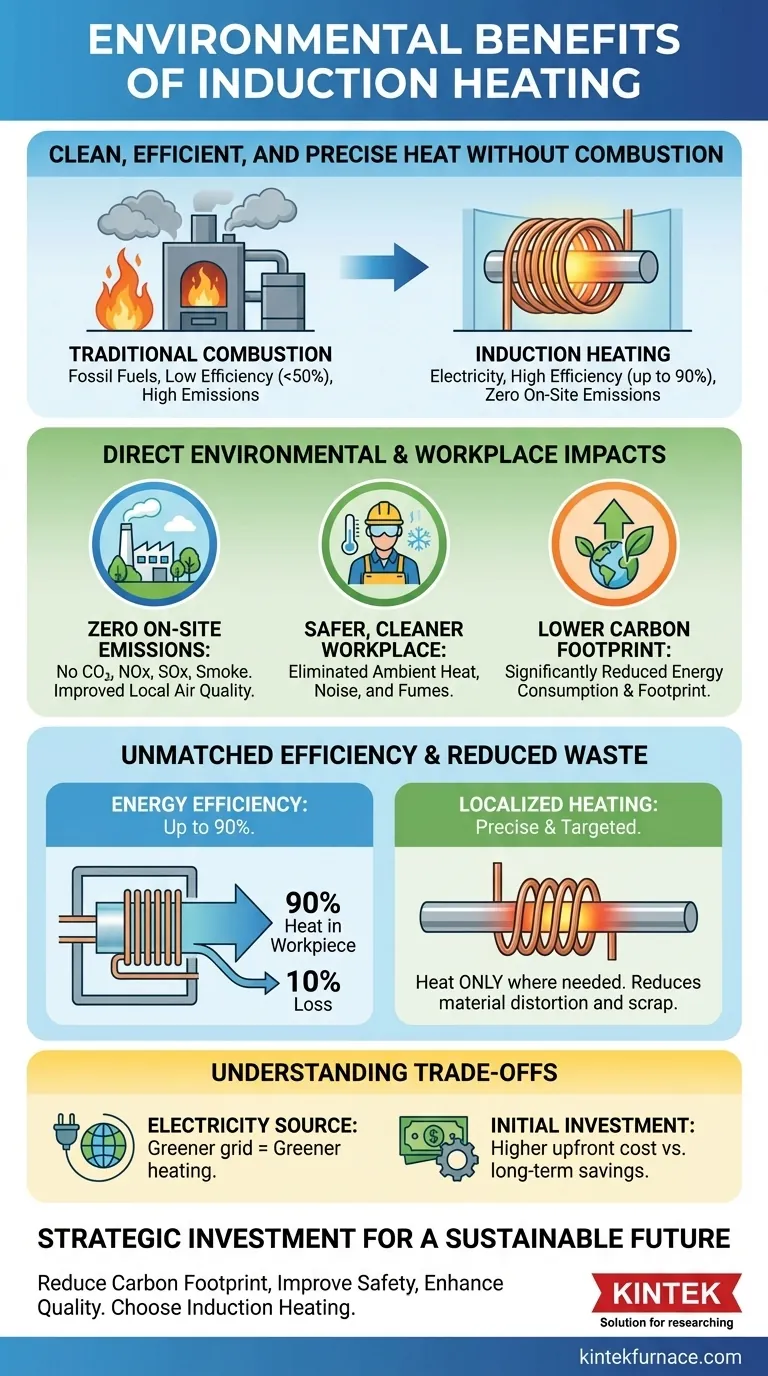
At its core, induction heating offers significant environmental benefits by fundamentally changing how energy is used in industrial processes. Unlike traditional methods that rely on burning fossil fuels, induction uses electricity to generate heat directly within a material, leading to dramatically higher energy efficiency, the complete elimination of on-site emissions, and a substantially cleaner and safer work environment.
The primary environmental advantage of induction heating stems from its shift away from combustion. By using electromagnetism instead of burning fuel, it decouples the heating process from direct pollution, offering a precise, efficient, and clean alternative for modern industry.

The Core Principle: From Combustion to Electromagnetism
To understand the environmental benefits, you must first understand the technological shift. Traditional furnaces heat an entire chamber by burning gas or other fuels, with massive energy losses to the surrounding structure and atmosphere. Induction heating works on a completely different principle.
