In materials science, inert ovens are specialized furnaces used to thermally process materials in an environment deliberately stripped of reactive gases, primarily oxygen. By replacing the ambient air with a stable gas like nitrogen or argon, these ovens prevent unwanted chemical reactions such as oxidation, allowing materials to be heated, cured, or annealed without degrading their fundamental properties.
The core function of an inert oven is not just to apply heat, but to create a chemically non-reactive atmosphere. This prevents sensitive materials from oxidizing or degrading at high temperatures, ensuring their structural and chemical integrity remains intact during processing.

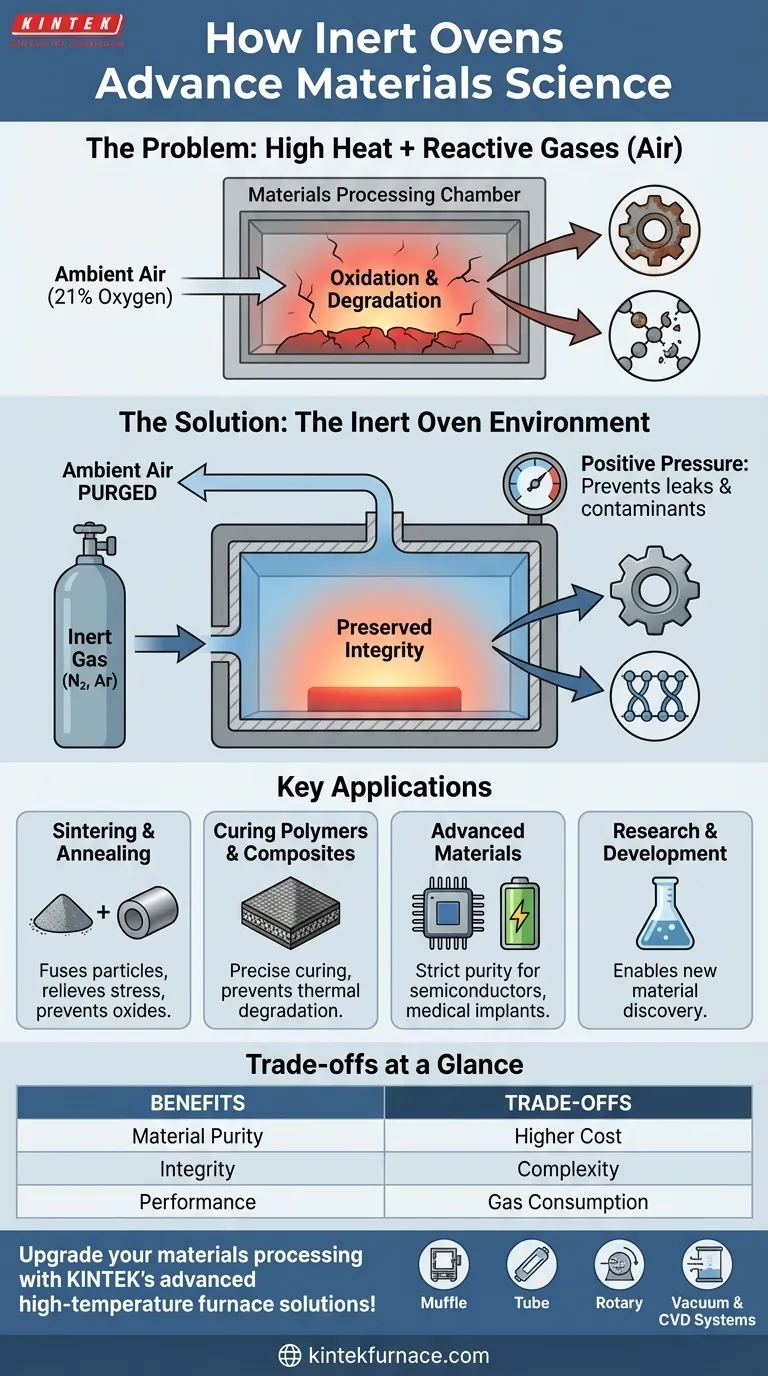
The Fundamental Problem: Heat and Reactive Gases
To understand the need for an inert oven, you must first understand the problem it solves. For many advanced materials, the combination of high temperature and ambient air is destructive.
