In a blast furnace, sinter is used as the primary iron-bearing raw material fed into the furnace to produce molten iron. It is not a raw mineral but a manufactured aggregate, created by heating a mixture of fine iron ore, coke breeze, limestone, and other recycled materials until they fuse together into a porous, clinker-like product. This process transforms otherwise unusable fine particles into an ideal feed for the furnace.
The core purpose of sinter is to convert fine, low-value iron ore particles and industrial waste into a uniform, strong, and permeable mass. This engineered material is essential for making the blast furnace operation more efficient, stable, and cost-effective.

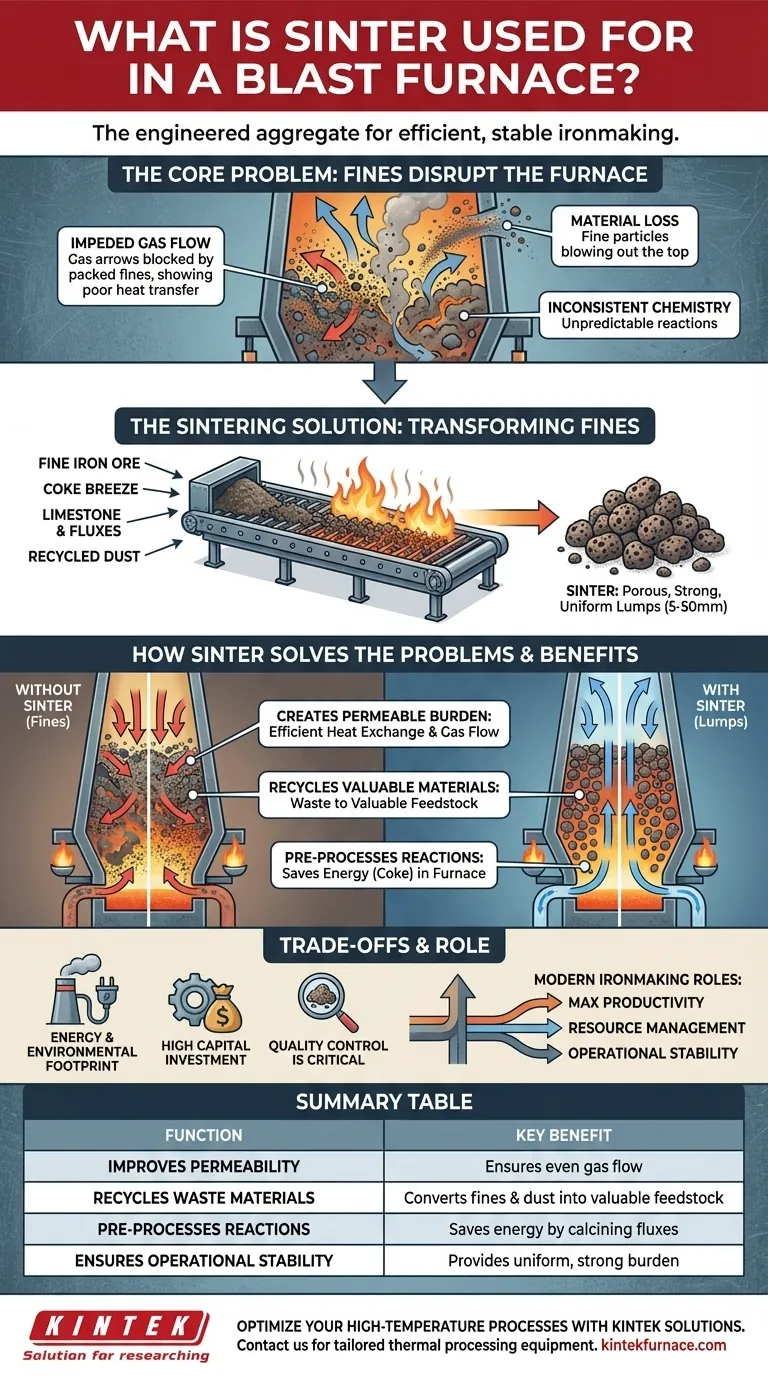
The Core Problem: Why Fines Disrupt the Blast Furnace
To understand why sinter is so critical, you must first understand the problems caused by feeding fine, unprocessed materials directly into a blast furnace. The furnace is a massive vertical reactor that relies on hot gas flowing up from the bottom to heat and chemically reduce materials moving down from the top.
