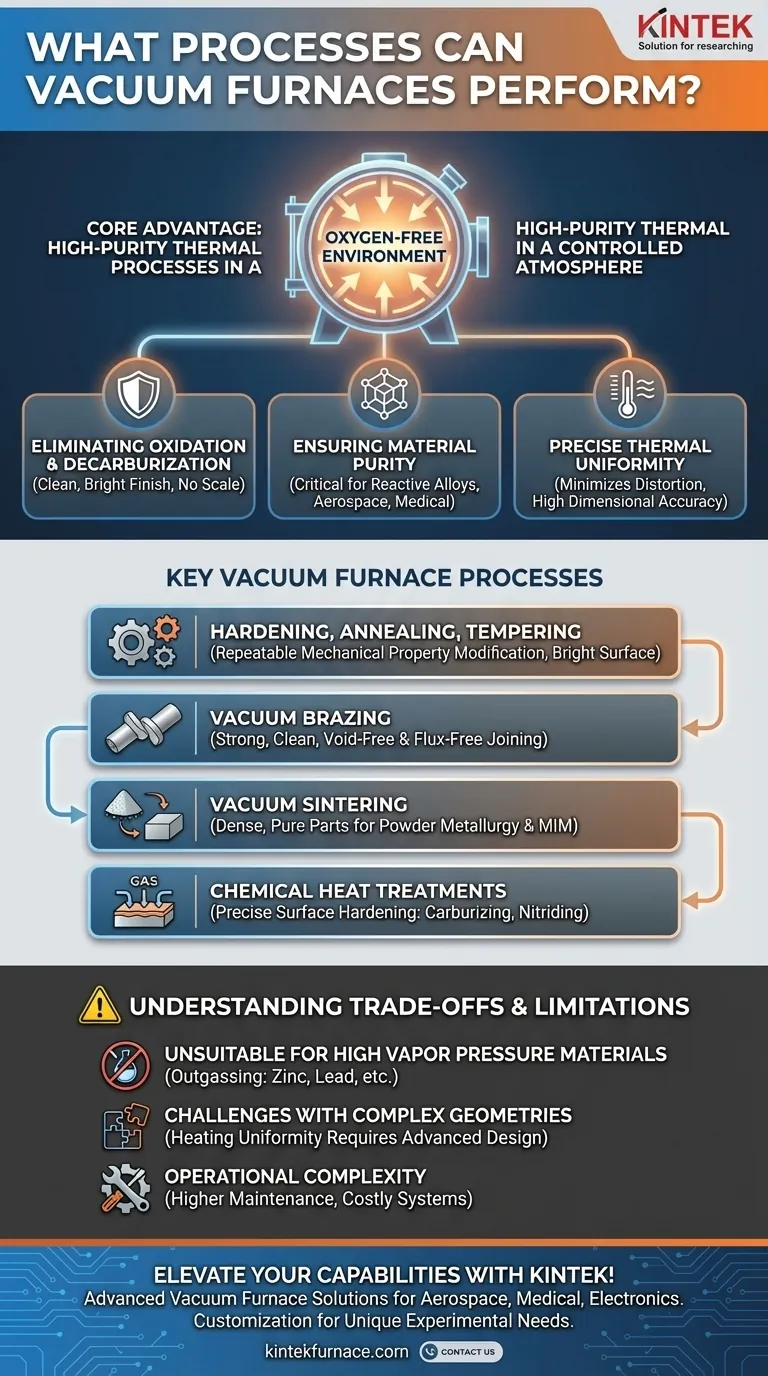
In short, vacuum furnaces execute a wide range of high-purity thermal processes by leveraging a controlled, oxygen-free environment. Their capabilities span from basic heat treatments like annealing and hardening to more specialized applications such as vacuum brazing, sintering of powdered metals, and precise chemical surface treatments.
The true value of a vacuum furnace isn't the list of processes it can perform, but the underlying benefit it provides: the near-total elimination of atmospheric contamination. This ensures unparalleled material purity, surface quality, and consistency, which is impossible to achieve in a standard atmosphere furnace.
