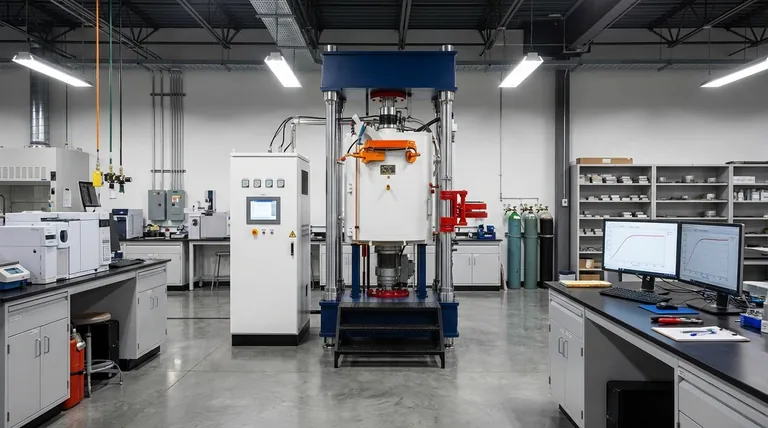
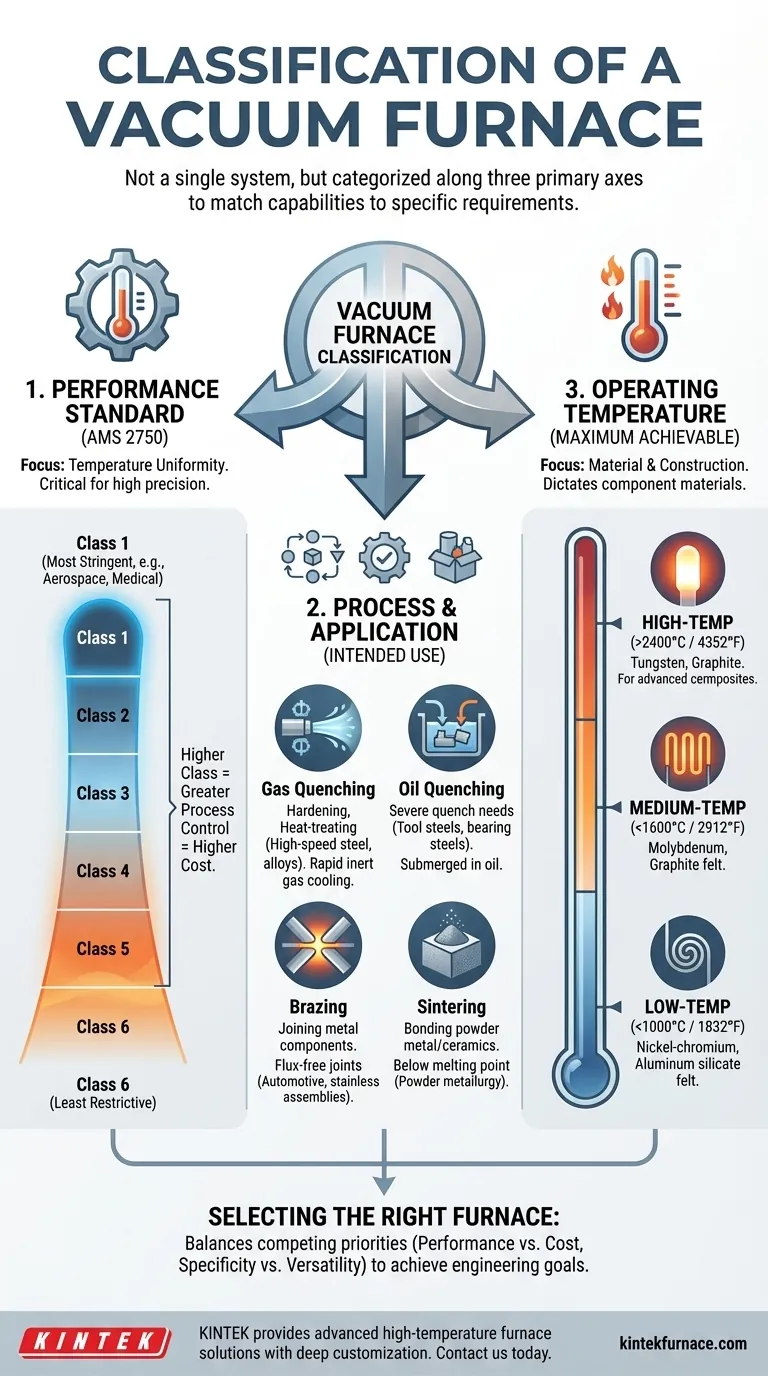
The classification of a vacuum furnace is not based on a single system. Instead, furnaces are categorized along three primary axes: by their performance standards (temperature uniformity), their specific industrial application (the process they perform), and their maximum operating temperature. Each classification system provides a different lens for evaluating a furnace's capabilities and suitability for a given task.
Understanding how vacuum furnaces are classified is less about memorizing categories and more about matching the furnace’s capabilities to your specific material, process, and quality requirements. The right furnace is the one whose specifications directly address your engineering goal.

