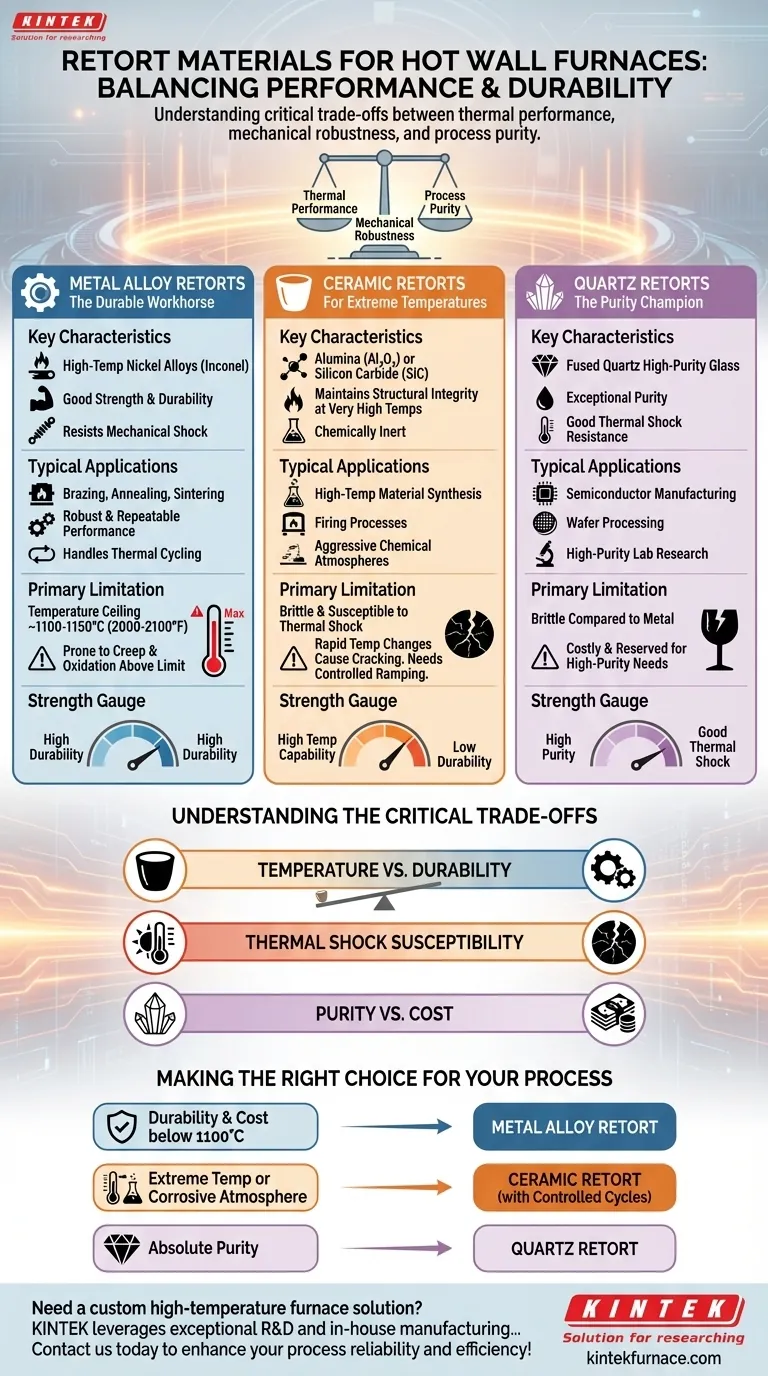
In a hot wall furnace, the retort can be constructed from three primary classes of materials: high-temperature metal alloys, ceramics, and quartz. Each material is chosen based on the specific demands of the thermal process, including maximum temperature, required chemical purity, and the need for mechanical durability.
The selection of a retort material is not about finding the single "best" option, but about understanding the critical trade-offs between thermal performance, mechanical robustness, and process purity for your specific application.