Impeded Gas Flow
A blast furnace requires good permeability—the ability for gas to pass through the solid material, or "burden." A column of fine particles acts like tightly packed sand, blocking gas flow and forcing it through narrow, inefficient channels. This leads to poor heat transfer and incomplete chemical reactions.
Material Loss
The powerful upward blast of hot air can easily blow fine particles straight out of the top of the furnace. This not only results in the loss of valuable iron-bearing material but also creates significant dust and environmental management issues.
Inconsistent Chemistry
Fine materials have a vast surface area and can react unpredictably. This, combined with poor gas distribution, leads to an unstable and inefficient process, making it difficult to control the quality of the final molten iron.
How Sinter Solves These Problems
The sintering process is an elegant engineering solution designed specifically to overcome the challenges of using fine particles.
Creating a Permeable Burden
Sinter consists of large, relatively uniform lumps (typically 5-50mm). When charged into the furnace, these lumps create ample space for hot gases to flow evenly throughout the entire burden. This ensures efficient heat exchange and uniform chemical reduction from top to bottom.
Recycling Valuable Materials
Sintering is fundamentally a resource consolidation process. It allows steel plants to take various fine-grained materials that would otherwise be waste—such as iron ore fines from mining, dust collected from pollution control systems, and fine coke particles (coke breeze)—and convert them into a high-quality, valuable feedstock.
Pre-processing for Efficiency
During sintering, some essential chemical reactions are completed before the material ever enters the blast furnace. For instance, the limestone and dolomite in the sinter mix (known as fluxes) are pre-calcined. This "off-loading" of work from the blast furnace saves a significant amount of energy (coke) and increases its overall productivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While sinter is the dominant burden material globally, it is not without its own set of considerations.
Energy and Environmental Footprint
The sintering process itself requires significant energy to heat the material mix. Sinter plants are also a source of emissions, including dust, SOx, and NOx, which require complex and expensive gas cleaning systems to manage.
High Capital Investment
A sinter plant is a massive and complex piece of industrial equipment. Building and maintaining one represents a major capital investment for any integrated steel mill.
Quality Control is Critical
The benefits of sinter are entirely dependent on its quality. Poor-quality sinter that is weak or breaks down easily inside the blast furnace negates its purpose. It will simply generate fines within the furnace, re-creating the very permeability problems it was designed to solve.
The Role of Sinter in Modern Ironmaking
Choosing the right raw materials is a strategic decision based on operational goals and available resources.
- If your primary focus is maximum productivity and fuel efficiency: Using a high percentage of quality-controlled sinter in the furnace burden is the global industry standard for achieving the lowest fuel rates and highest output.
- If your primary focus is resource management and cost reduction: Sintering provides an essential pathway to recycle internal plant wastes and utilize lower-cost iron ore fines, turning them into a prime furnace feed.
- If your primary focus is operational stability: A consistent, well-sized sinter ensures predictable gas flow and stable chemical reactions, which are fundamental to the smooth and safe operation of a blast furnace.
Ultimately, sinter transforms a collection of problematic fine materials into a highly engineered product that is the cornerstone of efficient and stable blast furnace performance.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Improves Permeability | Ensures even gas flow for efficient heat transfer and chemical reactions. |
| Recycles Waste Materials | Converts iron ore fines and plant dust into valuable feedstock. |
| Pre-processes Reactions | Saves energy by calcining fluxes before the material enters the furnace. |
| Ensures Operational Stability | Provides a uniform, strong burden for predictable and safe furnace operation. |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK solutions.
Just as sinter is engineered to solve specific blast furnace challenges, your laboratory requires precisely tailored thermal processing equipment to achieve peak efficiency and stability.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you engineer the ideal solution for your application.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















