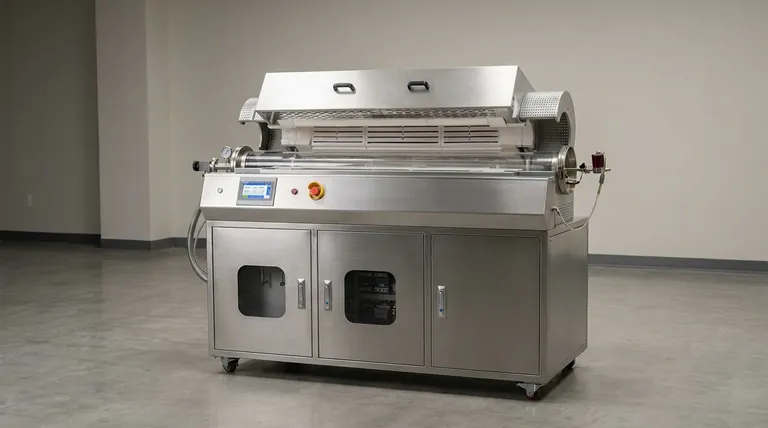
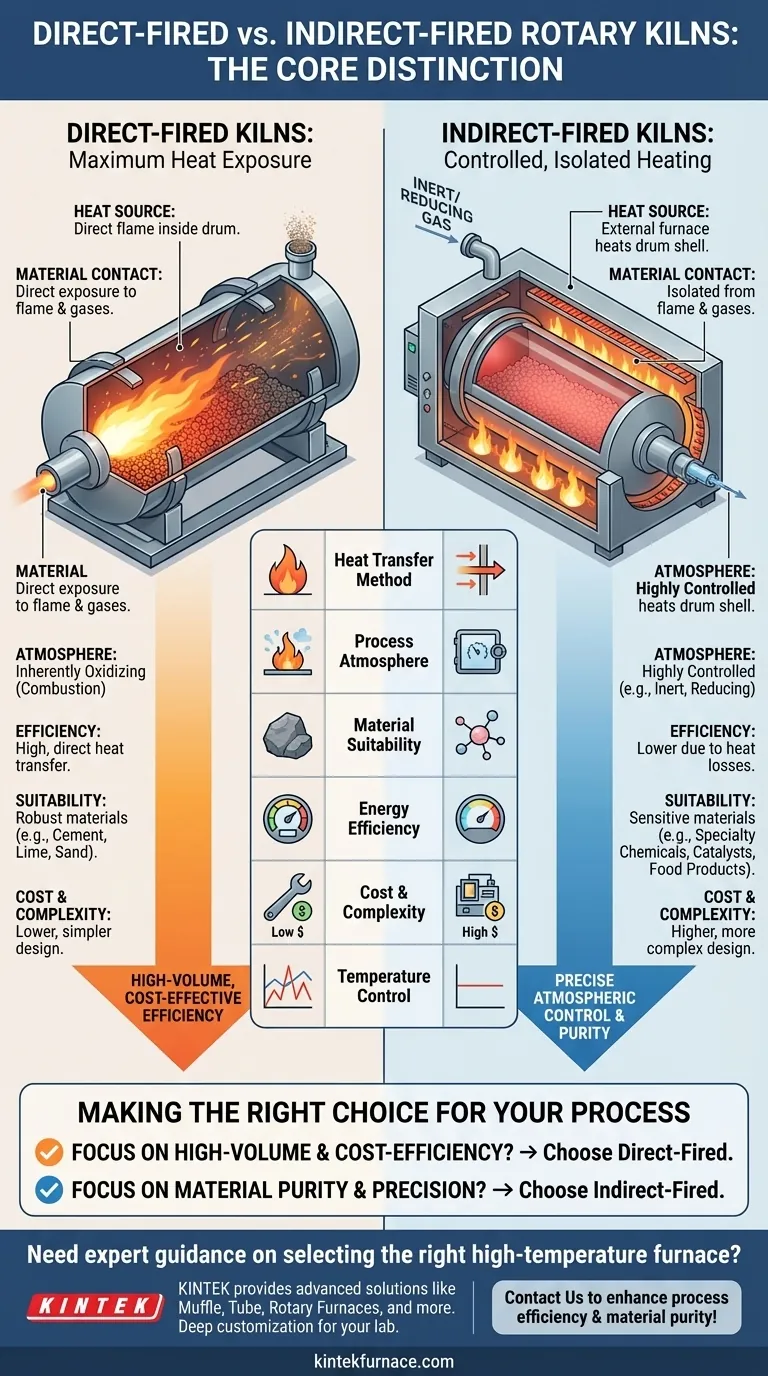
The fundamental difference between an indirect-fired and a direct-fired rotary kiln lies in how heat is introduced to the material. In a direct-fired kiln, the material is heated by direct contact with the flame and combustion gases inside the drum. Conversely, an indirect-fired kiln heats the material by burning fuel outside the drum and transferring that thermal energy through the shell wall, isolating the material from any combustion byproducts.
