In short, alumina ceramic tubes improve temperature control through their exceptional thermal stability and conductivity, which ensure uniform and efficient heating. They enhance safety by acting as a superior electrical insulator, preventing short circuits and protecting heating elements from overheating, even at extreme temperatures up to 1800°C.
Alumina's value is not in a single property, but in its unique combination of traits. It efficiently transfers heat where you want it (conductivity) while simultaneously preventing electricity and excess heat from going where you don't (insulation and resistance), creating a highly controlled and safe environment.

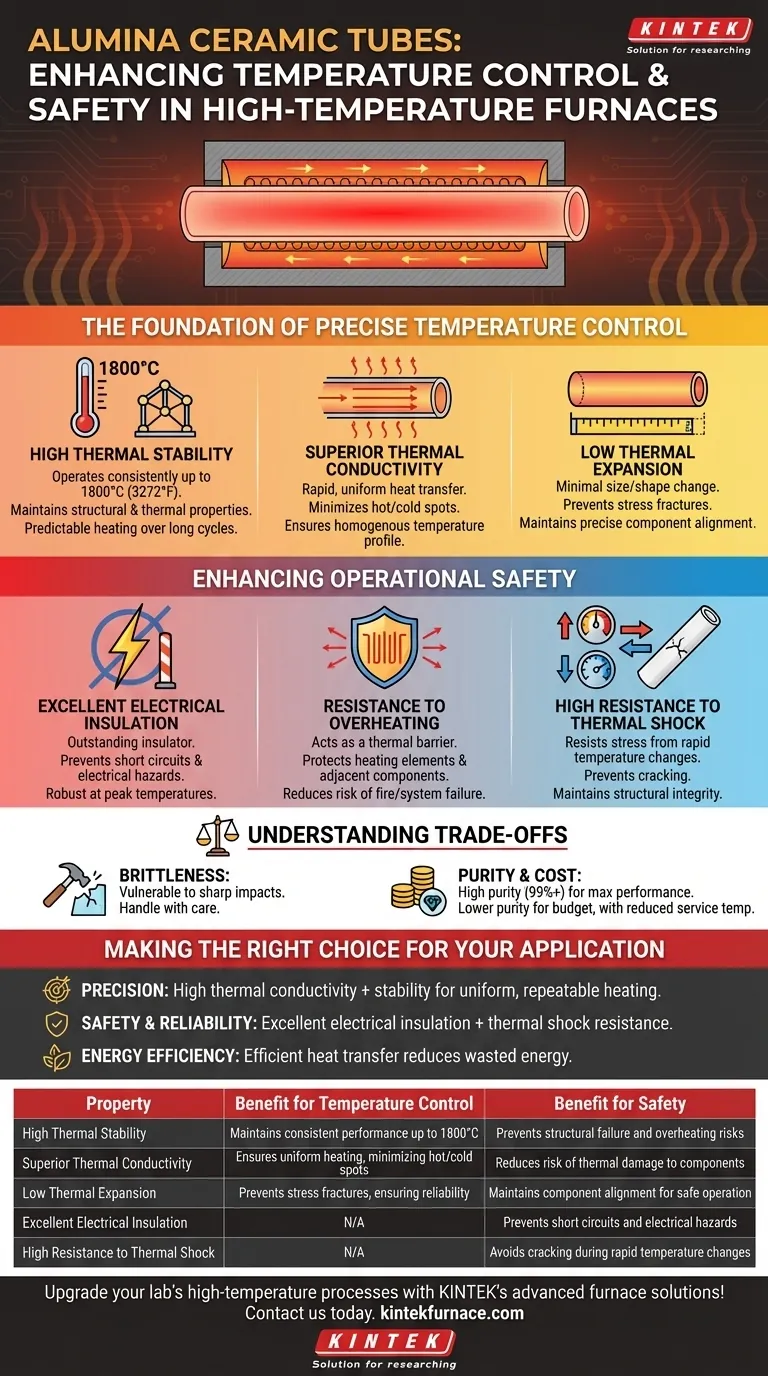
The Foundation of Precise Temperature Control
To control a process, you must first have a stable and predictable environment. Alumina ceramic tubes provide this foundation through their inherent material properties.
