The primary advantage of graphite's high melting point is its ability to operate reliably at extreme temperatures where most other materials would fail. This allows graphite heating elements to achieve and maintain temperatures well over 2000°C (3632°F) without degrading, melting, or losing structural integrity, making them indispensable for advanced industrial furnaces.
The core insight is that graphite's value isn't just its high melting point, but a unique combination of properties that emerge at extreme temperatures. Unlike metals that weaken, graphite gets stronger as it heats up, providing unmatched structural stability for the most demanding thermal processes.
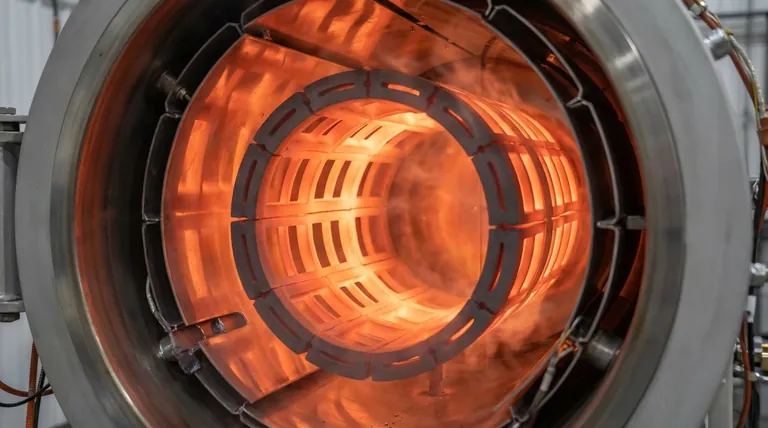
Why a High Melting Point is Mission-Critical
The choice of a heating element material dictates the absolute performance ceiling of a furnace. For high-temperature applications, graphite's properties place it in a class of its own.
Defining the Temperature Ceiling
A material's melting point is its ultimate operational limit. Graphite's is exceptionally high, around 3650°C (6602°F), far exceeding that of refractory metals like molybdenum (~2623°C) or even tungsten (~3422°C).
This thermal resilience allows graphite elements to create process environments hot enough for sintering advanced ceramics, growing synthetic crystals, and performing specialized metal heat treatments.
The Reality: Sublimation, Not Melting
At atmospheric pressure, graphite does not melt into a liquid. Instead, it sublimates, turning directly from a solid into a gas.
This process is extremely slow even at very high operating temperatures, ensuring the heating element has a long, predictable service life with minimal material loss. This stability is critical for maintaining vacuum purity and process repeatability.
Unique Structural Integrity Under Extreme Heat
This is graphite's most remarkable advantage. Most materials, especially metals, soften and lose their tensile strength as they approach their melting point, causing them to sag, stretch, and fail.
Graphite behaves in the opposite way. Its mechanical strength actually increases with temperature, peaking at around 2500°C. This means a graphite element becomes more rigid and robust precisely when it is under the most thermal stress, preventing deformation and ensuring furnace reliability.
The Practical Impact in High-Temperature Furnaces
Graphite's thermal properties translate directly into superior performance and design flexibility for vacuum and inert-atmosphere furnaces.
Enabling Advanced Manufacturing
Processes like producing silicon carbide (SiC) or annealing high-performance alloys require temperatures and environments that would instantly destroy conventional heating elements. Graphite's stability makes these modern industrial processes possible.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Graphite has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. It expands and contracts very little when heated and cooled.
This allows it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or shattering—a common failure mode for ceramic heating elements. This durability permits faster furnace cycle times, increasing throughput.
Design and Machining Flexibility
Graphite is easily machined into complex shapes, such as large cylinders, intricate rods, or flat panels.
Because it remains strong and stable at temperature, engineers can design large, self-supporting heating elements that provide excellent temperature uniformity across the furnace's hot zone, which is critical for process quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite's Achilles' Heel
While its high-temperature performance is unmatched, graphite has one significant limitation that dictates where and how it can be used.
The Critical Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Graphite's primary weakness is its reaction with oxygen. In the presence of air, graphite begins to oxidize (burn) at temperatures as low as 500°C.
This reaction rapidly consumes the element, leading to catastrophic failure. For this reason, graphite heating elements are never used in furnaces that operate in an air atmosphere.
Why Vacuum or Inert Gas is Non-Negotiable
To prevent oxidation, graphite elements must be operated in a vacuum or in a furnace backfilled with a non-reactive, inert gas like argon or nitrogen.
This protective atmosphere is the fundamental operating requirement for any graphite-heated system. The integrity of the vacuum or gas system is just as important as the element itself.
Potential for Process Contamination
As a carbon source, graphite can sometimes react with the materials being processed in the furnace, a phenomenon known as carburization. Engineers must account for this potential interaction when processing certain metals or ceramics to avoid altering the workpiece's chemical composition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element requires balancing your process requirements against the material's inherent properties.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature operation (>2000°C) in a controlled atmosphere: Graphite is often the only viable choice due to its unmatched thermal stability and strength at temperature.
- If your primary focus is operating in an air atmosphere: You must use a metallic alloy element (like Kanthal) for lower temperatures or a protected element (like silicon carbide) for higher temperatures, as graphite will rapidly oxidize and fail.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating/cooling cycles and thermal shock: Graphite's low thermal expansion makes it a superior choice over many brittle ceramics or metals that can fatigue under thermal stress.
Understanding graphite's unique thermal properties empowers you to specify heating systems that are not just functional, but fundamentally reliable at the extremes of material science.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Practical Impact |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Operation (>2000°C) | Enables processes like sintering advanced ceramics and crystal growth. |
| Increased Strength at High Temperatures | Prevents sagging and deformation, ensuring furnace reliability. |
| Superior Thermal Shock Resistance | Allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking. |
| Critical Limitation | Requires a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere to prevent oxidation. |
Need a heating solution for extreme temperatures?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements like yours.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our robust graphite heating elements can bring reliability and performance to your most demanding thermal processes.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency



















