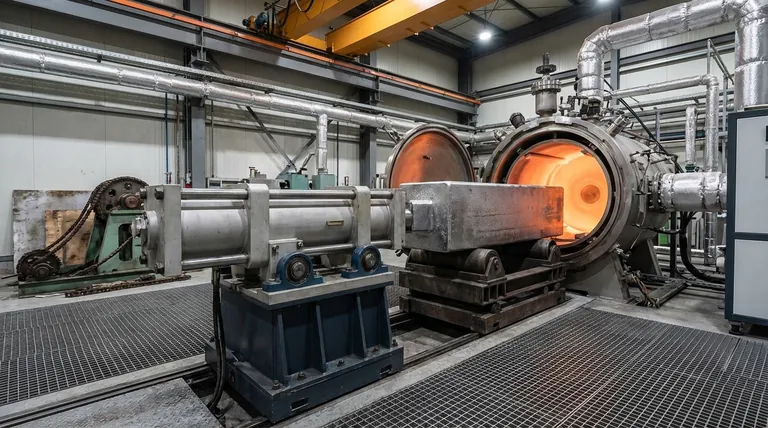
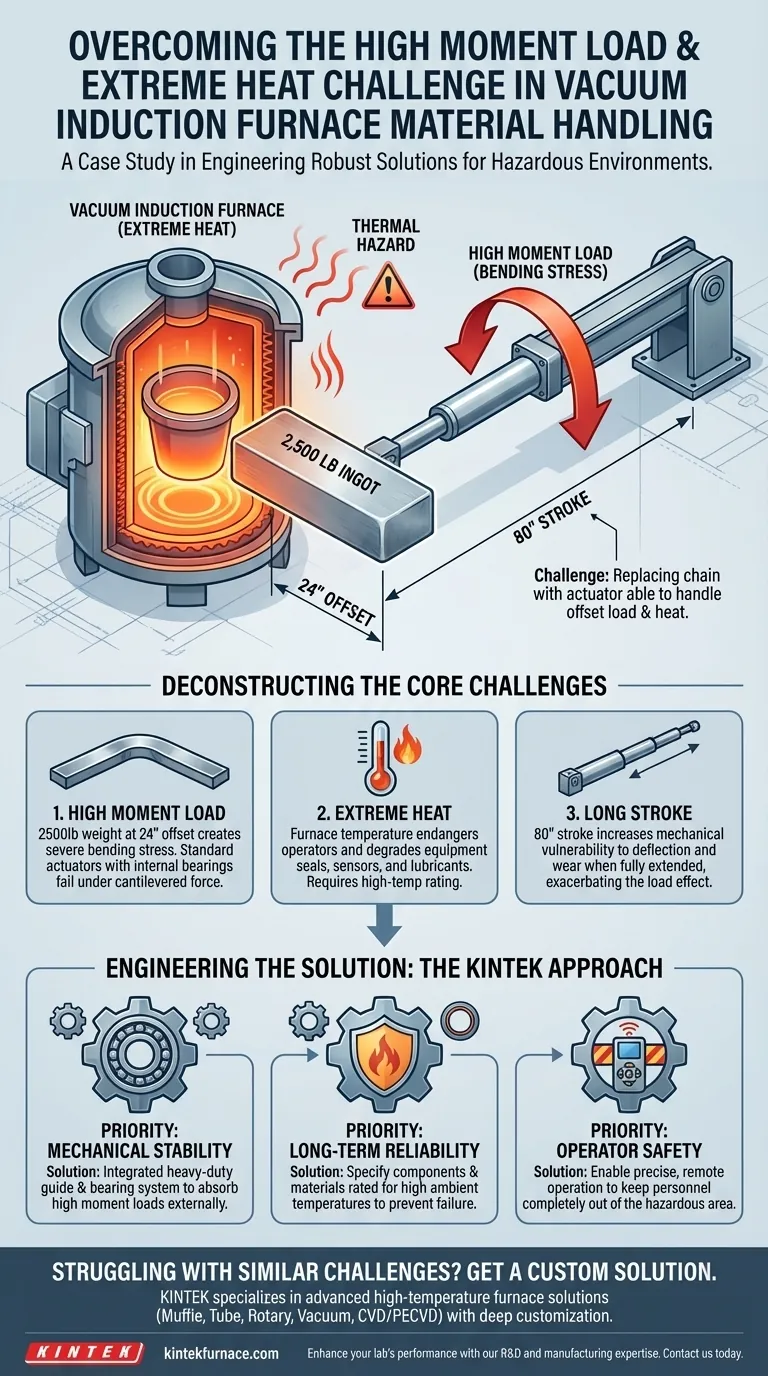
The primary challenge was twofold: a severe mechanical stress known as a high moment load, created by the system's geometry, and the significant operational hazard posed by extreme heat from the furnace. The task required replacing an existing chain drive system with an actuator that could handle a 2,500 lb ingot positioned 24 inches away from the actuator itself.