Why Air is the Enemy
Ambient air is approximately 21% oxygen, a highly reactive element. At room temperature, its effects are slow, but as temperature increases, the rate of chemical reactions accelerates dramatically.
This accelerated reaction with oxygen is called oxidation. It is the same process that causes iron to rust or a cut apple to turn brown, but it happens much faster and with more significant consequences at the processing temperatures used in materials science.
The Impact of Uncontrolled Oxidation
For sensitive materials, oxidation isn't just a surface-level issue. It can fundamentally alter the material's internal structure and performance characteristics.
This can lead to brittleness in metals, compromised electrical conductivity in electronic components, or a complete failure of the chemical structure in advanced polymers. The material you end up with is not the material you designed.
How Inert Ovens Provide the Solution
An inert oven is an engineered solution to control the chemical environment during heating. It works by creating an atmosphere that will not react with the material being processed, even at extreme temperatures.
The Principle of Inert Gas Displacement
The oven chamber is first sealed and then purged of ambient air. This air is replaced with a high-purity inert gas, most commonly nitrogen (N₂) or argon (Ar).
These gases are called "inert" because their electron shells are stable, making them extremely non-reactive. They serve as a neutral bystander, allowing heat to be applied without introducing a reactive chemical agent like oxygen.
Maintaining a Controlled Atmosphere
Once purged, a slight positive pressure of the inert gas is maintained inside the oven. This ensures that if any microscopic leaks exist, the inert gas will flow out, preventing any outside air from seeping in.
This process protects the material not only from oxygen but also from other potential contaminants in the air, such as moisture (water vapor), which can also cause unwanted reactions.
Key Applications in Materials Science
Inert ovens are critical for manufacturing and research processes where material purity and structural integrity are paramount.
Sintering and Annealing
In sintering, fine powders (like ceramics or metals) are heated below their melting point until their particles fuse together, increasing strength and density. An inert atmosphere prevents oxides from forming on the particle surfaces, which would inhibit proper bonding.
In annealing, a metal is heated to relieve internal stresses and improve ductility. Performing this in an inert oven prevents the formation of a brittle oxide scale on the metal's surface.
Curing Polymers and Composites
Many high-performance polymers and composite materials require a precise curing cycle at elevated temperatures. An inert atmosphere prevents the polymer matrix from thermally degrading or oxidizing, which would compromise the final strength and durability of the component.
Processing of Advanced Materials
Materials used in semiconductors, batteries, and medical implants often have stringent purity requirements. Any oxidation or contamination during heat treatment could lead to a catastrophic failure of the final product, making inert atmosphere processing an essential step.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for certain applications, inert ovens are not a universal solution. Their benefits come with clear trade-offs compared to standard industrial ovens.
Cost and Complexity
Inert atmosphere ovens are more expensive to purchase and operate than their standard counterparts. They require gas delivery systems, high-purity gas supplies, and more sophisticated sealing and control mechanisms.
Process Time and Gas Consumption
The initial purging cycle to remove all oxygen adds time to the overall process. Furthermore, the continuous consumption of high-purity nitrogen or argon represents a significant ongoing operational cost.
Atmosphere Monitoring
For critical applications, simply flooding an oven with inert gas is not enough. Oxygen sensors and other analytical tools are often required to continuously monitor the chamber and guarantee the atmosphere remains below a specified contamination threshold (measured in parts per million).
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding whether to use an inert oven depends entirely on your material's sensitivity to atmospheric reaction at your target processing temperature.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation in metals, ceramics, or sensitive alloys: An inert oven is non-negotiable to preserve the material's intended properties.
- If your primary focus is curing high-performance polymers at risk of thermal degradation: An inert atmosphere is critical for achieving the desired chemical structure and mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is simply drying a component or curing a robust material at low temperatures: A standard convection or vacuum oven is likely a more cost-effective and efficient tool.
Ultimately, using an inert oven is a deliberate choice to prioritize material purity and integrity over cost and simplicity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Heat materials in a non-reactive atmosphere to prevent oxidation and degradation. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) |
| Key Applications | Sintering, annealing, curing polymers, processing semiconductors and batteries. |
| Benefits | Preserves material purity, structural integrity, and performance characteristics. |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost, complexity, and gas consumption compared to standard ovens. |
Upgrade your materials processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable inert ovens, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, preventing oxidation and enhancing material integrity. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity



















