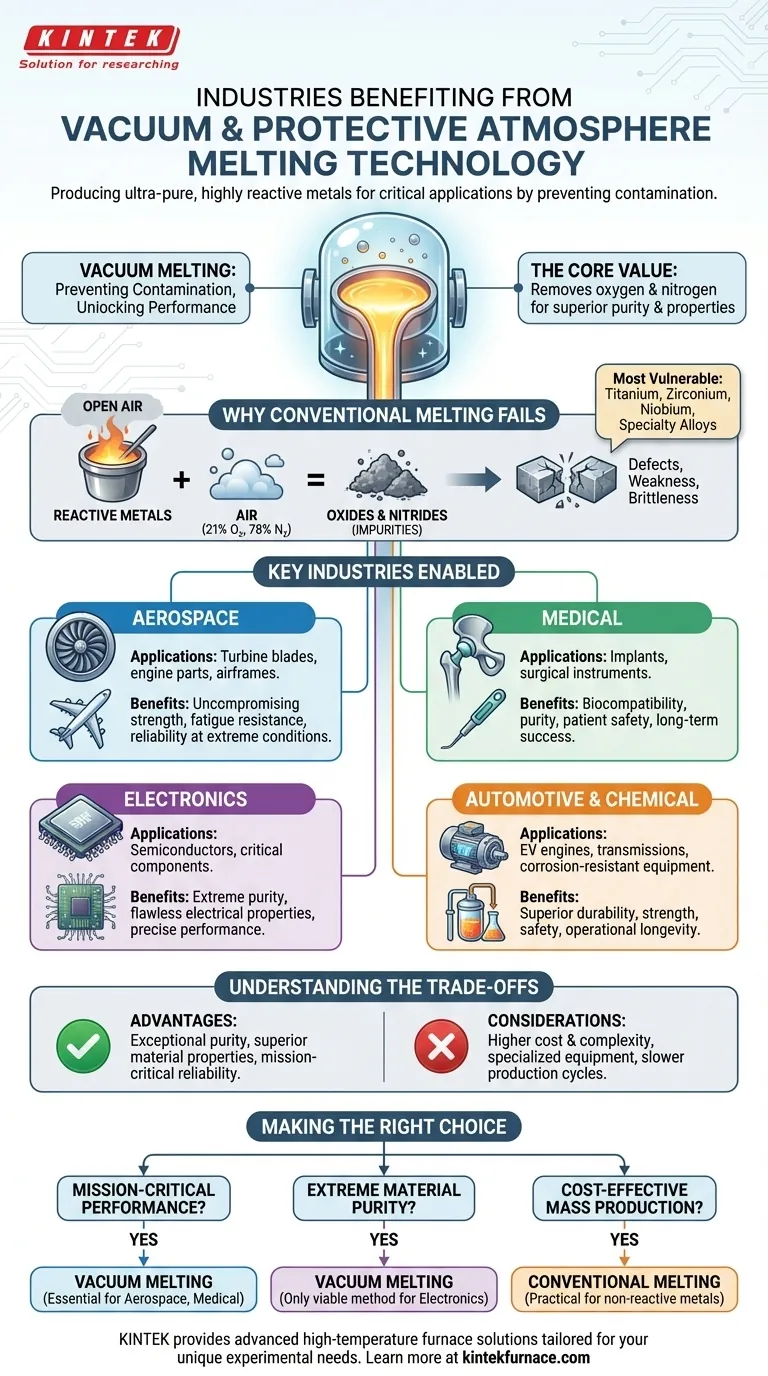
In short, any industry that relies on ultra-pure or highly reactive metals benefits from vacuum or protective atmosphere melting. This includes critical sectors like aerospace, medical, electronics, automotive, and chemical manufacturing. The technology is essential for producing high-purity metals, reactive metals like titanium, special alloys, and components where material failure is not an option, such as turbine blades and biomedical implants.
