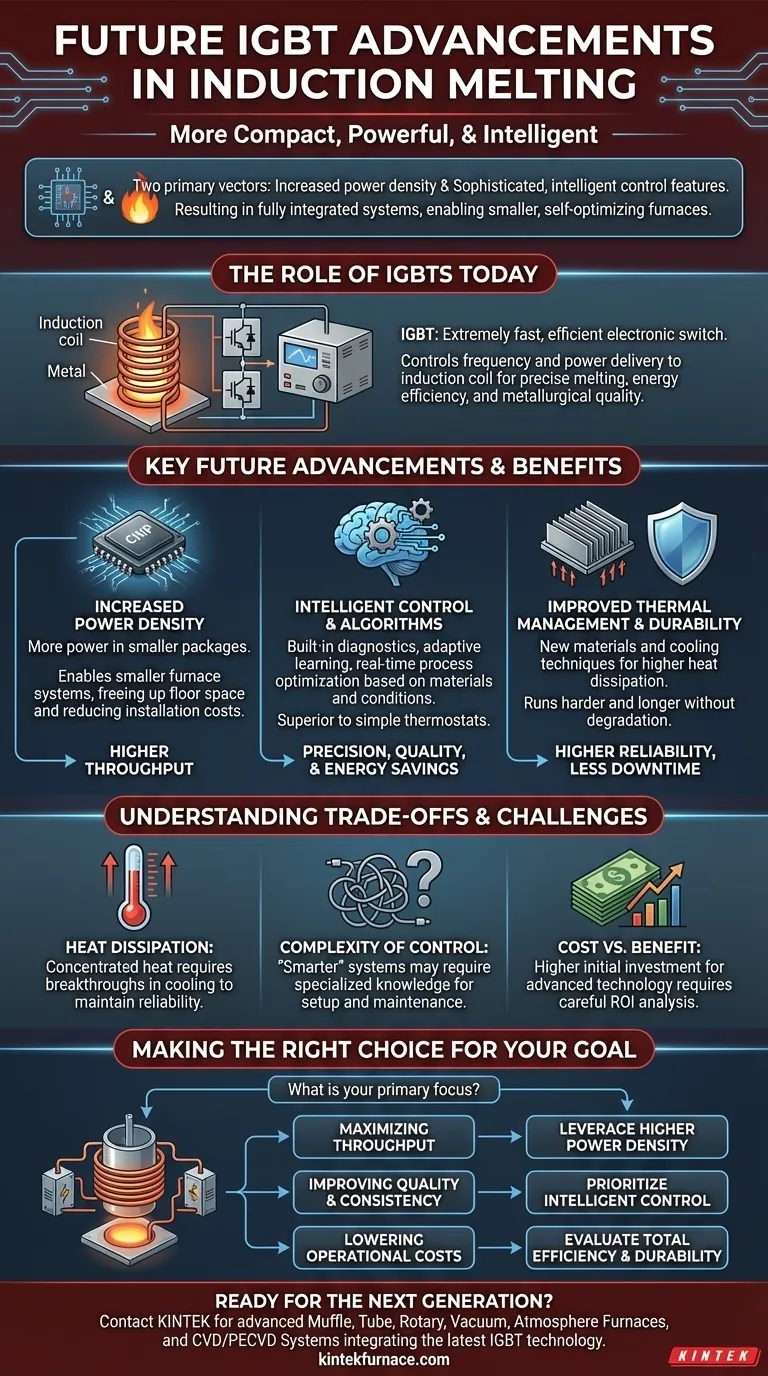
In short, the future of Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) in induction melting is defined by two primary vectors: increased power density and more sophisticated, intelligent control features. This means furnaces will become more compact and powerful, while offering unprecedented precision over the entire melting process. These advancements are not just incremental improvements; they represent a fundamental shift toward more automated and optimized industrial heating.
Future IGBT advancements are moving beyond simple component improvements. The goal is to create a fully integrated system where higher power density and intelligent control work together, enabling smaller, more efficient furnaces that can self-optimize for different materials and operating conditions.

The Role of IGBTs in Modern Induction Melting
To understand where the technology is going, we must first be clear on its current role. IGBTs are the heart of the modern induction power supply.
What is an IGBT?