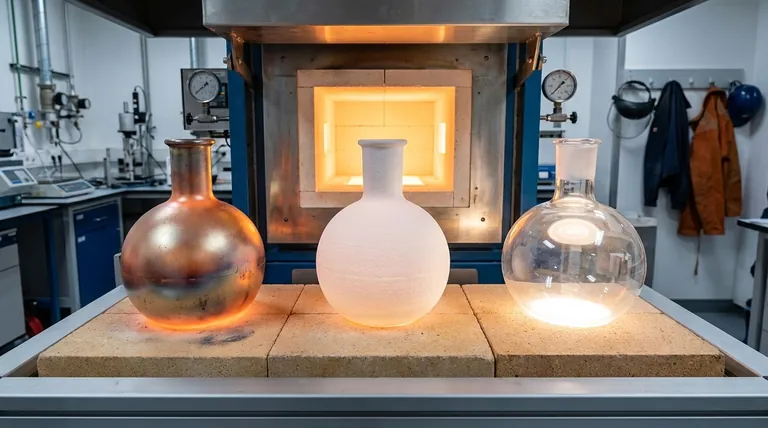

Metal Alloy Retorts: The Durable Workhorse
Metal retorts are the most common choice for a wide range of industrial heat-treating applications due to their excellent balance of properties.
Key Characteristics
High-temperature nickel-based alloys, such as Inconel, are frequently used. These materials offer good strength at elevated temperatures and, most importantly, high resistance to mechanical shock and vibration.
Typical Applications
Metal retorts excel in processes like brazing, annealing, and sintering where robust, repeatable performance is critical. They handle thermal cycling well and are less prone to catastrophic failure than brittle materials.
Primary Limitation
The main drawback of metal alloys is their temperature ceiling, typically around 1100-1150°C (2000-2100°F). Above this, they can suffer from creep, distortion, or rapid oxidation, significantly reducing their service life.
Ceramic Retorts: For Extreme Temperatures
When a process temperature exceeds the limits of metal alloys, ceramics become the necessary choice.
Key Characteristics
Materials like alumina (Al₂O₃) or silicon carbide (SiC) maintain their structural integrity at very high temperatures. They are also highly resistant to chemical attack and provide a chemically inert environment.
Typical Applications
Ceramic retorts are used in high-temperature material synthesis, firing processes, and applications involving aggressive chemical atmospheres that would corrode metal alloys.
Primary Limitation
Ceramics are brittle and highly susceptible to thermal shock. Rapid heating or cooling can cause them to crack, leading to process failure. They demand carefully controlled temperature ramp rates.
Quartz Retorts: The Purity Champion
For applications where even trace amounts of contamination are unacceptable, quartz is the material of choice.
Key Characteristics
Fused quartz is a form of high-purity glass with exceptional purity and good thermal shock resistance for a non-metallic material. It is a staple in industries where contamination control is paramount.
Typical Applications
Quartz is used almost exclusively in semiconductor manufacturing, wafer processing, and high-purity laboratory research. Its purity ensures that no contaminants from the retort leach into the product.
Primary Limitation
While superior to many ceramics in thermal shock resistance, quartz is still a brittle material compared to metal alloys. It can be a costly option and is generally reserved for applications where its purity is an absolute requirement.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing the right material requires balancing competing priorities. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is the most common source of failure.
Temperature vs. Durability
The fundamental trade-off is between the high-temperature capability of ceramics and the mechanical durability of metals. Pushing a metal retort beyond its temperature limit leads to failure, while heating a ceramic retort too quickly leads to fracture.
Thermal Shock Susceptibility
This is the single most important operational constraint for ceramic and quartz retorts. Rapid temperature changes create internal stresses that can shatter the material. A process designed for a metal retort cannot be run in a ceramic retort without adjusting the heating and cooling profiles.
Purity vs. Cost
High-purity ceramic and quartz retorts are significantly more expensive than their metal alloy counterparts. This cost is justified only when the process demands an extremely clean environment, as in semiconductor fabrication. For general heat treating, a metal alloy is far more cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your process requirements will dictate the correct material. Consider the primary goal of your application to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is durability and cost-effectiveness for general heat treating below 1100°C: A high-temperature metal alloy retort is the most practical and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is operating at extreme temperatures or in corrosive atmospheres: A ceramic retort is necessary, but you must implement slow, controlled heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is absolute process purity to prevent any contamination: A quartz retort is the industry standard and the only suitable option.
Ultimately, selecting the correct retort material is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts process reliability and success.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications | Primary Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Alloys | High strength, good thermal shock resistance, durable | Brazing, annealing, sintering | Temperature limit ~1100-1150°C, prone to oxidation |
| Ceramics | High-temperature capability, chemically inert | High-temperature synthesis, corrosive atmospheres | Brittle, susceptible to thermal shock |
| Quartz | High purity, good thermal shock resistance | Semiconductor manufacturing, lab research | Brittle, costly |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process reliability and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