Choosing between a direct and indirect-fired kiln is a critical decision that boils down to a single trade-off: the high-volume, cost-effective efficiency of direct heating versus the precise atmospheric control and purity of indirect heating.

The Core Distinction: Method of Heat Transfer
The method of heat transfer is the single design choice that dictates the capabilities, applications, and limitations of the entire system.
Direct-Fired Kilns: Maximum Heat Exposure
In a direct-fired system, a burner injects a flame directly into the rotary drum. The material being processed tumbles through this environment, coming into direct contact with the hot gases and products of combustion.
This method provides exceptionally efficient heat transfer because the energy is applied straight to the material, minimizing thermal losses.
Indirect-Fired Kilns: Controlled, Isolated Heating
An indirect-fired kiln functions more like an oven. The rotary drum is enclosed within a larger insulated furnace or heating shroud.
Fuel is burned within this external chamber, heating the drum's shell to the required temperature. The heat then conducts through the shell wall to the material inside, which never touches the flame or flue gas.
Key Operational Differences
This fundamental design difference creates significant operational distinctions that determine which kiln is right for a specific process.
Process Atmosphere and Contamination Control
This is the most critical advantage of an indirect kiln. Because the processing chamber is sealed from the outside environment, you have complete control over the internal atmosphere.
This allows for processing in inert or reducing atmospheres, which is impossible in a direct-fired system where the atmosphere is inherently oxidizing due to combustion. It also prevents any contamination of the material by ash or combustion byproducts.
Temperature Control and Precision
Indirect-fired systems offer more precise temperature control. Heating the external shroud allows for a more uniform and stable thermal environment, avoiding the intense hot spots created by a direct flame.
This level of control is essential for materials that are sensitive to thermal shock or require a very specific temperature profile to achieve the desired reaction.
Material Suitability
The choice of kiln is often dictated by the material itself.
Direct-fired kilns are ideal for robust, high-volume materials that are not harmed by contact with flue gases. Common examples include cement, lime, sand, and aggregates.
Indirect-fired kilns are necessary for sensitive materials where purity is paramount or a specific atmosphere is required. This includes specialty chemicals, catalysts, certain food products, and metal powders.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Efficiency vs. Purity
Selecting the right kiln involves a clear understanding of the trade-offs between thermal efficiency, cost, and process control.
Energy Efficiency and Throughput
Direct-fired kilns are generally more energy-efficient and can handle much larger volumes of material. Applying heat directly to the source is the most thermodynamically efficient path.
Indirect kilns lose a portion of their energy heating the external shroud and the air gap before it even reaches the drum shell. This makes them less efficient for large-scale, bulk processing.
System Complexity and Cost
Direct-fired systems are mechanically simpler and therefore less expensive to build and maintain.
Indirect-fired kilns are more complex. They require an external furnace, and the drum shell must often be constructed from high-temperature alloys to withstand the constant thermal stress without degrading. This significantly increases both the initial capital cost and potential maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific requirements of the material you are processing and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and cost-efficiency: A direct-fired kiln is the superior choice for materials that can tolerate contact with combustion gases.
- If your primary focus is material purity and precise atmosphere control: An indirect-fired kiln is the only viable option for protecting sensitive substances and enabling reactions in controlled environments.
Understanding this core distinction empowers you to select the kiln technology that aligns perfectly with your material requirements and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct-Fired Kiln | Indirect-Fired Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Method | Direct contact with flame and gases | Heat through drum shell, isolated from combustion |
| Process Atmosphere | Oxidizing, due to combustion | Controlled (e.g., inert or reducing) |
| Material Suitability | Robust materials (e.g., cement, lime) | Sensitive materials (e.g., chemicals, catalysts) |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Lower due to heat losses |
| Cost and Complexity | Lower cost, simpler design | Higher cost, more complex |
| Temperature Control | Less precise, potential for hot spots | More precise and uniform |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right high-temperature furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements for diverse laboratories. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and material purity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















