At its core, a vacuum furnace is constructed as a "cold wall" vessel with internal heating elements and is operated by first removing all air to create a vacuum. The material inside is then heated according to a precise, computer-controlled recipe before being cooled in a highly regulated manner. This process eliminates atmospheric contamination and allows for unparalleled control over the final material properties.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum furnace is not just to heat things without air; it is to achieve absolute process control. By removing the unpredictable variables of an atmosphere, these furnaces provide unmatched precision over temperature, material purity, and cooling, making them essential for manufacturing high-performance components.
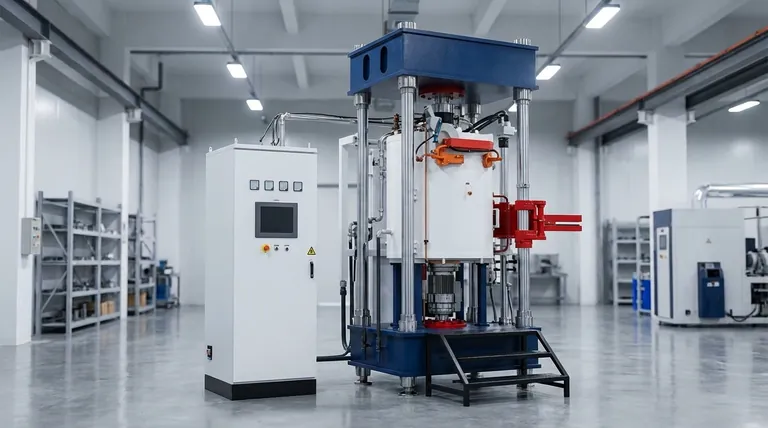

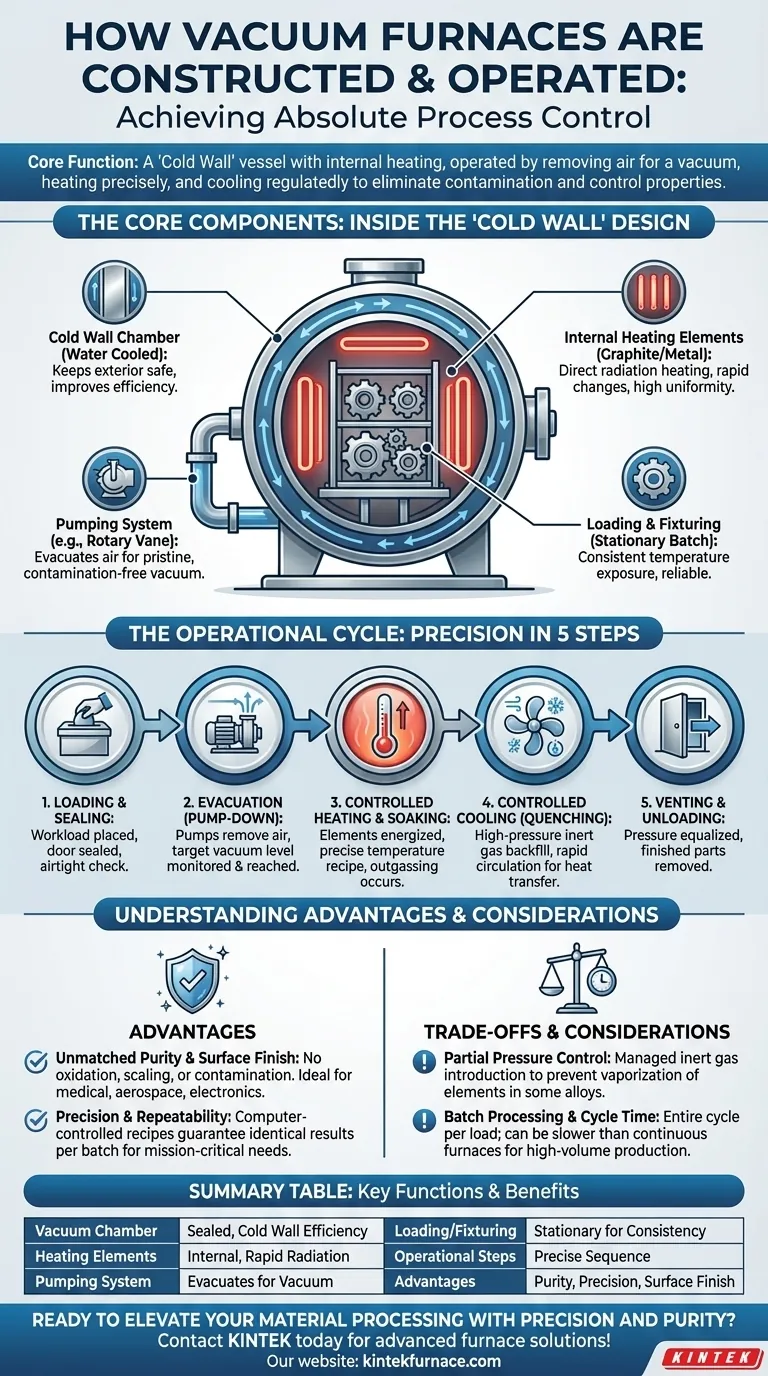
The Core Components: A Look Inside the 'Cold Wall' Design
A vacuum furnace's unique capabilities stem directly from its specialized construction, which is fundamentally different from a traditional refractory-lined furnace.