Classification by Performance Standard
The most formal classification system is based on temperature uniformity, which measures how consistent the temperature is throughout the furnace's working zone. This is critical for processes requiring high precision and repeatability, especially in the aerospace and medical industries.
The AMS 2750 Standard
This standard defines six classes of furnaces, from Class 1 to Class 6.
- Class 1 represents the most stringent requirement, with the smallest allowable temperature deviation.
- Class 6 is the least restrictive, allowing for the widest range in temperature uniformity.
Choosing a class is a direct function of the required part quality and industry specifications. A higher-class furnace provides greater process control but comes at a higher cost.
Classification by Process and Application
A more practical way to classify vacuum furnaces is by their intended use. Different industrial processes require unique features, such as specific quenching methods or chamber designs.
Gas Quenching Furnaces
These are versatile furnaces used for hardening and heat-treating a wide range of materials. They use high-pressure, high-flow-rate inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) to cool parts rapidly.
They are ideal for materials like high-speed steel, tool and die steel, high-temperature alloys, and titanium alloys.
Oil Quenching Furnaces
These furnaces are designed for materials that require a more severe quench than gas can provide. Parts are heated in a vacuum chamber and then moved to a separate, sealed chamber to be submerged in oil.
This method is suitable for certain tool steels, bearing steels, and spring steels that demand specific hardening characteristics.
Brazing Furnaces
Brazing furnaces are built specifically for joining metal components using a filler metal. The vacuum environment prevents oxidation, resulting in a clean, strong, and flux-free joint.
Applications include manufacturing automotive parts (radiators, evaporators), stainless steel assemblies, and high-temperature alloy components.
Sintering Furnaces
Vacuum sintering furnaces are used to heat compacted metal or ceramic powders to a temperature below their melting point. This process bonds the particles together to create a solid, dense object. This is a key technology in powder metallurgy.
Classification by Operating Temperature
The most fundamental classification is based on the furnace's maximum achievable temperature. This factor dictates the types of materials that can be processed and determines the furnace's internal construction.
The Link Between Temperature and Construction
A furnace's temperature rating directly impacts the selection of its core components.
- Heating Elements: Low-temperature furnaces might use nickel-chromium wire, while high-temperature models require materials like molybdenum, graphite, or tungsten.
- Insulation: Insulation must withstand the operating temperature, ranging from aluminum silicate felt at lower temperatures to graphite felt in high-temperature environments.
Temperature Ranges
Furnaces are generally grouped into three tiers:
- Low-Temperature: Up to approximately 1000°C (1832°F)
- Medium-Temperature: Up to approximately 1600°C (2912°F)
- High-Temperature: Can exceed 2400°C (4352°F) for advanced materials like ceramics and composites.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a vacuum furnace involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" furnace, only the most appropriate one for your specific needs.
Performance vs. Cost
A furnace with higher temperature capabilities and tighter temperature uniformity (a lower Class number) is a more complex and expensive piece of equipment. You must justify the investment with a clear process requirement.
Process Specificity vs. Versatility
A dedicated vacuum brazing furnace is optimized for one task, while a general-purpose high-pressure gas quench furnace can handle a wider variety of heat-treating cycles. The choice depends on whether your workload is repetitive or varied.
Quenching Method: Gas vs. Oil
High-pressure gas quenching is the modern standard, offering clean parts and precise control over cooling rates. However, oil quenching is still necessary for some legacy material specifications or alloys that require its unique cooling profile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct type of vacuum furnace, start by defining your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is meeting strict quality certifications (e.g., aerospace): You must prioritize the furnace's Performance Class and ensure its temperature uniformity meets the required standard.
- If your primary focus is a specific manufacturing process (e.g., joining parts): You should select a furnace based on its Application type, such as a vacuum brazing or sintering furnace.
- If your primary focus is processing a specific material (e.g., titanium alloys): Your first consideration should be the Operating Temperature range to ensure the furnace can reach the temperatures your material requires.
Ultimately, these classification systems work together to create a complete technical profile of the furnace's capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Classification Axis | Key Categories | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Performance Standard (AMS 2750) | Class 1 (Most Precise) to Class 6 | Aerospace, medical, and high-precision industries requiring strict temperature uniformity. |
| Process & Application | Gas Quenching, Oil Quenching, Brazing, Sintering | Hardening tool steels, brazing assemblies, sintering metal powders, and other specific industrial processes. |
| Operating Temperature | Low-Temp (<1000°C), Medium-Temp (<1600°C), High-Temp (>2400°C) | Processing specific materials like high-speed steels, titanium alloys, or advanced ceramics and composites. |
Struggling to Match a Vacuum Furnace to Your Unique Requirements?
Classifying a furnace is the first step; finding the one that perfectly aligns with your materials, process, and quality standards is the real challenge. KINTEK eliminates the guesswork.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line—including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental and production requirements.
Whether you need a high-uniformity furnace for aerospace certification, a specialized system for brazing, or a high-temperature furnace for advanced materials, we can build the solution you need.
Contact us today to discuss your specific goals and let our experts guide you to the ideal vacuum furnace solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















