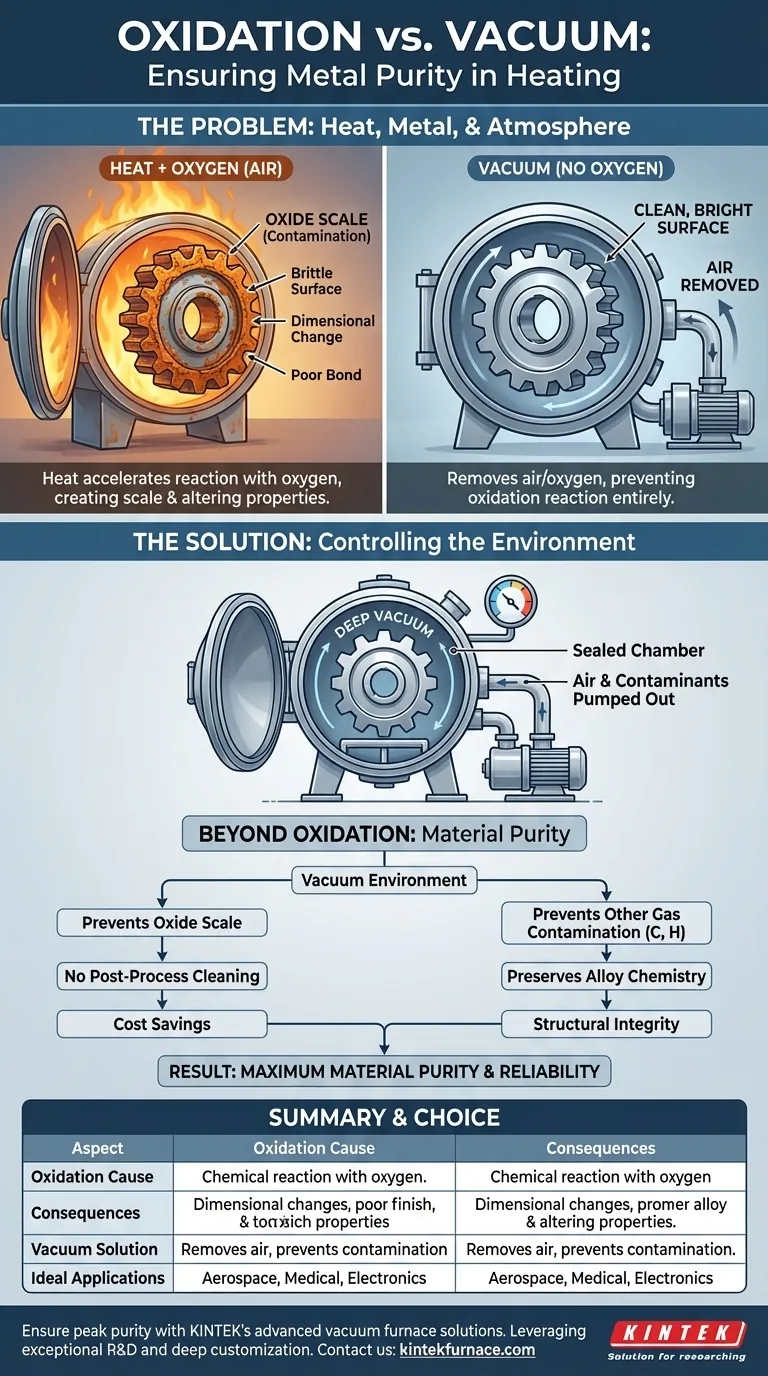
At its core, oxidation is a chemical reaction between a metal's surface and the oxygen in the air, a reaction that heat dramatically accelerates. This process creates an undesirable oxide layer, or scale, on the metal. A vacuum furnace directly counters this by physically removing the air—and therefore the oxygen—from the heating chamber, creating an environment where oxidation simply cannot occur.
