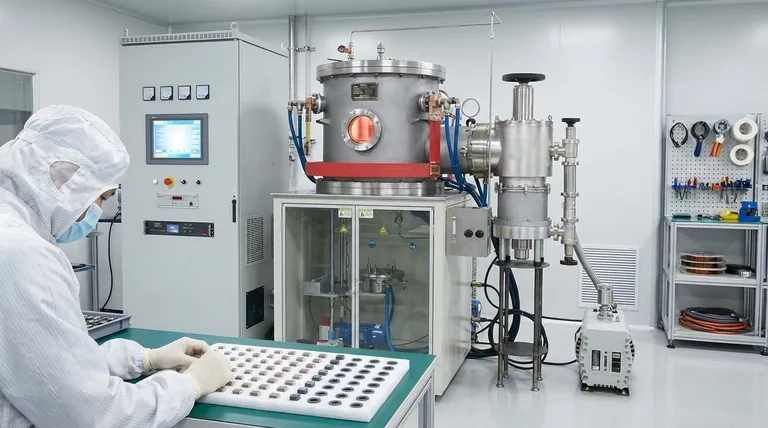
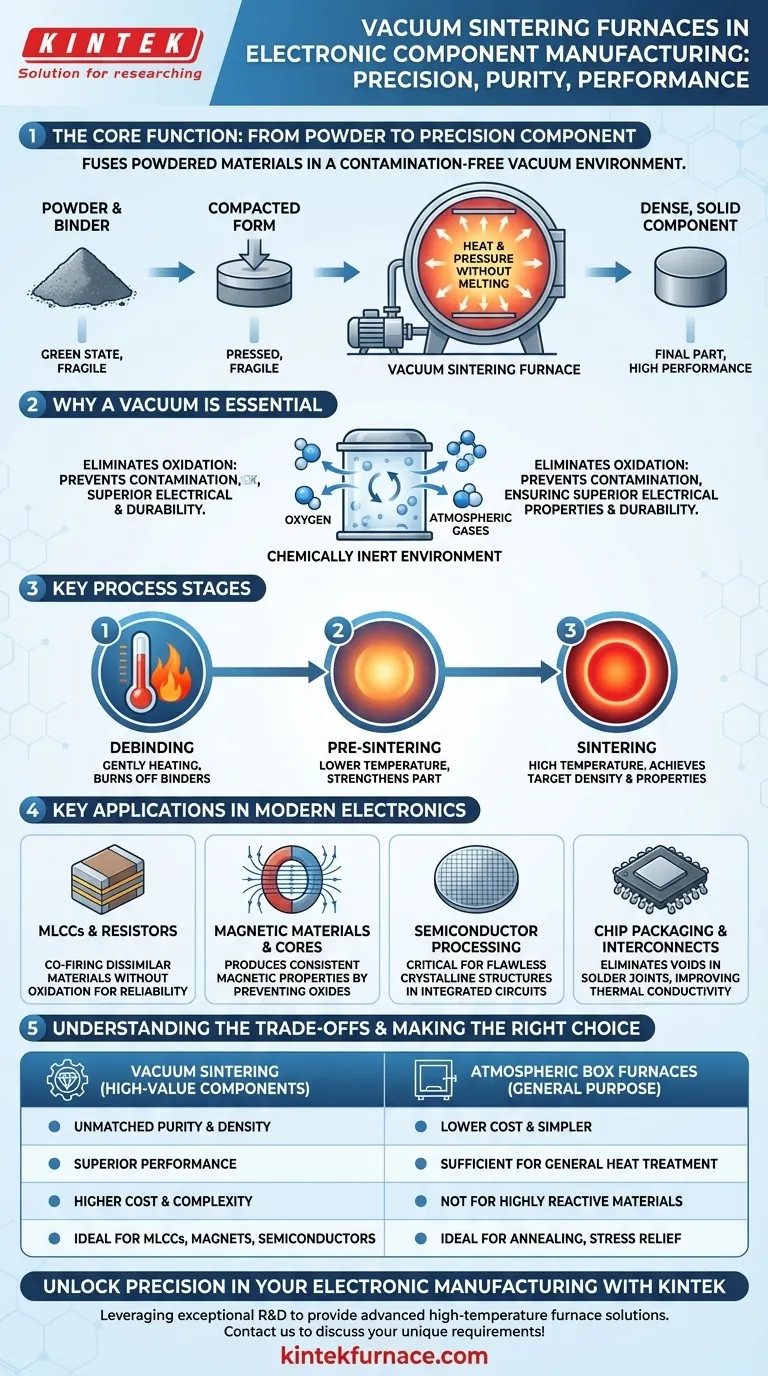
At its core, a vacuum sintering furnace is used in electronics manufacturing to fuse powdered materials into solid, high-performance components within a contamination-free environment. This process is critical for creating parts such as multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), magnetic materials, and specialized semiconductor substrates where material purity and structural density directly determine final performance.
