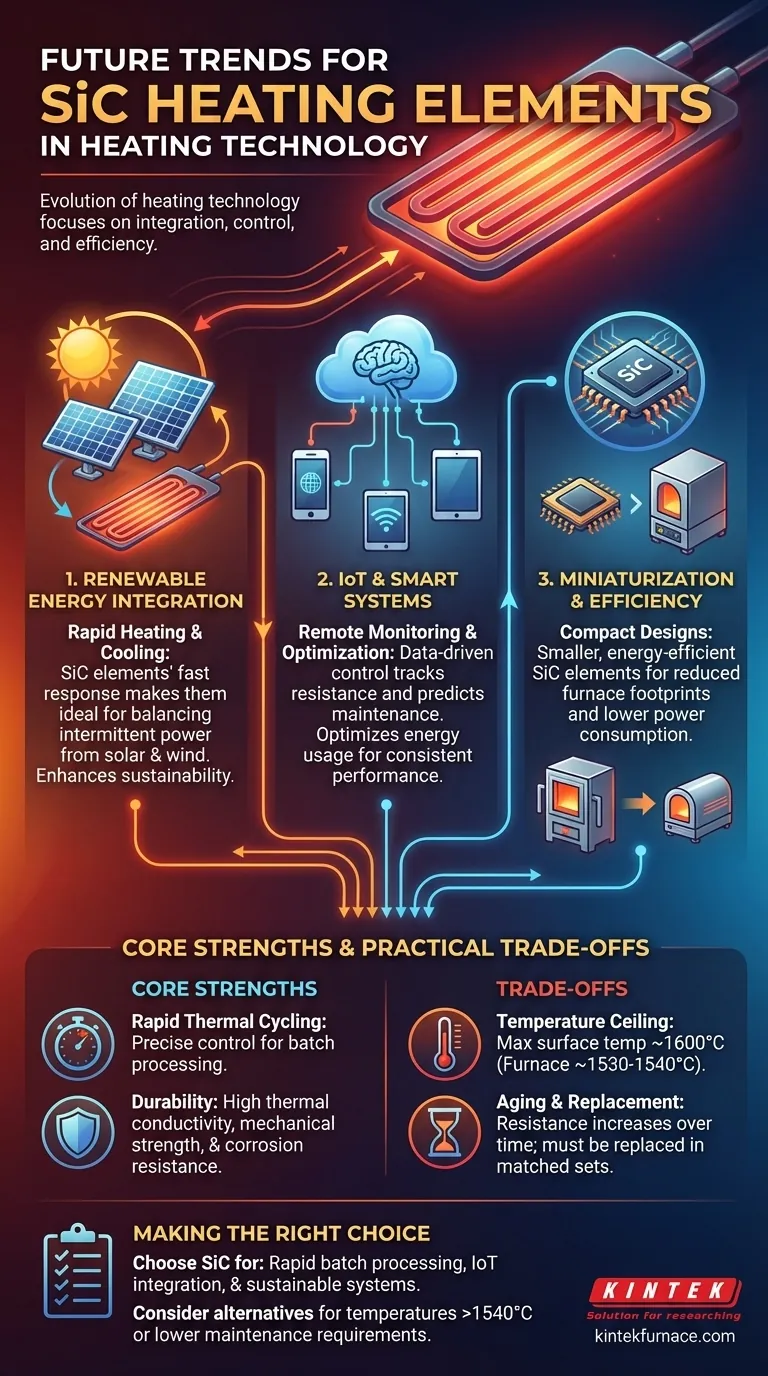
In the evolution of heating technology, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are poised for significant advancements. The key future trends focus on integrating them with renewable energy sources for sustainability, embedding them into IoT and smart home systems for superior control, and developing more compact, efficient designs to meet the demands of modern electrical systems.
The future of SiC is not simply about adding new features. It is about strategically leveraging its core strengths—rapid heating and durability—to create smarter, more sustainable systems, while navigating its inherent operational trade-offs like aging and temperature limits.

