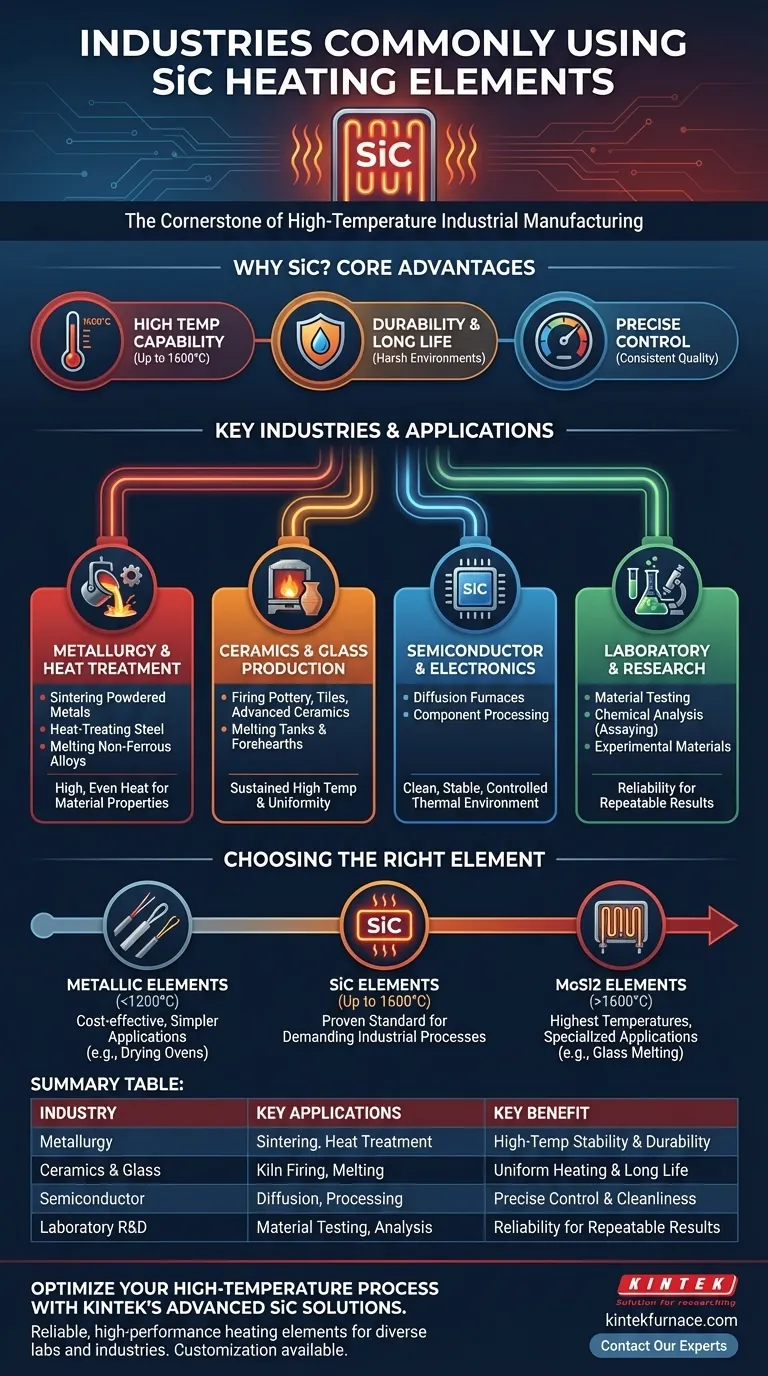
In short, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are a cornerstone of high-temperature industrial manufacturing. They are most commonly used in metallurgy, ceramics, glass production, semiconductor fabrication, and laboratory research settings where consistent, high-heat performance in harsh environments is critical.
The core reason SiC elements are so widely adopted is their unique combination of high-temperature capability, long service life, and resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack. This makes them the default choice for processes that demand extreme reliability and precision.
