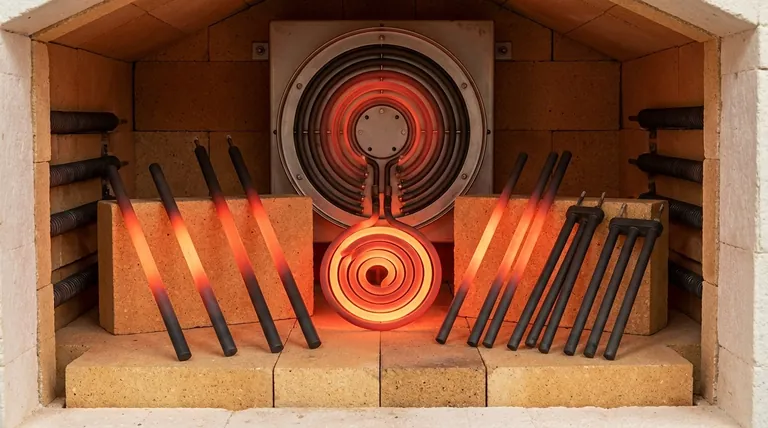
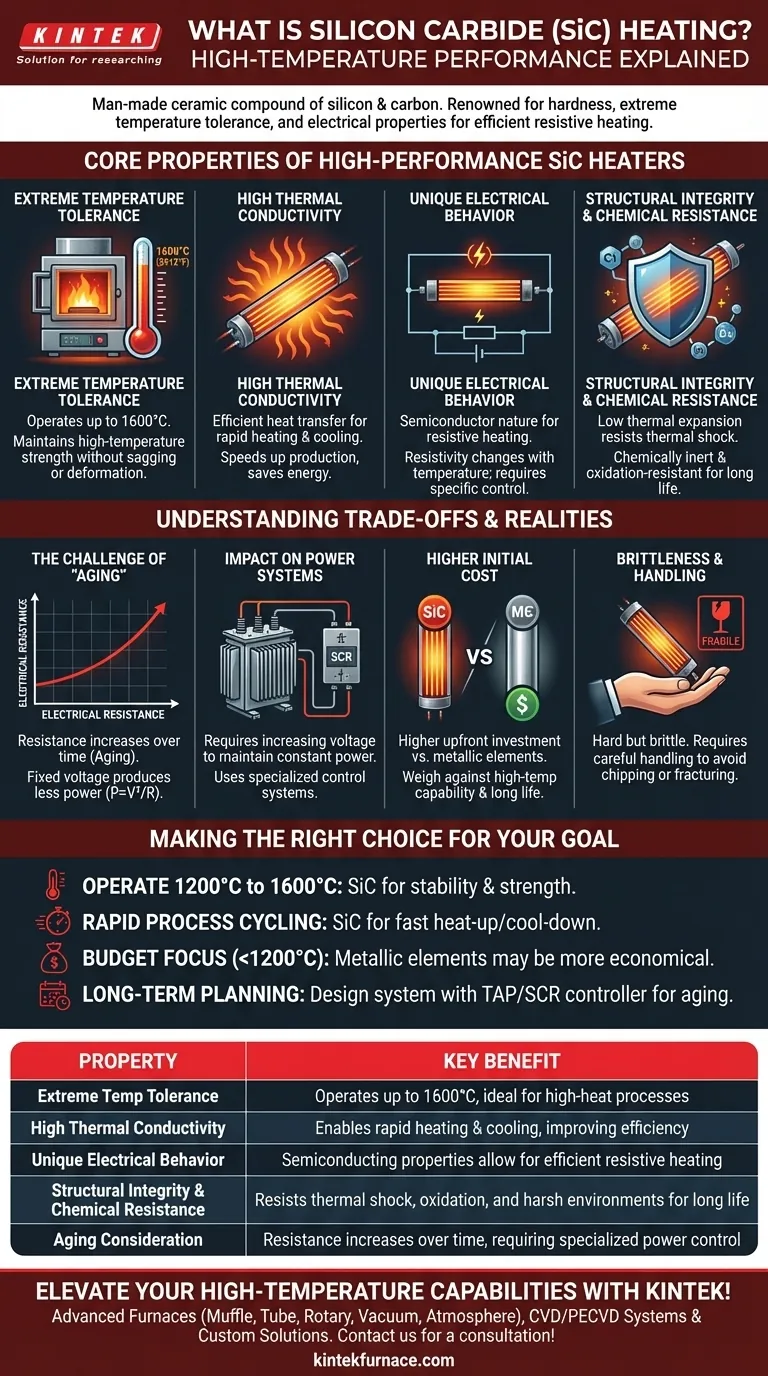
At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) is a man-made ceramic compound of silicon and carbon, renowned for its extreme hardness. It is used for electric heating elements because it uniquely combines high-temperature tolerance up to 1600°C, excellent heat transfer, and the electrical properties necessary to generate heat efficiently and reliably in demanding industrial environments.
