In short, melting under vacuum or a protective atmosphere preserves the intended composition of an alloy. By creating a controlled environment, these methods prevent key alloying elements from reacting with atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This ensures the final product precisely matches the initial recipe, resulting in a more uniform and reliable material.
The uniformity of an alloy's composition is a direct result of process control. Using a vacuum or protective gas doesn't just stop oxidation; it creates a chemically sterile environment that prevents element loss, removes unwanted impurities, and minimizes gas-related defects that compromise the final material.

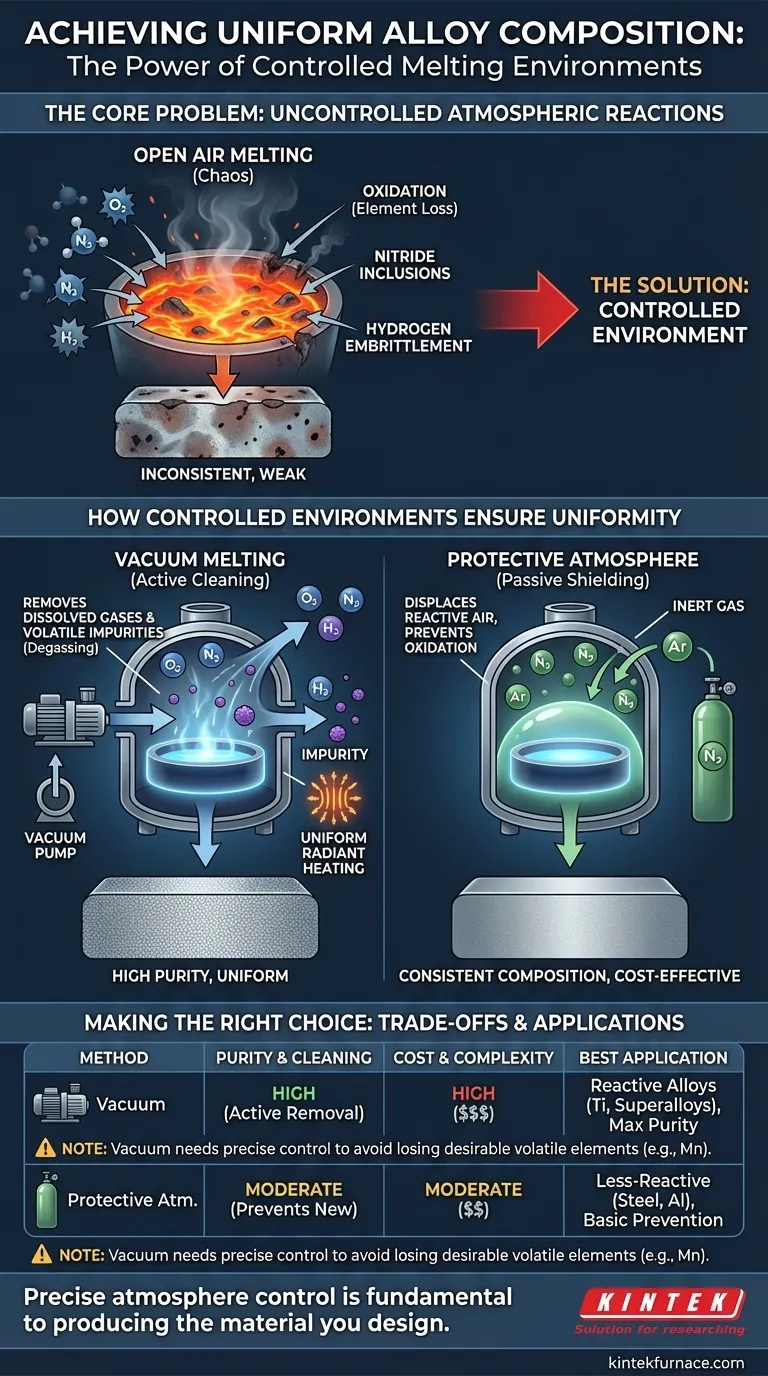
The Core Problem: Uncontrolled Atmospheric Reactions
When metals are melted in open air, the molten bath is exposed to a cocktail of reactive gases. This uncontrolled environment actively and unevenly alters the alloy's chemistry.