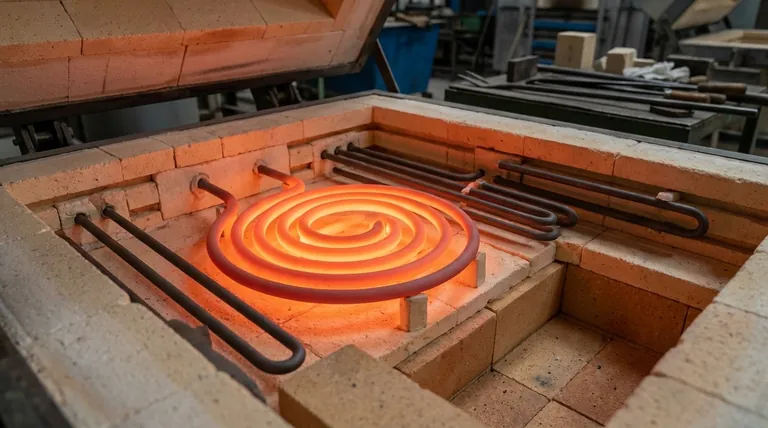

Why SiC is a Standard for High-Temperature Processes
The selection of a heating element is driven by the demands of the process. SiC elements have become an industry standard because they solve the core challenges of operating furnaces and kilns at extreme temperatures over long periods.
Exceptional Temperature Capability
SiC elements operate reliably at very high temperatures, often up to 1600°C (2912°F). This capability is essential for energy-intensive processes like melting, sintering, and forging metals and ceramics.
Durability in Harsh Environments
Industrial furnaces often contain reactive chemical atmospheres. SiC is highly resistant to oxidation and chemical wear, ensuring it performs consistently without rapid degradation, unlike some metallic elements.
Long Service Life and Reliability
The robust nature of SiC translates directly to a longer operational lifespan. For industries running 24/7, this means less frequent replacement, reduced maintenance downtime, and a lower total cost of ownership.
Precise Temperature Control
Manufacturing advanced materials like semiconductors or technical ceramics requires exacting temperature uniformity and control. SiC elements enable the precise thermal management needed to achieve consistent product quality.
Key Industrial Applications and Processes
The properties of SiC make it indispensable for specific, high-value manufacturing and research activities across several key industries.
Metallurgy and Heat Treatment
In metallurgy, SiC elements are used for processes like sintering powdered metals, heat-treating steel components, and melting non-ferrous alloys. Their ability to deliver high, even heat is crucial for achieving desired material properties.
Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing
Firing kilns for pottery, tiles, and advanced ceramics relies on SiC elements. In glass production, they are used in melting tanks and forehearths, providing the sustained high temperatures needed to create and shape molten glass.
Semiconductor and Electronics Production
The manufacturing of semiconductors and other electronic components involves diffusion furnaces and other heat-processing steps. SiC provides the clean, stable, and controlled thermal environment required for these delicate operations.
Laboratory and Research Settings
Research and development labs use SiC elements in furnaces for material testing, chemical analysis (assaying), and creating experimental materials. Their reliability makes them ideal for repeatable scientific work.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SiC is not the only option for high-temperature heating. Understanding its context helps clarify its ideal use case.
Comparison with MoSi2 Elements
For applications requiring even higher temperatures (above 1600°C), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are often used. MoSi2 can reach temperatures over 1800°C but can be more sensitive to specific furnace atmospheres.
Limitations and Considerations
SiC elements are a ceramic material and can be brittle, requiring careful handling and installation. Their electrical resistance also increases gradually with age, which must be managed by a capable power control system to maintain consistent output.
When Other Elements Are a Better Fit
For lower-temperature industrial processes (e.g., below 1200°C), simpler and more cost-effective metallic heating elements, such as wire, tubular, or band heaters, are often the more practical choice for applications like drying ovens or plastics production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct element requires matching its capabilities to your specific operational needs and temperature targets.
- If your primary focus is reliable high-temperature stability (up to 1600°C) for demanding industrial processes: SiC elements are the proven, go-to standard for applications like metal treatment and ceramic firing.
- If your primary focus is reaching the absolute highest temperatures (above 1600°C) for specialized applications: You should evaluate Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements, which excel in glass melting and advanced materials research.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heating for lower-temperature applications (below 1200°C): Simpler metallic heating elements are typically the most efficient and economical solution.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct properties of each heating element type is the key to optimizing the performance, reliability, and efficiency of your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Key Benefit of SiC |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Sintering, heat treatment, alloy melting | High-temperature stability & durability |
| Ceramics & Glass | Kiln firing, glass melting tanks | Uniform heating & long service life |
| Semiconductor | Diffusion furnaces, component processing | Precise control & clean environment |
| Laboratory R&D | Material testing, chemical analysis | Reliability for repeatable results |
Optimize your high-temperature process with KINTEK's advanced SiC heating solutions.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and industries with reliable, high-performance heating elements. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique thermal requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our SiC solutions can enhance your efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