How It Works: The Physics of Clean Heat
Induction heating operates using two key phenomena: electromagnetic induction and the Joule effect.
An alternating current flows through a copper coil, creating a rapidly changing magnetic field. When a conductive workpiece (like a piece of metal) is placed inside this field, the field induces electrical currents—called eddy currents—within the metal itself.
The natural resistance of the metal to the flow of these eddy currents generates precise and instantaneous heat. The heat is created inside the part, not applied from the outside.
The Unmatched Energy Efficiency
Because the heat is generated directly within the workpiece, very little energy is wasted. Modern induction systems can achieve energy efficiency levels of up to 90%.
In contrast, fuel-fired furnaces constantly lose heat to the environment, often struggling to reach 50% efficiency. This direct efficiency gain means lower overall energy consumption to perform the same task.
Localized Heating Reduces Waste
The magnetic field can be precisely shaped by the coil's design, meaning only the specific portion of the material that needs heating is affected.
This eliminates the need to heat an entire component or a large oven for a small task. This precision not only saves energy but also reduces material waste by preventing distortion and warpage in other parts of the component.
Direct Environmental and Workplace Impacts
The shift away from combustion delivers tangible benefits for both the environment and the people working in it.
Eliminating On-Site Emissions
This is the most direct environmental benefit. Induction heating produces no combustion byproducts.
There is no smoke, no carbon dioxide, and no noxious emissions like NOx or SOx released at the worksite. This dramatically improves local air quality inside the facility and in the surrounding community.
A Safer, Cleaner Work Environment
Traditional furnaces produce tremendous ambient heat and loud noise. Induction heating systems are comparatively quiet and do not radiate significant waste heat into the workspace.
This creates a more comfortable and safer environment for employees, reducing the risk of heat-related stress and improving overall well-being.
Lowering the Corporate Carbon Footprint
By consuming significantly less energy and using electricity instead of fossil fuels, induction heating directly reduces an organization's carbon footprint.
For companies with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals or those striving for carbon neutrality, adopting induction technology is a clear and measurable step toward achieving those targets.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, adopting induction heating requires a clear-eyed assessment of its context and limitations.
The Source of Your Electricity Matters
Induction heating is only as "green" as the grid that powers it. While it eliminates on-site emissions, its overall carbon footprint depends on how the electricity is generated.
If your power comes from coal, you are simply displacing emissions from your facility to the power plant. The full environmental benefit is realized when induction systems are paired with a grid increasingly powered by renewable sources.
Initial Investment and Infrastructure
Implementing induction heating systems requires a significant capital investment. The equipment is specialized and may require upgrades to a facility's electrical infrastructure to support the power draw.
This upfront cost must be weighed against the long-term savings from higher efficiency, reduced energy bills, and lower maintenance.
Material Compatibility
Induction heating works by inducing current in electrically conductive materials, primarily metals. It is not a universal solution for heating all materials, such as most ceramics or plastics, without the use of a conductive susceptor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Deciding to invest in induction heating depends on your primary strategic goals.
- If your primary focus is reducing your carbon footprint: Induction is a superior choice, especially when you can source power from a clean grid or on-site renewables.
- If your primary focus is improving workplace safety and air quality: Induction is the definitive winner, as it eliminates the heat, noise, and fumes associated with combustion.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product quality and reducing scrap: The precise, controllable, and repeatable nature of induction heating minimizes defects like warpage and oxidation, leading to less material waste.
Ultimately, adopting induction heating is a strategic investment in a cleaner, more precise, and highly efficient manufacturing future.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Benefit | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Up to 90% efficiency vs. <50% for traditional furnaces. |
| On-Site Emissions | Zero combustion byproducts (CO₂, NOx, SOx). |
| Workplace Safety | Eliminates ambient heat, noise, and fumes. |
| Material Waste | Localized heating reduces scrap and distortion. |
Ready to transition to a cleaner, more efficient heating process?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, high-temperature heating solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line, including Induction Heating Systems, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is designed for precision, efficiency, and sustainability.
Whether your goal is to reduce your carbon footprint, improve workplace safety, or enhance product quality, our team is ready to deliver a customized solution. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve your environmental and operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