The Primary Culprit: Oxidation
Atmospheric oxygen is highly reactive with many common alloying elements, such as aluminum, chromium, and titanium. At high temperatures, these elements are preferentially "burned off" as they form oxides (slag), depleting them from the melt.
This loss is not uniform. It occurs primarily at the surface of the molten metal, leading to a final composition that differs from the intended formula and varies throughout the solidified material.
Beyond Oxygen: Other Gas Contamination
Air is not just oxygen. Nitrogen can react with certain elements to form hard, brittle nitride inclusions. Hydrogen, present from moisture in the air, can dissolve into the melt and later cause catastrophic hydrogen embrittlement or porosity in the final casting.
The Impact on Final Quality
This chemical inconsistency leads directly to inconsistent performance. An alloy with non-uniform composition will have unpredictable variations in strength, corrosion resistance, and ductility. Furthermore, the byproducts of these reactions—oxides and nitrides—create inclusions that act as stress points, increasing the likelihood of cracks and material failure.
How a Controlled Environment Ensures Uniformity
Vacuum and protective atmospheres work by systematically eliminating the root cause of these issues: the uncontrolled, reactive atmosphere.
Preventing Element Loss
By removing the air, a vacuum simply eliminates the oxygen and nitrogen available to react. A protective atmosphere, typically an inert gas like argon, displaces the air, blanketing the melt and shielding it from contact with oxygen.
In both cases, the selective loss of reactive alloying elements is prevented. This allows for precise control over the final composition, making it highly uniform and repeatable.
Removing Undesirable Impurities
Vacuum melting offers a distinct advantage beyond simply preventing reactions: it actively cleans the metal. Under vacuum, elements with a high vapor pressure (impurities like lead, zinc, or cadmium) will essentially "boil off" and be pulled away by the vacuum system.
This process also removes dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen that were already present in the raw material, a phenomenon known as degassing. The result is a cleaner, purer, and more uniform alloy.
Promoting More Uniform Melting
In a vacuum, heat transfer is dominated by radiation rather than convection. This can lead to more even and efficient heating throughout the entire charge of metal.
A more uniformly heated melt is a more homogenous liquid pool, which reduces the chance of chemical segregation before the metal is cast.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, these methods are not without their own considerations. Choosing the right environment requires understanding their specific limitations and costs.
Vacuum vs. Protective Atmosphere
A vacuum is the superior choice for purity, as it actively removes gases and volatile impurities. However, vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to operate.
A protective atmosphere is simpler and more cost-effective. It is excellent for preventing oxidation but does not remove impurities or dissolved gases that are already in the metal.
The Risk of Losing Key Elements
The power of a vacuum can also be a liability. If not precisely controlled, a strong vacuum at high temperatures can accidentally boil off desirable alloying elements that have a high vapor pressure, such as manganese or even chromium. This requires a careful balancing act of temperature and vacuum level.
Cost and Complexity
The primary trade-off is cost. Both vacuum and protective atmosphere melting are more expensive than melting in an air furnace due to the cost of equipment, inert gases, and longer processing times. This investment is justified by the need for high performance, purity, and reliability in the final application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum or protective atmosphere depends entirely on the alloy's chemistry and the performance requirements of the end product.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for reactive alloys (like titanium or superalloys): Vacuum melting is the only choice, as it is essential for removing dissolved gases and ensuring superior mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is preventing basic oxidation in less-reactive alloys (like many steels or aluminum alloys): A protective atmosphere of argon or nitrogen is often the most cost-effective and sufficient solution.
- If your primary focus is maintaining precise levels of volatile alloying elements (like high-manganese steels): You must carefully control the process, potentially using a partial-pressure inert gas backfill instead of a hard vacuum.
Ultimately, controlling the atmosphere during melting is the fundamental step to ensuring the material you design is the material you produce.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Alloy Uniformity |
|---|---|
| Prevention of Oxidation | Stops loss of reactive elements like aluminum and chromium, maintaining intended composition |
| Removal of Impurities | Eliminates volatile elements and dissolved gases (e.g., hydrogen), reducing defects |
| Controlled Environment | Minimizes gas-related reactions and promotes even heating for homogenous melting |
| Trade-offs | Vacuum offers higher purity but higher cost; protective atmospheres are cost-effective for basic oxidation prevention |
Achieve precise alloy uniformity with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, whether you're working with reactive alloys or require cost-effective oxidation prevention. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material quality and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today



















