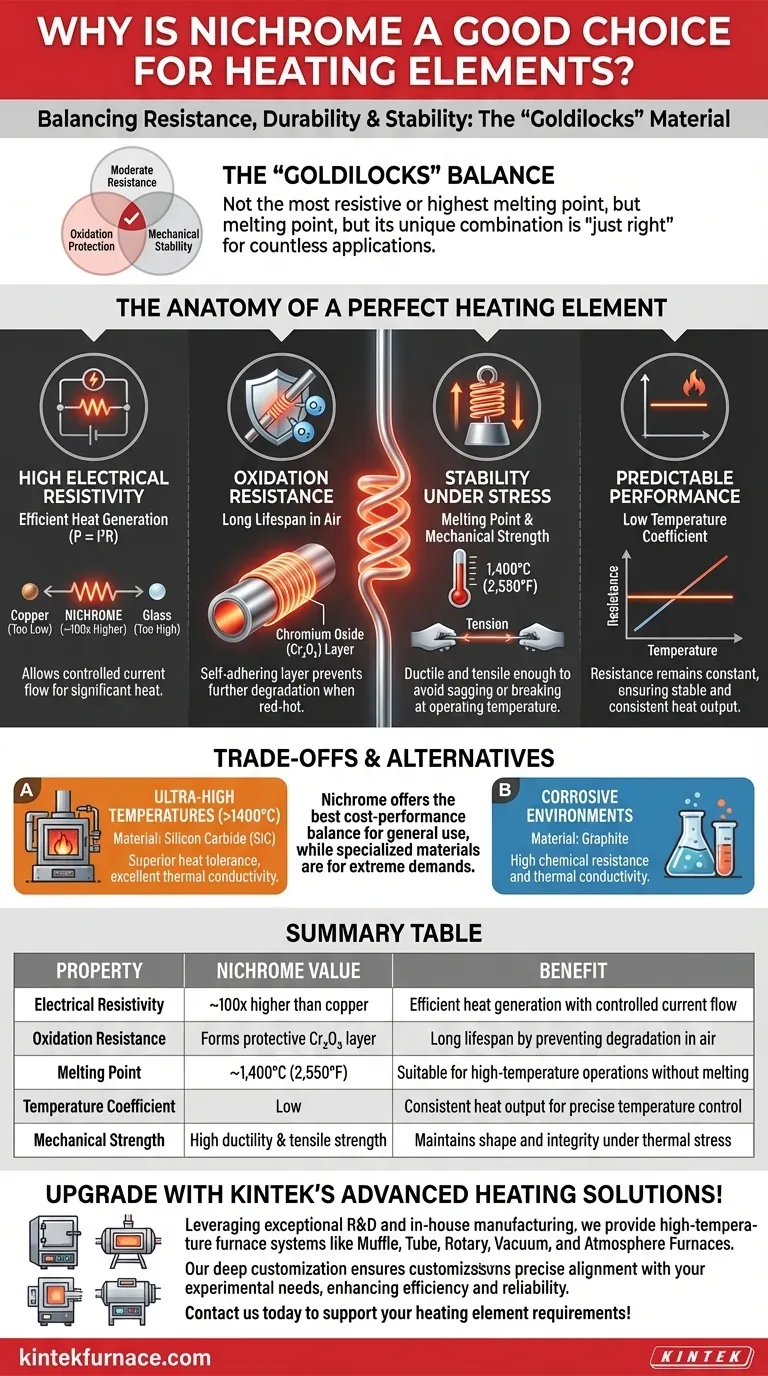
At its core, nichrome is an excellent material for heating elements because it masterfully balances high electrical resistance with exceptional durability at high temperatures. Unlike pure metals that oxidize and degrade quickly, nichrome forms a protective outer layer when heated, allowing it to glow red-hot for thousands of hours without failing. This unique combination makes it the workhorse for countless heating applications.
The key to understanding nichrome's value is realizing it’s a "Goldilocks" material. It's not the most resistive, nor does it have the highest melting point available, but its combination of moderate resistance, incredible oxidation protection, and mechanical stability is "just right" for creating reliable and long-lasting heating elements in everyday devices.