The fundamental purpose of using a vacuum is to eliminate atmospheric gases, primarily oxygen, that would otherwise react with and contaminate materials at high temperatures. This prevention of oxidation is the key to producing electronic components with superior electrical properties, high density, and enhanced durability.

The Core Function: From Powder to Precision Component
The term "sintering" refers to the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat and pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. A vacuum furnace elevates this process by providing an ideal environment for sensitive electronic materials.
The Sintering Process Explained
Sintering transforms a component from a fragile "green" state, made of pressed powder, into a dense, solid part. Heat encourages the particles to bond and diffuse into one another, reducing porosity and increasing the component's density and mechanical strength.
Why a Vacuum is Essential
Many advanced ceramics and metals readily oxidize when heated in the presence of air. This oxidation can catastrophically alter the material's electrical and magnetic properties. By removing the atmosphere, a vacuum furnace creates a chemically inert environment, ensuring that the material's integrity is preserved throughout the high-temperature process.
Key Process Stages
Manufacturing in a vacuum sintering furnace typically involves several controlled stages:
- Debinding: Gently heating the component to burn off binder agents used to hold the powdered material in its initial shape.
- Pre-sintering: A lower-temperature heating cycle that begins to strengthen the part.
- Sintering: The final high-temperature cycle where the material achieves its target density and final properties under precise atmospheric control.
Key Applications in Modern Electronics
The precise, pure environment of a vacuum furnace makes it indispensable for manufacturing a range of high-value electronic components.
Manufacturing Passive Components (MLCCs, Resistors)
Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) and other passive components are built from alternating layers of ceramic dielectric and metal electrode materials. Vacuum sintering is critical to co-fire these dissimilar materials without oxidation, ensuring proper function and reliability.
Creating Magnetic Materials and Cores
The performance of magnetic materials is highly dependent on their final chemical composition and physical density. Vacuum sintering produces magnets and ceramic cores with highly consistent and predictable magnetic properties by preventing the formation of non-magnetic oxide layers.
Advanced Semiconductor Processing
In semiconductor fabrication, vacuum furnaces are used for processes like wafer diffusion and oxidation. The extreme purity of the vacuum environment is non-negotiable for creating the flawless crystalline structures required for integrated circuits and preventing yield-killing defects.
Chip Packaging and Interconnects
Specialized vacuum furnaces are also used for packaging and assembly. Processes like vacuum reflow soldering and brazing help eliminate voids or gas pockets in solder joints, dramatically improving the thermal conductivity and reliability of high-power chip packages.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum sintering is not a universal solution. The decision to use it involves clear trade-offs against simpler, atmospheric heating methods.
The Primary Advantage: Unmatched Purity
The defining benefit of vacuum sintering is the ability to produce components with the highest possible material purity and density. This leads directly to superior performance, especially in demanding applications like high-frequency circuits or high-reliability systems.
The Main Limitation: Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts. They require complex vacuum pump systems, sophisticated controls, and longer cycle times to pump down the chamber, adding to operational costs.
When Alternatives are Sufficient (Box Furnaces)
For many general-purpose thermal processes like heat treatment, annealing, or some brazing applications, a standard atmospheric box furnace is sufficient. If the material is not highly reactive or if a protective atmosphere can be created using inert gases like nitrogen, the complexity of a vacuum system is unnecessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material requirements and final component goals.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, pure ceramic or metallic components (like MLCCs or magnets): A vacuum sintering furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and achieve the required material properties.
- If your primary focus is advanced semiconductor fabrication (like diffusion or annealing): A high-purity vacuum or controlled atmosphere furnace is non-negotiable for achieving defect-free results.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment or assembly (like stress relief or basic soldering): An atmospheric box furnace is often the more cost-effective and practical solution.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace technology hinges on a clear understanding of your material's sensitivity to atmospheric contamination.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Fuses powdered materials into solid components in a contamination-free vacuum environment. |
| Key Applications | MLCCs, magnetic materials, semiconductor substrates, chip packaging. |
| Main Benefits | Superior purity, high density, enhanced electrical properties, and durability. |
| Process Stages | Debinding, pre-sintering, sintering under precise control. |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost and complexity vs. atmospheric furnaces; ideal for sensitive materials. |
Unlock Precision in Your Electronic Manufacturing with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're producing MLCCs, magnetic cores, or semiconductor components, our vacuum sintering furnaces ensure unmatched purity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and elevate your manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary in copper slag impoverishment? Maximize Your Matte Separation Efficiency
- What processing conditions does a vacuum furnace provide for TiCp/Fe microspheres? Sintering at 900 °C
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- What is the role of sintering or vacuum induction furnaces in battery regeneration? Optimize Cathode Recovery
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density



