The decision to use silicon carbide heating elements is a strategic choice for high-temperature applications. While they offer superior performance and rapid heating, their primary trade-off is a gradual increase in electrical resistance over time, which requires specialized power control systems to manage.

The Core Properties of a High-Performance Heater
To understand why SiC is a go-to material for high-temperature furnaces, we must look at its specific combination of physical properties. Each one solves a critical challenge in industrial heating.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
Silicon carbide elements can operate at furnace temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). This far exceeds the limits of most metallic heating elements, opening up processes that require intense heat.
Its high-temperature strength ensures it maintains its structural integrity without sagging or deforming under its own weight when hot.
High Thermal Conductivity
SiC transfers heat very efficiently. This property means that the energy generated within the element is quickly and uniformly radiated into the furnace chamber.
The practical benefit is rapid heating and cooling rates. This speeds up production cycles, saves energy, and allows for more precise temperature control over the material being heated.
Unique Electrical Behavior
SiC is a semiconductor, meaning it conducts electricity, but not as freely as a metal. This inherent resistance is what generates heat when a current is passed through it (resistive heating).
Its resistivity also changes with temperature. This characteristic is a critical factor in the design of the power supply and control system.
Structural Integrity and Chemical Resistance
SiC has very low thermal expansion, which means it doesn't expand or contract much when heated and cooled. This drastically reduces internal stress, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and cracking over many cycles.
Furthermore, it is chemically inert and resistant to oxidation, allowing for a long service life even in harsh or reactive furnace atmospheres.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Realities
No material is perfect. The exceptional performance of SiC comes with specific operational considerations that are critical for any user to understand.
The Challenge of "Aging"
The most significant characteristic of SiC elements is that their electrical resistance increases over time. This process is known as aging.
As the element ages and its resistance goes up, a fixed voltage will produce less and less power (and therefore less heat), according to the formula P = V²/R.
The Impact on Power Systems
To compensate for aging, the power supply must be able to deliver an increasing voltage over the element's lifespan to maintain a constant power output.
This is typically accomplished with a multi-tap transformer that allows you to switch to a higher voltage tap as the element ages, or with a sophisticated SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) power controller.
Higher Initial Cost
SiC elements and their required power control systems represent a higher upfront investment compared to standard metallic heating elements like Kanthal (FeCrAl).
This cost must be weighed against their higher temperature capabilities, longer life in demanding applications, and potential for greater energy efficiency.
Brittleness and Handling
Like other ceramics, SiC elements are hard but brittle. They must be handled with care during installation and maintenance to avoid being chipped or fractured, which would lead to immediate failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on a clear-eyed assessment of your process requirements, budget, and operational capabilities.
- If your primary focus is operating at temperatures from 1200°C to 1600°C: SiC is one of the best and most reliable choices available for its stability and strength in this range.
- If your primary focus is rapid process cycling: The high thermal conductivity of SiC allows for fast heat-up and cool-down times that can significantly improve throughput.
- If your primary focus is budget and you operate below 1200°C: Traditional metallic elements are often a more economical and simpler solution.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational planning: You must design your system with a tapped transformer or SCR controller specifically to manage the predictable aging of SiC elements.
Ultimately, choosing silicon carbide is an investment in high-temperature capability that pays dividends when managed correctly.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Tolerance | Operates up to 1600°C, ideal for high-heat processes |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Enables rapid heating and cooling, improving efficiency |
| Unique Electrical Behavior | Semiconducting properties allow for efficient resistive heating |
| Structural Integrity & Chemical Resistance | Resists thermal shock, oxidation, and harsh environments for long life |
| Aging Consideration | Resistance increases over time, requiring specialized power control |
Elevate your laboratory's high-temperature capabilities with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Ready to optimize your heating processes? Contact us today for a tailored consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