This was not a simple linear motion task. The core challenge was designing a system robust enough to overcome the immense leverage of an offset load while ensuring the safety of operators and equipment in a high-heat industrial environment.

Deconstructing the Core Challenges
To fully grasp the difficulty, we must break down the mechanical and environmental pressures at play. Each factor presented a significant engineering hurdle that dictated the design of a viable solution.
The Problem of the High Moment Load
A moment load (or bending moment) occurs when a force is applied at a distance from an object's supporting points, creating a rotational or bending force. In this case, the 2,500 lb weight of the ingot material was located 24 inches away from the actuator.
This offset acted like a long lever, multiplying the force exerted on the actuator. A standard actuator is designed for axial loads (pushing or pulling in a straight line) and would quickly fail under such a high bending stress.
The Environmental Hazard: Extreme Heat
The vacuum induction furnace generates intense heat during the melting process. This heat posed a direct threat to any nearby equipment and, more importantly, to human operators.
Any solution had to be designed for remote operation to keep personnel out of the hazardous area. Furthermore, the components of the motion system itself, including seals, sensors, and lubricants, had to be specified to withstand high ambient temperatures without degrading or failing.
The Demands of the Application
The system had to move the 2,500 lb (1,134 kg) load over a long distance, requiring a stroke of 80 inches (2032 mm). Combining a long stroke with a high, offset load dramatically increases the mechanical difficulty, as a fully extended actuator is at its most vulnerable to bending and deflection.
Understanding the Engineering Constraints
The specified requirements pushed the boundaries of conventional actuator technology. The combination of a heavy offset load and a long stroke is a classic recipe for mechanical failure if not addressed with a specialized design.
Why a Standard Actuator Fails
A typical rod-style actuator supports its load through internal bearings. The high moment load would place an extreme, cantilevered force on these bearings and the actuator rod itself.
This would lead to premature wear, seal failure, and potentially catastrophic bending of the rod. The system required an actuator with a robust, external bearing system specifically designed to support and guide the load independently.
The Inadequacy of the Old System
The decision to replace the previous chain drive system suggests it had its own liabilities. Chain drives can be prone to stretch, misalignment, and require regular maintenance, especially in harsh environments. The move toward a new actuator was likely driven by a need for greater precision, reliability, and lower maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing for such demanding applications, your primary goal will dictate your engineering priorities.
- If your primary focus is mechanical stability: Prioritize an actuator with an integrated, heavy-duty guide and bearing system designed to absorb high moment loads.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Select a system with components and materials specifically rated for the high-temperature environment to prevent premature failure.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: The solution must be capable of precise, remote operation to completely remove personnel from the hazardous area.
Successfully engineering a solution required addressing the interconnected challenges of mechanical stress and environmental hazards as a single, unified problem.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Description | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| High Moment Load | 2,500 lb ingot at 24-inch offset creates bending stress | Requires heavy-duty guide and bearing systems |
| Extreme Heat | Furnace heat threatens equipment and operator safety | Use high-temperature rated components and remote operation |
| Long Stroke | 80-inch stroke needed for material positioning | Increases vulnerability to deflection and failure |
Struggling with high moment loads and extreme heat in your furnace operations? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