An IGBT is a powerful semiconductor that acts as an extremely fast and efficient electronic switch. It combines the simple gate control of a MOSFET with the high-current and high-voltage capability of a bipolar transistor.
In an induction furnace, the IGBT's job is to switch power on and off thousands of times per second. This rapid switching action is what creates the high-frequency alternating current in the induction coil, which in turn generates the powerful magnetic field required for heating and melting metal.
Why It's Critical for Induction Melting
The precision of IGBTs is what separates modern systems from older technologies. By precisely controlling the frequency and amount of power delivered to the coil, operators gain exact control over the melting rate and final temperature. This leads directly to higher energy efficiency, faster melting times, and superior metallurgical quality.
Key Future Advancements on the Horizon
The core benefits of IGBTs are already established. The next wave of innovation will amplify these strengths, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in induction melting.
Increased Power Density
Power density refers to the amount of electrical power an IGBT module can handle relative to its physical size. The clear trend is toward packing more power into smaller packages.
This advancement allows for the design of smaller, more compact induction power supplies. For a factory or foundry, this frees up valuable floor space and can simplify the overall system layout, reducing installation costs.
Enhanced and Intelligent Control
This is arguably the most transformative area of development. Current IGBT systems offer precise control, but future systems will offer intelligent control. This includes built-in diagnostics, adaptive learning algorithms, and seamless integration with factory automation systems.
Think of it as the difference between a simple thermostat and a smart climate control system. The future IGBT controller won't just hold a setpoint; it will actively adjust power delivery in real-time based on the specific type and amount of metal in the furnace, optimizing for both speed and energy use.
Improved Thermal Management and Durability
As power density increases, so does the challenge of heat dissipation. A critical area of ongoing research is the development of new materials and cooling techniques.
These improvements will allow next-generation IGBTs to run harder and longer without degrading. For the end-user, this translates directly to higher reliability, reduced maintenance requirements, and less unplanned downtime.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While the future is promising, it is important to approach these advancements with a clear understanding of the associated engineering challenges.
The Heat Dissipation Problem
Higher power density inevitably generates more concentrated heat. The primary obstacle to unlocking even greater power in smaller modules is the ability to draw this heat away effectively. Without corresponding breakthroughs in cooling technology, the reliability benefits could be compromised.
Complexity of Control
"Smarter" control systems are, by nature, more complex. While they offer greater capability, they may also require more specialized knowledge for initial setup, calibration, and troubleshooting. The industry must balance advanced features with user-friendly interfaces.
Cost vs. Benefit Analysis
Leading-edge technology commands a premium price. The initial investment for a furnace equipped with the latest IGBTs will be higher. A decision to upgrade will require a careful return-on-investment (ROI) analysis that factors in projected gains from energy savings, increased throughput, and reduced maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
As these technologies become available, the right choice will depend on your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Look for systems that leverage higher power density, as this will be the key to achieving faster melt cycles and processing more material.
- If your primary focus is improving quality and consistency: Prioritize advancements in intelligent control features and adaptive algorithms to ensure repeatable, high-precision results for specialty alloys.
- If your primary focus is lowering long-term operational costs: Evaluate the total picture, including the energy efficiency gains from smart controls and the reduced maintenance promised by more robust, durable IGBT modules.
Ultimately, these advancements empower industries to achieve a more efficient, precise, and sustainable melting process.
Summary Table:
| Advancement | Key Benefit | Impact on Induction Melting |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Power Density | More power in a smaller package | Smaller, more compact furnace systems; higher throughput |
| Intelligent Control & Algorithms | Adaptive, real-time process optimization | Superior metallurgical quality, energy savings, and consistency |
| Improved Thermal Management | Enhanced heat dissipation and durability | Higher reliability, reduced maintenance, and less downtime |
Ready to leverage the next generation of induction melting technology?
At KINTEK, we understand that the future of efficient and precise metal processing lies in advanced power supply systems. Our commitment to exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing allows us to deliver high-temperature furnace solutions that integrate the latest in IGBT technology.
Whether you are melting specialty alloys or scaling up production, our team can help you select or customize a system that maximizes your throughput, quality, and operational savings.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our advanced Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—backed by deep customization capabilities—can meet your unique experimental and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity



