The fundamental problem isn't just heat, but the combination of heat and atmosphere. By removing the atmosphere, a vacuum furnace moves beyond simply preventing cosmetic rust; it guarantees the metallurgical purity and structural integrity of the final component.

The Problem: Heat, Metal, and Atmosphere
When you heat a metal part for processes like brazing, annealing, or hardening, you are introducing energy. This energy doesn't just affect the metal's internal structure; it supercharges its interaction with the surrounding environment.
What is Oxidation?
Oxidation is the process where metal atoms on the surface give up electrons to oxygen atoms from the air. This forms a new, often brittle and discolored compound known as a metal oxide.
In ambient temperatures, this process is very slow for most metals, like the gradual rusting of iron.
Why Heat Accelerates Oxidation
Heat acts as a catalyst for this chemical reaction. It provides the necessary "activation energy" that allows the metal and oxygen atoms to combine much more rapidly and aggressively.
The higher the temperature, the faster the oxidation, leading to the formation of a thick, flaky layer of scale on the component's surface.
The Consequences of Uncontrolled Oxidation
This oxide layer is more than a cosmetic issue. It can lead to a host of problems, including dimensional changes, poor surface finish, and a compromised ability to braze or weld.
Critically, it alters the material properties of the surface, potentially impacting hardness, fatigue life, and the component's overall performance and reliability. It introduces contamination into what should be a pure material.
The Solution: Controlling the Environment
Since the reaction requires both heat and oxygen, the most effective solution is to remove one of the reactants. A vacuum furnace is engineered to remove the oxygen.
How a Vacuum Furnace Works
A vacuum furnace is a sealed, robust vessel connected to a series of pumps. Before the heating cycle begins, these pumps remove the air from the chamber, reducing the internal pressure to a near-vacuum.
By pumping out the air, the furnace removes the oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor, and other gases that could react with the hot metal.
Beyond Preventing Oxidation
The primary benefit is preventing oxidation, resulting in clean, bright parts straight out of the furnace. This often eliminates the need for post-process cleaning, grinding, or machining to remove scale.
However, a vacuum environment also prevents contamination from other atmospheric gases, such as carbon or hydrogen, which can diffuse into the metal at high temperatures and alter its alloy chemistry.
The Result: Material Purity
By processing parts in a vacuum, you ensure that the end product has the highest possible material purity. The surface is pristine, and the base alloy's composition remains unaltered.
This level of control is essential for high-performance applications in industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics, where even minor surface contamination can lead to catastrophic failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not the default solution for every heating application. It's a specialized tool with specific considerations.
Process Time and Cost
Achieving a deep vacuum takes time, which can make cycle times longer compared to a conventional atmosphere furnace. The equipment itself is also more complex and carries a higher initial investment and maintenance cost.
Material Limitations
Certain materials are not well-suited for vacuum processing. Metals with high vapor pressures, like zinc, magnesium, or cadmium, can begin to "boil" or outgas in a vacuum at high temperatures, vaporizing off the part's surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating method depends entirely on the requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is simple shaping or annealing where surface finish is not critical: A standard atmosphere furnace is often more cost-effective and faster.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, clean, and scale-free surface finish: A vacuum furnace is the ideal choice, often saving money by eliminating secondary cleaning operations.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum material purity for mission-critical components: A vacuum furnace is the only method that guarantees protection from all atmospheric contaminants.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about precisely controlling the environment to achieve the exact material properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Oxidation Cause | Chemical reaction with oxygen, accelerated by heat, forming brittle oxide layers. |
| Consequences | Dimensional changes, poor surface finish, contamination, and compromised material properties. |
| Vacuum Solution | Removes air/oxygen, prevents oxidation and other contamination, ensures clean, bright parts. |
| Ideal Applications | Aerospace, medical, electronics where high purity and reliability are critical. |
Ensure your materials achieve peak purity and performance with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your processes and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- How are parts loaded into a vacuum furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency in Your Process
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?



















