is more than sufficient to prevent back-diffusion of air and maintain a pure environment.
By treating gas flow as a critical thermal parameter, you can protect your equipment and ensure the repeatability of your results.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Alumina Tube | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive Gas Purging Rate | Creates large temperature gradient, inducing thermal stress and cracking | Reduce flow to minimum needed at high temperatures; purge at low temps only |
| Rapid Cooling Rates | Causes outer surface contraction, leading to stress and potential failure | Use controlled cooling ramps of 5-10°C per minute |
| Loading/Unloading at High Temperatures | Localized cooling creates focused thermal shock | Avoid quick introductions; handle samples slowly when hot |
Protect your lab's efficiency and avoid costly downtime! At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're dealing with thermal shock issues or need reliable equipment for demanding processes, our expertise ensures optimal performance and longevity. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory operations with durable, customized furnace solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