High Thermal Stability
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) is exceptionally stable at high temperatures, capable of operating consistently at up to 1800°C (3272°F).
Unlike metals that can warp or degrade, alumina tubes maintain their structural and thermal properties. This ensures that the heating performance remains predictable and repeatable over long operational cycles.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Effective temperature control requires that heat is delivered evenly and efficiently from the heating element to the furnace chamber.
Alumina’s high thermal conductivity ensures that heat generated by the internal element is transferred rapidly and uniformly through the tube wall. This minimizes hot spots and cold spots within the furnace, which is critical for processes requiring a homogenous temperature profile.
Low Thermal Expansion
Materials expand when heated, which can cause mechanical stress on the furnace assembly. Alumina has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion.
This means the tube does not significantly change its size or shape, even during large temperature swings. This stability prevents stress fractures and maintains the precise alignment of internal components, contributing to long-term reliability.
Enhancing Operational Safety
Safety in high-temperature electrical furnaces is paramount. Alumina tubes mitigate the two primary risks: electrical hazards and uncontrolled heat.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
The core function of the tube is to house an electrical heating element. Alumina is an outstanding electrical insulator, meaning it does not conduct electricity.
This property is crucial for preventing electrical short circuits between the heating element and the furnace body or other components. This insulative capability remains robust even at peak operating temperatures, preventing a major cause of equipment failure and electrical shock hazards.
Resistance to Overheating
While it conducts heat well through its wall, the material also acts as a thermal barrier, containing the intense energy of the heating element.
This insulating effect prevents the heating element itself from overheating, extending its operational life. It also protects adjacent structural components from thermal damage, reducing the risk of fire or system failure.
High Resistance to Thermal Shock
Furnaces often undergo rapid heating or cooling cycles. Thermal shock is the stress induced in a material when it experiences a rapid temperature change, which can cause cracking.
Alumina ceramics are engineered to resist this stress. A tube that doesn't crack maintains its structural integrity, ensuring that the live heating element remains safely contained and electrically isolated.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Objectivity requires acknowledging the limitations of alumina ceramics.
Brittleness
While extremely hard and resistant to wear, alumina is a brittle material. It can shatter from sharp mechanical impacts. Care must be taken during installation and maintenance to avoid dropping or striking the tubes.
Purity and Cost
The exceptional properties described are most prominent in high-purity alumina (typically 99% or higher). Lower-purity formulations are less expensive but have a lower maximum service temperature and reduced performance. The choice is a direct trade-off between performance requirements and budget.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your material specification.
- If your primary focus is process precision: The combination of high thermal conductivity and thermal stability makes alumina the superior choice for uniform, repeatable heating.
- If your primary focus is safety and long-term reliability: Alumina's excellent electrical insulation and resistance to thermal shock are its most critical safety features.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: The efficient heat transfer means less wasted energy is required to bring the furnace to its setpoint and maintain it, reducing operational costs.
Ultimately, alumina ceramic tubes provide a level of performance and safety that is essential for demanding high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Temperature Control | Benefit for Safety |
|---|---|---|
| High Thermal Stability | Maintains consistent performance up to 1800°C | Prevents structural failure and overheating risks |
| Superior Thermal Conductivity | Ensures uniform heating, minimizing hot/cold spots | Reduces risk of thermal damage to components |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Prevents stress fractures, ensuring reliability | Maintains component alignment for safe operation |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | N/A | Prevents short circuits and electrical hazards |
| High Resistance to Thermal Shock | N/A | Avoids cracking during rapid temperature changes |
Upgrade your lab's high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing temperature control, safety, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your setup and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions



















