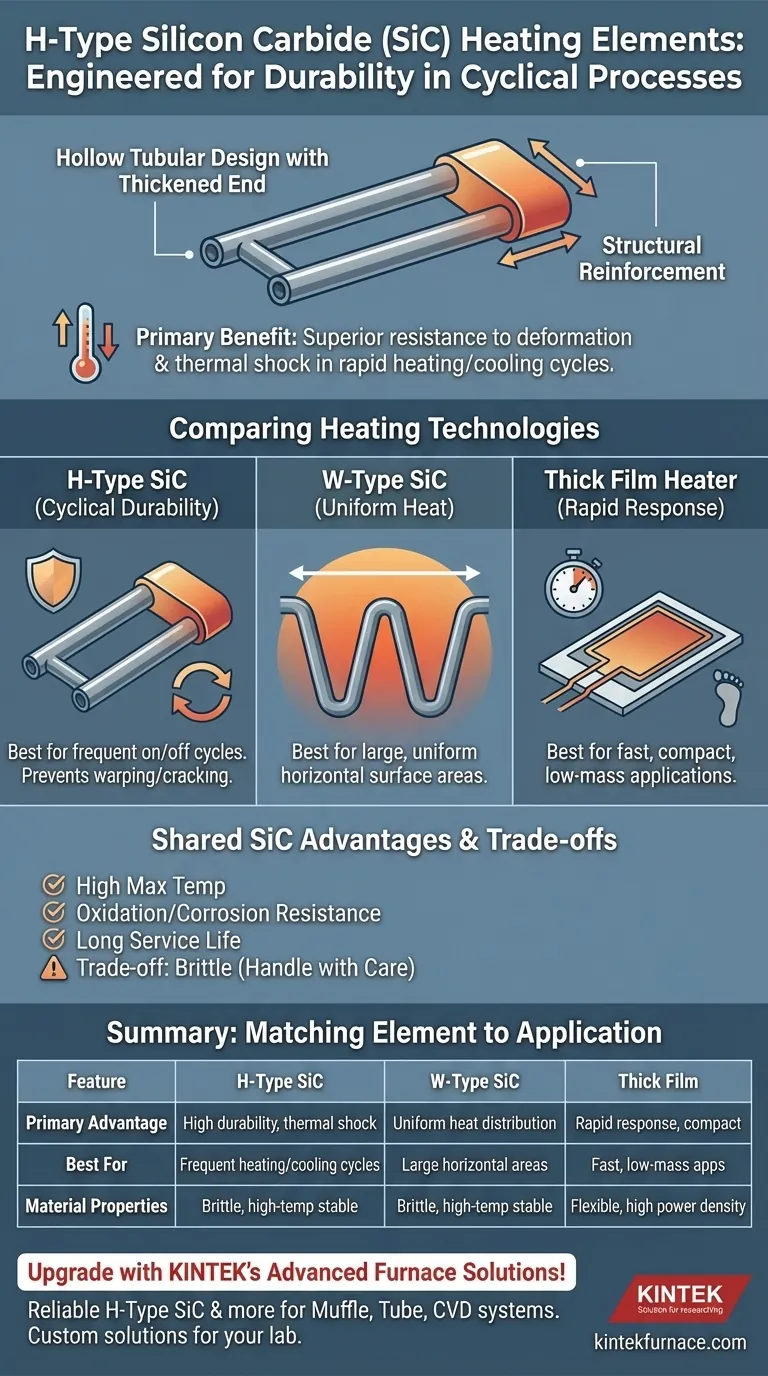
At its core, the H Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating element is distinguished by its specific physical construction: a hollow tubular design featuring a thickened end. This unique shape is not an arbitrary choice; it is engineered to provide superior durability and resistance to deformation, especially in environments with rapid and repeated temperature changes.
While all silicon carbide elements offer high-temperature operation, the H-Type's value is in its structural integrity. Its design directly addresses the mechanical stress caused by thermal shock, making it the ideal choice for applications with frequent heating and cooling cycles.

The Defining Characteristic: Engineered for Durability
The primary differentiator for an H-Type element is its physical form and the performance benefits that result from it. Understanding this design is key to understanding its purpose.
A Unique Structural Design
The element consists of a single, hollow SiC tube with one end manufactured to be significantly thicker and more robust than the main body. This "thickened end" acts as a structural reinforcement.
Built for Thermal Shock Resistance
This reinforcement is specifically designed to withstand the mechanical stresses of rapid thermal expansion and contraction. In furnaces or processes that cycle on and off frequently, this design prevents warping, cracking, or premature failure where other elements might deform.
Superior High-Temperature Stability
Like all SiC elements, the H-Type is hard, brittle, and does not deform under high temperatures. Its specialized design simply enhances this inherent stability, ensuring a longer operational life in demanding, cyclical applications.
How H-Type Compares to Other Heating Technologies
Choosing the right heating element requires comparing it not only to its close relatives but also to entirely different technologies that solve different problems.
H-Type vs. W-Type SiC Elements
The W-Type SiC element features multiple silicon carbide rods joined at one end to form a "W" shape. Its primary advantage is providing uniform heat distribution over a large, often horizontal, surface area.
In contrast, the H-Type is optimized for point-of-failure resistance in thermally dynamic environments. The choice between them is a classic engineering decision: uniform heat coverage (W-Type) versus cyclical durability (H-Type).
The Broader Silicon Carbide Advantage
It's important to remember that all SiC elements, including the H-Type, share a common set of powerful advantages over traditional metallic heaters. These include a much higher maximum operating temperature, superior resistance to oxidation and chemical corrosion, and a significantly longer service life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technology is universally superior. Acknowledging the limitations of SiC elements is critical for making an informed decision.
The Brittleness Factor
Silicon carbide is an exceptionally hard ceramic material, but this hardness comes with brittleness. All SiC elements, including the H-Type, must be handled and installed with care to avoid mechanical shock or fracture.
When SiC Is Not the Right Choice
For applications demanding extremely fast response times, low thermal mass, and high power density in a compact footprint—such as in medical devices or precision automotive systems—other technologies are superior. Thick film heaters, for example, are printed onto a substrate and excel in these areas where a large, high-mass SiC element would be inefficient and impractical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your process. Match the element's core strength to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is durability under frequent temperature cycling: The H-Type's thickened-end design is engineered specifically for this and is your optimal choice.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating across a large horizontal area: The W-Type's geometry is better suited for this heat distribution requirement.
- If your primary focus is general high-temperature stability in a stable process: Any standard SiC element will perform well, but the H-Type offers an added margin of durability.
- If your primary focus is rapid response and compact, low-mass heating: You should look beyond SiC technology to alternatives like thick film heaters.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating element is about matching its structural design to the thermal and mechanical stresses of your application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | H-Type SiC Element | W-Type SiC Element | Thick Film Heater |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | High durability, thermal shock resistance | Uniform heat distribution | Rapid response, compact design |
| Best For | Frequent heating/cooling cycles | Large horizontal heating areas | Fast, low-mass applications |
| Material Properties | Brittle, high-temperature stable | Brittle, high-temperature stable | Flexible, high power density |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable heating elements like H-Type SiC, designed for durability in cyclical processes. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