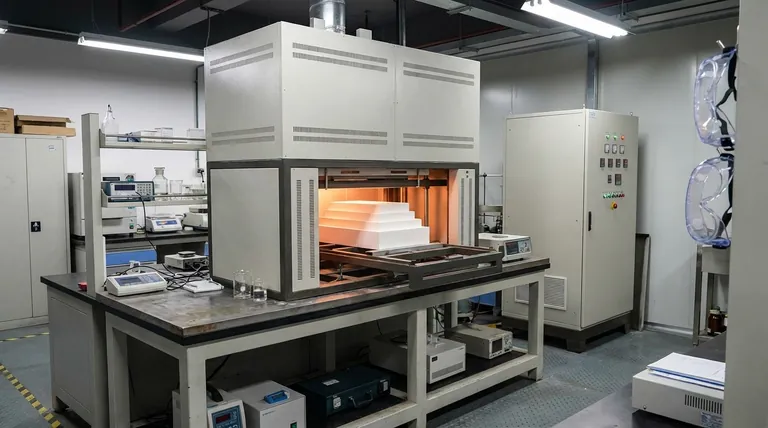

The Anatomy of a Perfect Heating Element
To understand why nichrome excels, we must first define the ideal properties of a heating element. It's a demanding job that requires a material to survive extreme conditions while performing its function predictably.
The Critical Role of Resistivity
A heating element works by converting electrical energy into heat, governed by the principle of resistive heating (P = I²R). The material's resistance is the key.
If resistance is too low (like copper), current flows too easily without generating significant heat. If it's too high (like glass), it acts as an insulator, preventing current from flowing at all.
Nichrome's resistivity is about 100 times higher than copper, making it highly effective at generating heat. Yet, it remains conductive enough to allow a controlled current to flow, striking the perfect balance for efficient heating.
Surviving the Heat: Oxidation Resistance
This is arguably nichrome's most important feature. When materials get red-hot in the presence of air, they rapidly oxidize (effectively, they rust or burn out).
Nichrome, an alloy of typically 80% nickel and 20% chromium, forms a thin, stable layer of chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃) on its surface when first heated. This layer is self-adhering and impervious to oxygen, protecting the metal underneath from further degradation and dramatically extending the element's lifespan.
Stability Under Stress: Melting Point and Mechanical Strength
A heating element must maintain its physical shape and integrity at operating temperature.
Nichrome has a high melting point of approximately 1,400°C (2,550°F), well above the operating temperature of most appliances like ovens and water heaters.
Furthermore, it possesses sufficient ductility to be drawn into thin, uniform wires and enough tensile strength to avoid sagging or breaking when glowing hot.
Predictable Performance: Low Temperature Coefficient
For a heater to be controllable, its output must be stable. Nichrome has a low temperature coefficient of resistance, meaning its electrical resistance remains relatively constant even as its temperature changes drastically.
This stability ensures that the element produces a consistent and predictable amount of heat, allowing for precise temperature control in devices like toasters and lab furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While nichrome is a fantastic general-purpose material, it is not the universal solution for every heating application. Its limitations reveal why other specialized materials exist.
When Nichrome Isn't Enough: Extreme Temperatures
For industrial furnaces operating at temperatures that would melt nichrome, more robust materials are required.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a ceramic that excels in these environments. It can withstand much higher temperatures and offers excellent thermal conductivity for efficient heat transfer, making it ideal for demanding industrial processes.
Chemical Resistance in Harsh Environments
In applications involving corrosive chemicals, a material's inertness is paramount.
Graphite elements are often chosen in these scenarios. While also capable of high-temperature operation, their primary advantage is high chemical resistance, preventing them from being eaten away by harsh compounds.
The Cost-Performance Balance
Nichrome represents an outstanding compromise between cost, durability, and performance. It is affordable enough for mass-produced consumer appliances but robust enough for many light industrial uses.
Specialized materials like Silicon Carbide are significantly more expensive and are reserved for applications where their superior thermal properties are an absolute necessity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a heating element material requires matching its properties to the specific demands of the task.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating for consumer or commercial appliances: Nichrome is the default choice for its ideal balance of durability, stable performance, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high-temperature industrial heating (above 1400°C): A ceramic like Silicon Carbide (SiC) is the necessary choice for its superior heat tolerance and longevity in extreme conditions.
- If your primary focus is heating within a chemically corrosive environment: Graphite is a strong candidate due to its exceptional chemical inertness and high thermal conductivity.
Ultimately, choosing the right material is an exercise in understanding and balancing these critical engineering trade-offs.
Summary Table:
| Property | Nichrome Value | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity | ~100x higher than copper | Efficient heat generation with controlled current flow |
| Oxidation Resistance | Forms protective Cr₂O₃ layer | Long lifespan by preventing degradation in air |
| Melting Point | ~1,400°C (2,550°F) | Suitable for high-temperature operations without melting |
| Temperature Coefficient | Low | Consistent heat output for precise temperature control |
| Mechanical Strength | High ductility and tensile strength | Maintains shape and integrity under thermal stress |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your heating element requirements and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity



