The Vacuum Chamber and 'Cold Wall' Principle
The furnace itself is a sealed vessel, typically a horizontal or vertical cylinder. It features a double-skinned wall with water actively circulating between the layers.
This "cold wall" design keeps the exterior of the furnace near room temperature even when the interior is at thousands of degrees. This improves energy efficiency and creates a safer working environment.
Internal Heating Elements
Unlike conventional furnaces where burners are outside the chamber, a vacuum furnace's heating elements are located inside the vacuum.
These elements, often made of graphite or refractory metals, heat the workload directly through radiation. This allows for very rapid temperature changes and exceptional uniformity, as there is no massive refractory brick structure to heat or cool.
The Pumping System
The heart of the system is a series of pumps, such as a rotary vane pump, responsible for evacuating the chamber. This system removes air and other gases to achieve the desired vacuum level, which can be as low as near-interstellar space.
This vacuum is critical for preventing oxidation and removing volatile impurities from the materials being processed.
Loading and Fixturing
Parts are typically loaded onto rolling racks or specialized trays and moved into the chamber. In most batch vacuum furnaces, which are the industry standard, the workload remains stationary throughout the entire heating and cooling cycle.
This eliminates the need for complex transfer mechanisms within the hot zone, increasing reliability and ensuring consistent temperature exposure for the entire load.
The Operational Cycle: From Loading to Unloading
Every vacuum furnace cycle is a precisely choreographed sequence managed by a computer to ensure perfect, repeatable results.
Step 1: Loading and Sealing
The cycle begins by placing the workload into the chamber and securely sealing the furnace door. A thorough check of all manual valves ensures the vessel is airtight and ready for evacuation.
Step 2: Evacuation (Pump-Down)
The vacuum pumps are activated to remove the air from the chamber. The system controller constantly monitors the vacuum level, only proceeding to the next step once the target pressure is reached. This step is what creates the pristine, contamination-free environment.
Step 3: Controlled Heating and Soaking
Once the vacuum is established, the internal heating elements are energized. The temperature is raised according to a pre-programmed recipe specific to the material and desired outcome.
During this phase, the furnace temperature can be controlled with extreme precision, often based on thermocouples placed directly on the workload. This step also facilitates outgassing, where the vacuum pulls unwanted residual elements out of the material itself.
Step 4: Controlled Cooling (Quenching)
After the heating cycle is complete, the workload must be cooled. This is often done rapidly by backfilling the chamber with a high-pressure inert gas like nitrogen or argon. A powerful fan circulates the gas to transfer heat away from the parts quickly. The cooling rate is just as precisely controlled as the heating rate.
Step 5: Venting and Unloading
Finally, the chamber pressure is equalized back to atmospheric levels. The door can then be safely opened and the finished, high-purity components are removed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
While incredibly powerful, vacuum furnaces involve specific considerations that make them ideal for some applications and less suitable for others.
Advantage: Unmatched Purity and Surface Finish
The primary benefit is the elimination of oxidation, scaling, and contamination. The vacuum environment ensures parts emerge from the furnace clean and bright, with superior surface integrity. This is non-negotiable for medical implants, aerospace components, and electronic devices.
Advantage: Precision and Repeatability
Computer-controlled recipes govern every variable, from vacuum level to temperature ramp rates and cooling speeds. This guarantees that every part in every batch receives the exact same treatment, ensuring unparalleled process repeatability for mission-critical manufacturing.
Consideration: Partial Pressure Control
A perfect vacuum is not always the goal. For certain alloys, a high vacuum can cause essential elements, like chromium in steel, to vaporize from the surface. Advanced furnaces manage this by introducing a controlled, low-level "partial pressure" of an inert gas to suppress this effect while still preventing oxidation.
Limitation: Batch Processing and Cycle Time
The most common vacuum furnaces are batch systems. The entire cycle—including pump-down, heating, soaking, and cooling—must be completed for a single load. This can result in longer overall cycle times compared to continuous atmosphere furnaces, making them less ideal for high-volume, low-margin production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a thermal process depends entirely on the required material properties and performance standards.
- If your primary focus is material purity and surface integrity: A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and remove contaminants, a critical need for aerospace, medical, and high-performance alloys.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and precision: The computer-controlled cycles of a vacuum furnace ensure identical results for every batch, which is vital for strict quality control in modern manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or advanced materials: The inert environment is non-negotiable for materials like titanium, superalloys, and advanced ceramics that would be ruined by exposure to air at high temperatures.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace is an investment in process control, enabling the creation of materials with properties that are simply unattainable through other means.
Summary Table:
| Component/Step | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed vessel with cold wall design for efficiency and safety |
| Heating Elements | Internal elements for direct radiation heating and rapid temperature changes |
| Pumping System | Evacuates air to create vacuum, preventing oxidation and impurities |
| Loading/Fixturing | Stationary batch loading for consistent temperature exposure |
| Operational Steps | Loading, evacuation, heating, cooling, and unloading for repeatable cycles |
| Advantages | Unmatched purity, precision, and surface finish for high-performance materials |
| Considerations | Batch processing may have longer cycle times; partial pressure control for specific alloys |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or advanced materials, we can help you achieve unparalleled process control and superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density



