The core value of this technology is not just melting metal; it's about preventing contamination. By removing air, vacuum furnaces stop molten metal from reacting with oxygen and nitrogen, which preserves the material's purity and unlocks the superior properties required for high-performance applications.

The Core Problem: Why Conventional Melting Fails
When certain metals are heated to their melting point, they become highly reactive. Melting them in the open air, a process filled with reactive gases, fundamentally compromises their quality.
The Threat of Atmospheric Contamination
Standard air is about 21% oxygen and 78% nitrogen. At high temperatures, these gases readily react with molten metal to form impurities like oxides and nitrides.
These unwanted chemical reactions change the very nature of the final material, often introducing brittleness, weakness, or other defects.
Which Metals Are Most Vulnerable?
Reactive metals are the primary beneficiaries of vacuum melting. This group includes titanium, zirconium, and niobium, which have a strong affinity for oxygen.
Many specialty alloys and oxygen-sensitive metals also require a controlled atmosphere to achieve their designed properties without being compromised by contamination.
How Vacuum Melting Enables Key Industries
By eliminating atmospheric contamination, this technology allows manufacturers to produce materials with exceptional purity, strength, and reliability. This is not a luxury but a necessity for many advanced sectors.
Aerospace: For Uncompromising Strength
In aerospace, components like turbine blades, engine parts, and airframes are subjected to extreme stress and temperatures. Even microscopic impurities can lead to catastrophic failure.
Vacuum melting produces the high-performance, fatigue-resistant alloys required for an aircraft to operate safely and reliably under these demanding conditions.
Medical: For Biocompatibility and Purity
For materials that go inside the human body, such as surgical instruments and medical implants, purity is non-negotiable. Contaminants can cause adverse biological reactions or implant rejection.
This technology creates the ultra-pure, biocompatible metals (like titanium) needed to ensure patient safety and the long-term success of the device.
Electronics: For Flawless Performance
The electronics industry depends on materials with precise electrical properties. Manufacturing semiconductors and other critical components requires metals of extreme purity.
Even trace amounts of impurities can disrupt conductivity and render a delicate electronic part useless. Vacuum melting is the only way to achieve the required purity standards.
Automotive & Chemical: For Durability and Resistance
In high-performance automotive applications, such as engines and transmissions for electric vehicles (EVs), vacuum-melted materials provide superior strength and durability.
Likewise, the chemical processing industry uses equipment made from these materials to handle corrosive substances without degrading, ensuring both safety and operational longevity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum melting is a specialized process with specific considerations. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution for every metalworking application.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive to acquire, operate, and maintain than conventional air-melting furnaces. The process requires specialized equipment and trained personnel.
Slower Production Cycles
Achieving and maintaining a vacuum adds time to the melting process. For applications where high throughput is the main priority and material purity is less critical, this can be a significant drawback.
It's a Targeted Solution
For many common metals and applications, such as casting standard steel or aluminum parts, conventional air melting is perfectly sufficient and far more economical. Vacuum melting is reserved for high-value materials where the end-use performance justifies the cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum melting hinges entirely on the requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical performance: Vacuum or protective atmosphere melting is essential for components in aerospace or medical implants where failure carries severe consequences.
- If your primary focus is extreme material purity: This technology is the only viable method for achieving the purity levels demanded by advanced electronics and semiconductors.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Conventional air melting is almost always the more practical and economical choice for materials that are not highly reactive.
Ultimately, matching the melting technology to the material's required properties is the key to engineering success.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, engine parts, airframes | High strength, fatigue resistance, reliability under extreme conditions |
| Medical | Surgical instruments, implants (e.g., titanium) | Biocompatibility, purity, patient safety, long-term success |
| Electronics | Semiconductors, critical components | Extreme purity, precise electrical properties, flawless performance |
| Automotive | EV engines, transmissions | Superior strength, durability, corrosion resistance |
| Chemical | Corrosion-resistant equipment | Safety, operational longevity, handling of corrosive substances |
Ready to enhance your material purity and performance? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum melting technology can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