The Foundation: Why SiC Remains a Critical Technology
Silicon Carbide's role in modern heating is not accidental. Its fundamental physical properties make it uniquely suited for demanding industrial and commercial applications.
Unpacking the Core Properties
SiC elements are valued for their exceptional thermal conductivity, allowing them to transfer heat quickly and efficiently. They also possess high mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock, meaning they can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or failing.
Furthermore, their resistance to chemical corrosion makes them durable in harsh atmospheres often found in metal treatment, electronics manufacturing, and the firing of ceramics and glass.
The Advantage of Rapid Thermal Cycling
One of SiC's most significant advantages is its ability to perform fast heating and cooling cycles. This capability is essential for batch processing in industries like electronics and ceramics.
This rapid response allows for precise control over heat distribution and processing times, improving product quality and throughput.
Emerging Trends: Pushing the Boundaries of Efficiency
The future development of SiC heating elements builds directly on these core strengths, aiming to enhance control, sustainability, and overall system performance.
Trend 1: Integration with Renewable Energy
SiC's ability to heat up and cool down quickly makes it an ideal partner for intermittent renewable energy sources like solar power.
When power is available, the elements can rapidly reach temperature and utilize the energy effectively. This responsiveness helps smooth out the inconsistencies of renewable generation, contributing to more sustainable operations.
Trend 2: The Rise of IoT and Smart Systems
Incorporating SiC heaters into the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem unlocks a new level of control and optimization.
Smart systems can enable remote monitoring and adjustment, but more importantly, they can use data to optimize energy usage. This includes tracking element resistance as it ages to predict maintenance needs and adjust power delivery for consistent performance.
Trend 3: Miniaturization and System Efficiency
As electronics and industrial systems become smaller and more power-conscious, so must their components.
A key trend is the development of more compact and energy-efficient SiC element designs. This allows for smaller furnace footprints and reduced overall energy consumption without sacrificing heating performance.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
To leverage SiC effectively, it is crucial to understand its limitations. These are not flaws, but rather design considerations that define its ideal use cases.
The Temperature Ceiling
SiC elements have a maximum surface temperature of approximately 1600°C, which typically results in a maximum furnace temperature of 1530-1540°C. For applications requiring temperatures beyond this, other materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) must be considered.
The Challenge of Element Aging
Over their operational life, SiC elements experience an increase in electrical resistance. This change is a natural part of the aging process and must be accounted for in the power supply and control system design.
Maintenance and Replacement Strategy
When an SiC element fails, it cannot be replaced individually. Due to the resistance changes with age, elements must be replaced in matched pairs or as a complete set to ensure a balanced electrical load and uniform heating.
Lifespan and Cost Considerations
Compared to some alternatives, SiC elements generally have a shorter operational lifespan. However, they are often a more cost-effective choice for applications where their specific temperature range and rapid cycling capabilities are the primary requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use SiC heating elements hinges on balancing its unique advantages against its operational realities.
- If your primary focus is rapid batch processing and upfront cost-effectiveness: SiC is an excellent choice, provided your temperature requirements are below its ~1540°C operational limit.
- If your primary focus is building a sustainable or IoT-integrated system: SiC's fast response time makes it ideal for pairing with intermittent renewables and for precise, data-driven energy management.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures with minimal maintenance: You may need to explore alternatives, as SiC has a defined temperature ceiling and a shorter operational lifespan requiring periodic replacement.
Understanding these factors empowers you to select the right heating technology not just for today's needs, but for the demands of tomorrow.
Summary Table:
| Trend | Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Integration | Rapid heating/cooling | Smooths intermittent power, boosts sustainability |
| IoT and Smart Systems | Remote monitoring and data optimization | Improves energy efficiency and predictive maintenance |
| Miniaturization | Compact, efficient designs | Reduces system footprint and energy consumption |
Ready to upgrade your lab with advanced SiC heating solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and sustainability in your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