The Core Advantage: Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
A vacuum furnace's primary function is to remove the atmosphere—specifically oxygen and other reactive gases—from the heating chamber. This fundamental difference unlocks several key benefits.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
By removing oxygen, a vacuum furnace prevents the formation of scale and oxides on the material's surface. This results in a clean, bright finish that often requires no post-process cleaning. It also prevents the loss of carbon from the surface of steels (decarburization), preserving the material's designed hardness and wear resistance.
Ensuring Material Purity
The vacuum environment is critical when working with reactive metals or alloys that can be contaminated by trace elements in the air. This controlled space ensures that the material's chemical composition remains unchanged throughout the thermal cycle, which is vital for high-performance applications in aerospace, medical, and electronics.
Achieving Precise Thermal Uniformity
Modern vacuum furnaces offer exceptional control over heating, soaking, and cooling rates. This precision minimizes thermal shock and distortion, especially in complex or thin-walled parts, leading to higher dimensional accuracy and more uniform metallurgical properties throughout the workpiece.
Key Vacuum Furnace Processes Explained
While the list of potential processes is long, they generally fall into a few key categories, each benefiting uniquely from the vacuum environment.
Hardening, Annealing, and Tempering
These are foundational heat treatments used to modify a material's mechanical properties. Performing them in a vacuum guarantees that the results—such as achieving a specific hardness or ductility—are highly repeatable and the parts emerge with a clean, bright surface finish.
Vacuum Brazing
Vacuum brazing is a superior method for joining components. The vacuum prevents oxides from forming on the joint surfaces, allowing the filler metal to flow freely and create a strong, clean, and void-free bond. This process eliminates the need for corrosive fluxes, which can become trapped and compromise the integrity of the assembly.
Vacuum Sintering
This process is essential for powder metallurgy and Metal Injection Molding (MIM). Fine metal powders are heated just below their melting point, causing the particles to fuse together. The vacuum is critical to prevent the oxidation of the vast surface area of the powders, ensuring strong, dense, and pure final parts.
Chemical Heat Treatments
Processes like vacuum carburizing and nitriding involve introducing specific gases (e.g., acetylene for carbon, ammonia for nitrogen) into the furnace at low pressure. The vacuum environment ensures that only the intended process gas reacts with the material surface, allowing for exceptionally precise control over the case depth and surface hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
A vacuum furnace is a specialized tool, not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for making an informed decision.
Unsuitability for High Vapor Pressure Materials
Materials with a high vapor pressure can turn into a gas (outgas) under heat and vacuum. This is a significant issue for metals like zinc, lead, manganese, copper, and aluminum, as their evaporation can alter the alloy's composition and contaminate the furnace interior.
Challenges with Complex Geometries
While a vacuum is an excellent insulator, this can make it difficult to achieve perfectly uniform heating on very large or intricate parts via radiation alone. This often requires advanced furnace designs with convection-assist fans or specialized tooling to ensure all sections of the workpiece reach the target temperature simultaneously.
Operational Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and costly to operate than conventional atmosphere furnaces. They require robust vacuum pumping systems, reliable seals, and rigorous maintenance to ensure performance and prevent leaks, which can compromise the entire process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice should be driven by the final properties your material requires.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest surface purity and a bright finish: Vacuum annealing or hardening is the ideal choice, as it completely prevents surface oxidation.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies without flux: Vacuum brazing provides superior joint integrity and cleanliness that is unmatched by other methods.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, high-purity parts from metal powders: Vacuum sintering is essential for preventing powder oxidation and ensuring strong diffusion bonds.
- If your primary focus is applying a highly controlled and uniform surface hardening layer: Vacuum carburizing or nitriding offers unparalleled precision over case depth and surface chemistry.
Ultimately, selecting a vacuum furnace process is a decision to prioritize material integrity, cleanliness, and precision above all else.

Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening, Annealing, Tempering | Modifying mechanical properties | Clean surface finish, no oxidation, repeatable results |
| Vacuum Brazing | Joining components | Strong, flux-free bonds, no contamination |
| Vacuum Sintering | Powder metallurgy, MIM | Dense, pure parts, prevents powder oxidation |
| Chemical Heat Treatments (e.g., Carburizing, Nitriding) | Surface hardening | Precise control over case depth and hardness |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is enhanced by deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Achieve unparalleled material purity and precision—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















